![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
84 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Schizophrenia |
Excessive dopamine levels Hence antipsychotics antagonize dopamine as side effect |
|
|
|
Depression |
Low NE and 5HT |
Hence SSRIs and SNRIs work |
|
|
Solitary nucleus receives input from which cranial nerves? |
7,9 and 10 Therefore involved in reflexes initiated through vagus or glossopharyngeal nerves |
Carotid sinus reflex Gag reflex Chemoreceptor |
|
|
Murmur types Mitral valve |
Left 5th inter costal mid clavicular Holosystolic= regurgitation Stenosis= diastolic |
|
|
|
Murmur types Tricuspid valve |
Left 4th intercostal parasternal line Holosystolic= regurgitation Stenosis= diastolic |
|
|
|
Murmur types Aortic valve |
Right 2nd intercostal parasternal line Stenosis= systolic Regurgitation= diastolic |
|
|
|
Plummer vinson syndrome |
Anyone with iron deficiency anemia that also has: glossitis and esophageal webs |
Fatigue, menorrhagia, sob |
|
|
Decreased fine touch suggests what deficiency and which area affected? |
Fine touch and pinprick sensation are mediated by the dorsal columns and spinothalamic tracts. Suggest Vit B12 def or Neurosyphillis |
|
|
|
Hyperkalemia can cause |
Peaked T waves and wide QRS complexes Myalgias Paresthesias Nausea and vomiting |
Etiology of hyperkalemia: Insulin deficiency Beta 2 adrenergic antagonist Acidosis TMP-SMX ACE inhibitors |
|
|
Glucagon can be used to treat what overdose? |
Beta blocker toxicity Stimulates cAMP which is independent of adrenergic receptor |
|
|
|
Acromegaly testing Test for screening and monitoring? Test for confirmation of Dx? |
Screen with IGF-1 which has a long half life and its produced by liver after stimulation of GH. IGF-1 is main mediator of GH action. To confirm Dx a GH suppression test following an oral glucose load following a positive screening for IGF-1 |
|
|
|
HLA related ds |
DR3 = Graves DQ2/DQ8= Celiac ds DR4= RA DR5= Pernicious anemia and Hashimotos |
|
|
|
Testicular germ cell tumors most common? |
Seminoma: Painless + malignant + large nucleus to cytoplasm ratio + similar to dysgerminoma in females |
Tumor marker= ALP |
|
|
Testicular germ cell tumor Yolk sac tumor |
Endodermal sinus+ yellow mucinous+ Shiller- Duval bodies resemble primitive glomeruli+ high AFP |
|
|
|
Testicular germ cell tumors Choriocarcinoma |
Disordered trophoblasts Mets to brain and lungs High BHCG |
Any tumor or ds with increased bHCG can have hyperthyroidism symptoms bc of the alpha chain structure |
|
|
Testicular germ cell tumor Embryonal carcinoma |
Hemorrhagic necrotic tumor Painful+malignant+MC mixed cell tumor+ increased AFP and hCG |
|
|
|
Testicular NON germ cell tumors Mostly benign |
Leydig cell tumors Golden brown Gynecomastia+ precocious puberty+ increased estrogen and androgens+ Reinke crystals |
|
|
|
Testicular NON germ cell tumors Sertoli cell tumor |
Sertoli+ Androblasta from sex cord stroma+ estrogen increase |
Androblastoma |
|
|
Testicular lymphoma |
NHL in older men in testicles From metastasis Aggressive and hemorrhagic |
|
|
|
Polyhydramnios is associated with |
25 cm or more of amniotic fluid pockets Anencephaly, gesttional diabetes or duoden atresia which is accompanied by double bubble sign (trisomy 21) |
|
|
|
CMV on AIDS pt causes |
Retinitis(cotton whool)+ esophagitis (linear)+ colitis+ pneumonitis+encephalitis w the classic owl eye inclusion bodies |
|
|
|
AIDS pt with CNS lymphoma= |
EBV causing B cell lymphoma |
|
|
|
MAC in AIDS pt shows as |
Nonspecific systemic symptoms and focal lymphadenitis= MAC Tx with azythromycin + Rifabutin |
|
|
|
Congenital complete heart blcok |
Seen in Sjogrens syndrome Associated with SS-A(Ro) SS-B (La) |
|
|
|
Bundle branch block |
After MI Wide splitting and a bifid R wave (rabit ears) in leads V1 V2 between bundle of His and Purkinje fibers |
|
|
|
Thiamine deficiency |
Triad : confusion+ophtalmoplegia+ataxia along w lactic acidosis Confirmed deficiency by# decreased activity of transketolase activity in RBCs |
|
|
|
Scurvy confirmation test |
Vit C deficiency is confirmed through WBCs ascorbic acid levels |
|
|
|
Sarcoma botryoides or embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma |
Grape like bunches out of vagina in 8yo or less females Skeletal muscle origin+desmin positive |
|
|
|
Tumor marker Chromogranin |
Marker for both benign and malignant neuroendocrine cells Inclusing pheochromocytoma merkell cell cancer |
|
|
|
CD15 and CD30 tumor markers |
Mark HL Reed steinberg cells lymphoma |
|
|
|
Cyrokeratin is a marker for |
Epithelial cell malignancies such as: HCC, Adenocarcinoma of stomach, squamous cell carcinoma and more |
|
|
|
Pyogenic granuloma |
Rapidly growing benign capillary hemangioma which cam ulcerate and bleed associated with trauma and pregnancy |
|
|
|
Trache anatomy |
Starts at C7 ends at T4/5 in the carina |
|
|
|
Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia |
According to the name there is less Ca urine excretion and hypercalcemia.
|
1ry Parathyroidism vs FHH= PTH has hypercalciuria and is part of MEN 1 which have to undergo parathyroid excission |
|
|
Acyclovir MOA |
Treats herpes and its a lrodrug that gets converted by thymidine kinase to acyclovir monophosphate and in turn to acyclovir triphosphate by host cell kinases |
|
|
|
Tuberous sclerosis inheritance and features |
TSC gene Hypopigmented macules Mitral valve regurg Seizures |
|
|
|
Dystonia is treated with |
Anticholinergics like benztropine and diphenhydramine |
|
|
|
What is healing by 1ry 2ry and 3ry intention? |
1° sutures bringing the two sides close for healing 2° granulation tissue 3° granulation and then closing wound like in grafts |
|
|
|
Fronto-temporal dementia |
Personality Behavioral, memory and language inpairment |
|
|
|
Fronto-parietal dementia |
Language and cognitive deficiencies |
|
|
|
Drugs that cause gingival hyperplasia |
Phenytoin Nifedipine |
|
|
|
Narcolepsy tx |
Methylphenidate which is a inhibitor of reuptake of NE and Dopa |
|
|
|
Acute interstitial nephritis pathognomic finding |
Eosinophilia in urine |
|
|
|
Acute pyelonephritis finding |
WBC casts and bacteria |
|
|
|
Acute tubar necrosis finding |
Muddy brown casts |
|
|
|
Dantrolene |
Treats NMS by blocking calcium release from sarcoplasmic reticulum through binding to ryanodine receptor |
|
|
|
Erythema multiforme |
Type 4 HSN by HSV specially HSV2 |
|
|
|
Polyarteritis nodosa features and tx |
Segmental Necrotizing vasculitis assoc w HepB and no lung involvement. 3 phases of vasculitis: Fibrinoid necrosis Fibroblast proliferation Nodular fibrosis |
|
|
|
Temporal or giant cell arterities |
Multinucleated giant cells with nodular thickening of the intima and fragmentation of internal elastic lamina |
|
|
|
Von hyppel lindau |
Cavernous hemangiomas Hemnagioblastomas of retina and cerebellum producing EPO Pheochromocytoma Renal cell carcinoma Pancreatic tumors |
|
|
|
Heparin induced thrombocytopenia |
Antibodies against platelet factor 4 |
|
|
|
DKA derrangements explained |
Hyperkalemia: acidemia (ketones) drive cells K/H exchange and insulin tendency to drive K intracellularly is missing Hyponatremia: hyperflycemia induces osmotic diuresis Hyperammonemia: muscle degradation |
|
|
|
Insulin synthesis |
Preproinsulin: cytosol Proinsulin: RER Insulin + C peptide: inside secretory granules to be secreted |

|
|
|
Sweating is part of which nervous system and how to tx hyperhidrosis |
Sympathetic Tx: syatemic anticholinergic (Ocybutinin), local botulinim or surgical sympathectomy at T2 level for axilla 😓 |
|
|
|
Hodgkin lymphoma is associated with which paraneoplastic syndromes |
Cholestatic liver ds Alcohol induces pain Skin lesions Neurologic Nephrotic syndrome |
|
|
|
Small cell lung cancer is associated with which autoimmune syndrome |
Lamber Eaton |
|
|
|
Mullerian agenesis |
Absent pr rudimentary uterus and upper vagina but normal ovaries |
|
|
|
Complete androgen insensitivity syndrome in male |
X linked mutation of androgen receptor Absent uterus and upper vagina Cryptorchid testes Minimal or absent pubic hair |
|
|
|
Primary carnitine deficiency |
Muscle weakness Cardiomyopatht Hypoketotic hypoglycemia Elevated muscle TGs |
Acyl CoA synthase deficiency therefore FA cant be converted into Acyl CoA to go into mitochondria and make ketones |
|
|
Medium chain Acyl CoA dehydrogenase deficiency |
Hypoglycemia Hypoketotic hypoglycemia after prolonged fasting |
|
|
|
Von Gierkes is a glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency |
Fasting hypoglycemia seen as well in MCAD and Primary Carnitine def BUT here there are no problems making ketone bodies there is just excessive glycogen bc it cannot be broken |
|
|
|
Translation in Eukariotes vs Prokaryotes |
Kosak : Eukaryotes : 5'cap initiation Shine Delgarno : Prokaryotes : translation initiation
|
KEu 5cap Pro-Shine |
|
|
Apoptosis in eukaryotes |
Caspases result in eukaryotic initiatiob factor degradation leading to interruption of translation therefore the proteins needed for apoptosis that need to be translated do so by Internal Ribosome Entry |
|
|
|
Chrons likes which part of the GI most? |
Terminal Ileum... Ily (I love you) Ileum |
|
|
|
Tx of hepatic encephalopathy |
Lactylose which is a disacharide degraded by colonic bacteria to form lactic acid and acetic acid... Acidifying the GI contents increasing osmotic peristalsis |
|
|
|
R/L recurrent laryngeal nerves innervate which muscles |
All muscles of larynx except CRYCOTHYROID |
|
|
|
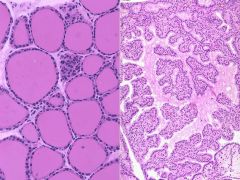
Histology of graves |
|
|
|
|
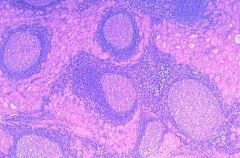
Hystology of hashimoto |
|
|
|
|
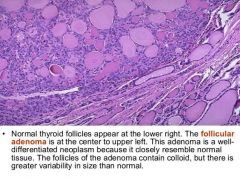
Hystology of follicular adenoma |
|
|
|
|
Skin callous is a thickening of which layer of skin |
Stratum corneum of epidermis |
|
|
|
Pt with atrophic glossitis+macrocytic anemia+peripheral neuropathy+hypothyroidism) |
Hashimotos+ Pernicious anemia cause obce u have an autoimmune ds another one is easier to get |
Low IF, low vit B12, hypochlodria, increased gastrin bc of loss of negative feedback |
|
|
Cool clamy skin |
Alpha 1 vasoconstriction Gq PIP3 DAG IP3 |
|
|
|
TNF alpha is responsible for systemic effects like |
Fever Cachexia C-RP CRH Septic shock |
|
|
|
Idiopathic increased intracranial pressure specially targets which cranial nerve |
CN6 is very sensitive to increase in pressure bc it passes through Dorellos canal These pts hace increased intracranial pressure but normal CSF |
Also called pseudotumor cerebri: tx wt loss and acetozolamide |
|
|
Very long chain fatty acids and some branched chain FAs cannot undergo mitochondrial beta oxidation therefore |
They are metabolized within peroxisomes When peroxisomes are absent these VLCFA accumulate in tissue |
Zellweger syndrome=peroxisomal ds = unable to form myelin |
|

Urea cycle |
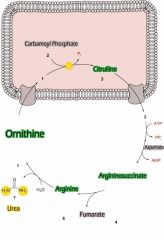
|
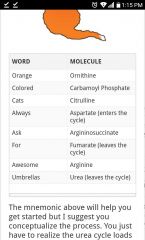
|
|
|
Pinpoint pupils = |
Opioid toxicity Tx w Naloxone |
|
|
|
Essential tremor is tx with |
Propranolol and Primidone Phenobarbital is an active metabolite of Primidone |
|
|
|
Lactase deficiency can be primary or secondary name the differences |
1* lactase (beta galactosidase) deficiency 2* association w celiac sprue or viral gastroenteritis due to lactase containing microvili in small intestine being damaged |
|
|
|
How many calories per gram |
Protein or Carb =4 Alcohol= 7 Fat =9 |
|
|
|
Thiamine dependent enzymes |
Pyruvate dehydrogenase Alpha keto glutarate dehydrogenase |
|
|
|
Heparin binds to ... |
ATIII + Plasma proteins like acute phase reactants whose levels vary by patient |
Heparin also binds to PF4 also which can neutralize the anticoagulant effect of heparin |
|
|
Chemical antagonism is |
A drug that binds to another drug to inhibit it Ex protamine which is + charge and basic binds to heparin - charged forming an inactive complex |
|
|
|
21 hydroxylase deficiency |
Chromosome 6 HLA locus Causing congenital adrenal hyperplasia |
|

