![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
129 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
TPN Complications
|
Most common- catheter tip infection.
Others: fluid overload, refeeding syndrome (hypokalemia, hypo Po4, hypo Mg) if too fast. |
|
|
Thyroid hormones and pregnancy
|
Normal preg inscreases thyroid gland size, total T3 and T4, and TBG. Free T3 and T4 are w/in normal. TSH and TRH are often decreased.
|
|
|
Do you keep synthroid levels the same? increase? or decrease? them if a patient becomes pregnant?
|
Increase them.
|
|
|
Describe the nonstress test in pregnancy
|
Tests for fetal hypoxemia. Its "reactive" if 2+ accels of 15bpm above baseline that last for 15 secs over 20 min of observation.
|
|
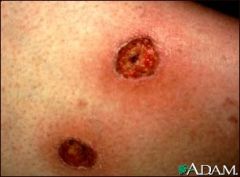
What is this lesion?
|
Ecthyma gangenosum from P. aeruginosa. Rapid growing skin lesion that become nontender nodules w/ central nextrosis. Occurs in immunecompromised pts.
Tx= piperacillin w/ gentamicin |
|
|
Most common cause of infectious myocarditis and pericarditis
|
Coxsackie virus
|
|
|
Patients with chest pain, decreased cardiac output, and pulsus paradoxus following a viral infection probably have:
|
cardiac tamponade secondary to acute pericarditis.
|
|
|
Pulsus paradoxus:
definintion. causes. |
bp inc with exhalation. dec with inhalation
on clinical examination, one can detect beats on cardiac auscultation during inspiration that cannot be palpated at the radial pulse.[1] It results from an accentuated decrease of the blood pressure, which leads to the (radial) pulse not being palpable and may be accompanied by an increase in the jugular venous pressure height (Kussmaul sign). As is usual with inspiration, the heart rate is slightly increased,[2] due to decreased left ventricular output. cardiac tamponade, pericarditis, chronic sleep apnea, croup, and obstructive lung disease (e.g. asthma, COPD). |
|
|
Most common cause of infectious myocarditis and pericarditis
|
Coxsackie virus
|
|
|
Patients with chest pain, decreased cardiac output, and pulsus paradoxus following a viral infection probably have:
|
cardiac tamponade secondary to acute pericarditis.
|
|
|
Describe xanthochromia and its significance
|
yellow discoloration of CSF secondary to degradation of elevated CSF RBCs.
Classic for HSV encephalitis. |
|
|
Describe HSV encephalitis
|
Presentation: fever, HA, seizure, confusion, stupor over a few days.
Frontotemporal region affected thus temporal-based seizures, anosmia, gustatory hallucinations and bizzare/psychotic behavior. CSF: lymphocytic pleocytosis, normal glucose and protein, and xanthochromia b/c hemorrhagic destruction of frontotemporal lobes. |
|
|
What is "normal" FEV/FVC ratio?
|
80%-120%
|
|
|
Describe pseudoclaudication
|
lower extremity pain w/ walking and prolonged standing; particularyly evident with downhill walking.
Difference b/w claudication; pseudo is still bad with prolonged standing whereas claudication would improve. |
|
|
Describe paraneoplastic Cushing's
|
ectopic ACTH production by small cell lung CA. Can't be suppressed with dexamethason, hyperpigmentation (MSH is breakdown product from ACTH), Other sx: truncal obesity, moon facies, buffalo hump, striae, htn, fatigue, glucose intol, osteopenia, weakness, easy bruising, edema, electrolyte probs.
|
|
|
Complication of peritoneal dialysis
|
Most common= Peritonitis.
fever, ab pain, rebound tenderness. mc organism= staph epidermidis, and staph aureus. NOTE: peritonitis from divertiulitis is often polymicrobial |
|
|
SBP: define,
|
SBP- common complication of ascities; enteric org translocates from intestinal wall. Dx: >250 neutrophils in ascitic fluid.
|
|
|
Bullous pemphigoid vs pemphigus vulgaris
|
BP: autoimmune SUBepidermal blistering in flexural areas, pruiritis, >60 y.o., 1/3 have oral lesions
tx= topical/oral steriods BV: autoimmune INTRAepidermal blistering. Oral cavity involvement ALMOST ALWAYS! tx= corticosteriods. IvIG, etc. |
|
|
Most common intracranial tumors in adults
|
Brain mets (mcc CA: lung, breast, renal)
|
|
|
MRI findings w/ MS
|
Ovoid plaques in periventricular region, corpus collosum and deep white matter.
|
|
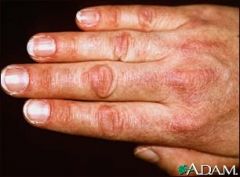
pt has this finding plus heliotrope rash, symmetric prox muscle weakness. What is treatment?
|
Dx- dermatomyositis.
tx- high dose steroids then taper to low dose. Adjunct w/ azathoprine or MTX as needed. |
|
|
/absence seizures
|
Usually occur in kids. i.e. child w/ multiple staring episodes per day. No post-ictal confusion
|
|
|
Complex partial seizures
|
Pts often stare blankly for several min and may do automatisms (lip smacking, chewing, etc.). POST-ICTAL CONFUSION or paralysis (Todd's paralysis) often occurs.
|
|
|
SLE
|
Migratory, polyarticular symmetric joint pain. (knees, hands often involved).
Photosensitivity, renal disease( proteinuria w/ normal creatinine in early stages). Young female |
|
|
Adenosine
|
Treats SVT
|
|
|
Digoxin
|
sometimes treats SVT
|
|
|
Verapimil
|
treats SVT, not effective for V tach
|
|
|
Metroprolol
|
treats SVT, not V tach
|
|
|
Amiodarone
|
treat stable V TACH!!!
|
|
|
Mediastinitis
|
complication from esophageal rupture from previous esophageal dilation procedures. Often gives left sided pleural effusion, pneumomediastinum, hemodyn instab and fever.
Dx with esophagram or chest CT |
|
|
Mallory weiss versus Boerhave
|
MW- partial thickness
B- full thickness (can lead to mediastinitis) |
|
|
Assessment for PVD
|
Ankle brachial index.
|
|
|
Severe symptomatic hypercalcemia is most often caused by?
|
Malignancy; hyper PTH can give increased Ca, but NOT AS HIGH AS MALIGNANCY
|
|
|
Prevention of gallstones
|
Ursodeoxycholic acid.
|
|
|
What procedure gives VERY high risk of gallstones in the future?
|
Gastric bypass.
if have symptomatic stones before surg then do cholexxystectomy. If not symptomatic give prophylactic ursodeoxycholic acid for 6 mos after surgery. |
|
|
ANA
|
SLE
|
|
|
anti-ds-DNA
|
SLE
|
|
|
Anti-smith
|
SLE
|
|
|
Anti-centromere Ab
|
Scleroderma (Esp CREST syndrome)
|
|
|
ANCA
|
Small vessel vascultitis (ex. Wegener;s granulomatosis).
|
|
|
anti-smooth muscle antibodies
|
autoimmune hepatitis
|
|
|
Anti-mitochondrial
|
Primary biliary cirrhosis
|
|
|
Prevention on variceal hemorrhage?
|
Non-selective beta blockers (propranolol or nadolol).
|
|
|
What is the effect of multiple myeloma on the kidneys?
|
MC: renal tubular damage by the light chain casts.
Glom damage from amyloidosis or monoclonal Ig deposition also occurs less commonly. |
|
|
Fragile X- diagnosis
|
Molecular analysis of # of CGG repeats in FMR-1 gene
Cell culture in folate deficient media. |
|
|
Fragile X- what is it?
|
MOST COMMON INHERITED FORM OF MENTAL RETARDATION; Pts get seizures, elongated gace, large ears, enlarged testes.
|
|
|
Treatment of delirium
|
Haloperidol (i.e. antipsychotics)
NOTE: Benzos can worsen relirium unless the delirium is secondary to alcohol or benzo withdrawal. |
|
|
HPV screening
|
Pap at three years past sexual intercourse or at age 21 (whichever first).
|
|
|
Normal vaginal pH
|
4-4.5;
BV= higher pH Yeast= normal pH Trich= higher pH |
|
|
Heterozygous alpha thalassemia
|
(a, a,)(-,-) OR (a,-)(a,-)
Typicall asymptomatic; although can have mild fatigue, mild hypochromic anemia, severe microcytosis, target cells. |
|
|
Diagnostic test for carcinoid syndrome
|
24 hr urine 5-HIAA
|
|
|
Rosacea
|
Middle age, episodic facial flushing to spicy food or alcohol, facial telangiectasias, pustules. Treatment- metronidazole (first line)
|
|
|
Agitated patients
|
If agitated and pose danger to themselves or others must give IM meds (loraz, haloperidol) and even physical restraints
|
|
|
Workup of NEW onset psych symptoms
|
head CT, CBC, TSH, syphilis screen, BMP, urine tox.
|
|
|
Young patient with recent viral illness, heart failure, chest pain or arrhythmias.
|
Suspect myocarditis.
|
|
|
Iron poisoning
|
GI HEMORRHAGE; bloody diarrhea, hematemesis. Severe poisoning=> metabolic acidosis, hepatotoxicity, bowel obstruction, or death.
|
|
|
Patients with A-fib and weight loss should get what test?
|
Thyroid! TSH, Free T4. Hyperthyroid can give weight loss and a fib.
|
|
|
What is both diagnostic and therapeutic for SVT?
|
Carotid sinus massage.
|
|
|
New-onset seizures
|
Think brain tumors; most common in adults are astrocytoma. The degree of anaplasia marks the prognosis.
|
|
|
CD20
|
CLL
|
|
|
EGFR
|
Colon cancer therapy
|
|
|
IL-1
|
RA treatment
|
|
|
TNF-alpha
|
RA, Chron's, inflamm diseases.
|
|
|
BCR-ABL
|
CML (tyrosine kinase)
|
|
|
Focal neuro findings plus increased intracranial pressure, plus fever plus new murmur
|
Brain abcess from endocarditis. Confirm with CT or MRI.
|
|
|
Bacteremia in pts with sickle cell disease is most commonly caused by....
|
strep pneumo (b/c its encapsulated and pts autoinfarct their spleen).
|
|
|
Who needs prophylactic antibiotics for dental procedure?
|
High risk conditions- prosthetic heart valves, history of IE, unrepaired CONGENITAL heart disease.
WHO DOES NOT: bicuspid aorta, acquired aortic valve disease, acquired mitral valve disease (including MVP w/ regurg). |
|
|
How to reverse EPS from haloperidol?
|
Give diphenhydramine and anticholinergic meds (benztropine, or trihexyphenidyl).
|
|
|
Where do the following get damaged with fractures?
Brachial artery Median Nerve Radial Nerve Ulnar Nerve Musculocutaneous Nerve |
1. midshaft frac of humurus (RARE!)
2. Supracondylar region of humerus 3. Middle portion humurus 4. Medial epicondyle 5. RARE; hypertrophy or entrapment b/w biceps. |
|
|
Exudative pleural effusion w/o evidence of infection
|
Think MALIGNANCY!
MCC- lung or breast cancer. (lung is less likely if pt didn't smoke) |
|
|
A fib treatment
|
Anticoagulation plus rate/rhythm control with B block or CCB.
|
|
|
What causes a "step-wise" deterioration of cognitive functioning?
|
Vascular dementia
|
|
|
three risk factors for torsades de pointes
|
long QT, hypokalemia, congenital deafness(!)
|
|
|
Torsades tx
|
correct hypokalemia, withdraw offending drugs. Give Mg initially and cardiovert if unstable.
|
|
|
Dressler's syndrome
|
PERICARDITIS: Autoimmune process occurring 2-10 weeks post-MI; Sx= fever, pericarditis, pleural effusion, leukocytosis, inc ESR.
|
|
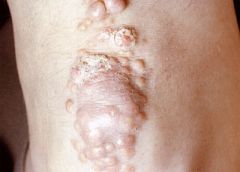
|
Xanthoma- eruptive nocules in skin over tendons w/ hypercholesterolemia.
|
|
|
Causes of secondary hypertension?
|
CHAPS- Cushings, hyperaldosterone, Aortic coarc, Pheochromocytoma, Stenosis of renal artery.
|
|
|
Antihypertensive with the following side effects: Headache, lupus like syndrome
|
hydralazine
|
|
|
Antihypertensive with the following side effects: orthostasis, facial hirsutism
|
Minoxidil
|
|
|
Antihypertensive with the following side effects: headache, flushing, peripheral edema
|
dihydropyridines- i.e. nifedipine, felodipine, amlodipine.
|
|
|
Antihypertensive with the following side effects: somnelence, orthostatic hypotension, impotence, rebound htn.
|
methyldopa, clonidine (central acting adrenergic agonists- on alpha2--- they inhibit sympathetic nervous system via central a-2 adrenergic receptors).
|
|
|
Causes of pulsus paradoxus
|
Cardiac:
cardiac tamponade pericardial effusion pulmonary embolism cardiogenic shock Pulmonary: tension pneumothorax asthma chronic obstructive pulmonary disease Non-pulmonary and non-cardiac: anaphylactic shock superior vena cava obstruction |
|
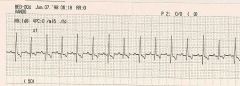
|
electrical alternans- cardiac tamponade
|
|
|
Anemia with DIC is caused from
|
Microangiopathic hemolytic anemia
|
|
|
CSF findings with Guillian Barre
|
albuminocytologic dissociation:
increasd protein but normal WBC. |
|
|
MCC of Guillian Barre
|
Post-campylobacter.
|
|
|
Electrolyte abnormalities with tumor lysis syndrome
|
hypocalcemia, hyperphosphatemia, hyperkalemia, increased uric acid.
Also, nausea, vomiting, change bowel habits, dec urine output, acute renal insufficiency, seizure, tetany and/or arrhythmia. |
|
|
How to treat these types of meningitis:
1. Nocardia 2. Toxoplasmosis 3. listeria monocytogenes 4. cryptococcus 5. s. pneumo |
1. tmp-sulfa
2. pyrimethamine and sulfadiazine 3. ampicillin (added to cephalosporin) 4. amphotericin B or flucytosine 5. ceftriaxone + vanco if cef- resistant |
|
|
Myelodysplastic syndrome
|
Ages 65+, macrocytic anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, and decreased segmentation of neutrophils (as opposed to b12 or folate deficiency).
Dx- via bone marrow biopsy. |
|
|
auer rods
|
AML
|
|
|
Heinz cells
|
G6PD deficiency or thalasemmia
|
|
|
Smudge cell
|
CLL
|
|
|
Spherocytosis leads to what?
|
gallstones b/c chronic hemolysis
|
|
|
入場
|
입장
entrance, [관객 등의] admission, admittance. [enter + place] |
|
|
acid ingestion is a risk factor for what future GI abnormality?
|
Gastric outlet obstruction
|
|
|
Causes of primary adrenal insufficiency
|
TB, fungal, CMV.
|
|
|
What androgen hormone is elevated in pts with increased ADRENAL androgen secretion?
|
DHEAS; the other androgens are also produced by the ovaries (i.e. are not specific to the adrenals)
|
|
|
OCPs can lead to what liver problem in women?
|
Hepatic adenoma- Complications include intra-tumor hemorrhage, malignant transformation.
|
|
|
treatment of benign essential tremor?
|
Betablocker- propranolol
|
|
|
加害
|
가해
assault, violence, wrong, wrongdoing [add + harm] |
|
|
防禦
|
방어
defense, safeguard, protection [defend + protect] |
|
|
Complications of hepatitis C
|
1. Cryoglobulinemia (membranoproliferative glomerularnephritis)
2. B-Cell lymphoma 3. Plasmacytoma 4. Auto-immune (Sjogren's, thyroiditis) 5. Lichen planus 6. Porphyria cutanea tarda 7. ITP |
|
|
Toxoplasmosis treatment/prevention?
|
tx- sulfadiasine & pyrimethamine
prev- tmp-sulfa. |
|
|
Complication of infectious mono?
|
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia (coombs positive) and thrombocytopenia.
And splenic rupture. (don't play contact sports) |
|
|
Side effect of succinylcholine?
|
Hyperkalemia.
|
|
|
Side effect of dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers (i.e. amlodipine)
|
Peripheral edema
|
|
|
Lenticular nuclear atrophy
|
Wilson's disease
|
|
|
Renal disease associated with Hep B
|
Membranous glomerulonephritis
|
|
|
Steroids effect on CBC
|
erythrocytosis
|
|
|
Initial treatment of acute mania (IN the manic episode!)
|
Antipsychotic (haloperidol); and start lithium, but it'll take lithium 4 days+ to start working
|
|
|
Mirtazepine
|
TCA antidepressant, increases appetite.
|
|
|
Asymptomatic increase of alkaline phoshatase
|
Paget's disease
|
|
|
Components of the fetal biophysical profile
|
Fetal movement
Fetal tone Fetal breathing Amniotic fluid volume Results of nonstress testing |
|
|
HLA DR3
HLA DR4 |
Type I Diabetes
|
|
|
smudge cells
|
CLL
|
|
|
Auer rods
|
AML
|
|
|
TRAP positive
|
Hairy cell
|
|
|
Gleevac (Imatinib) treats...
|
CML
|
|
|
Tumor lysis:
Calcium, Potassium, PO4, Uric acid |
DEC Ca++; all else high
|
|
|
Normal ECG is upright in which axes?
|
I and avF.
|
|
|
Long QT can lead to?
|
Torsades.
|
|
|
What makes a Q wave significant?
|
>1/3 QRS amplitude or >40ms.
|
|
|
Q wave indicates?
|
past MIs.
|
|
|
Inverted T indicates?
|
possible ischemia
|
|
|
Management of A-Fibb?
|
ABCD-
anticoag b block for rate control ccbs or cardiovert(?) digoxin |
|
|
cannon A waves
|
RA contraction against closed tricuspid
|
|
|
A flutter treatment
|
Rate and anticoag; cardiovert according to a fibb criterea (i.e. only if <48hrs without evidence of thrombi on echo; or after 4-6 weeks of anticoag.
|
|
|
AVNRT treatment
|
Carotid massage, valsalva, cold water on face (all dec AV node conduction by inc vagal tone). Give Adenosine if needed.
Cardiovert if hemo unstable |
|
|
PVC treatment
|
B-blockers
|

