![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
71 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Coronary Vasospasm
|
1. COCAINE
2. SUMATRIPTAN 3. ERGOT |
|
|
|
Cutaneous Flushing
|
1. Vancomycin
2. Adenosine 3. Niacin 4. Calcium Channel Blockers |
VANC
|
|
|
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
|
1. Doxorubicin
2. Daunorubicin |
|
|
|
Torsades de Pointes
|
1. Sotalol Class III
2. Quinidine Class IA 3. Macrolide Anitbiotics 4. Antipsychotics 5. TCA's: [ssri nsri] |
|
|
|
Adrenocortical Insufficiency
|
HPA suppression secondary to glucocorticoid withdrawal
|
|
|
|
Hot Flashes
|
1. Tamoxifen
2. Clomiphene: [induce ovulation] |
|
|
|
Hyperglycemia
|
1. Tacrolimus
2. Protease Inhibitors: [Antiviral for HIV and Hep C] 3. Niacin 4. HCTZ 5. Beta Blockers 6. Corticosteroids |
Taking Pills Necessitates Having Blood Checks
|
|
|
Hypothyroidism
|
1. Lithium
2. amioderone: [anti arrhythmic] 3. sulfonamides |
|
|
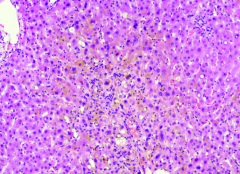
Acute Cholestatic Hepatitis, Jaundice
|
Erythromycin: [Macrolide Antibiotic]
|
|
|
|
Diarrhea
|
1. Metformin
2. Erythromycin 3. Colchicine: [Gout-binds microtubules] 4. Orlistat: [Obesity-Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitor] 5. Acarbose: [DM II-alpha glucosidase inhibitor] |
Might Excite Colon On Accident
|
|
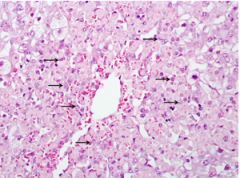
Focal To Massive Hepatic Necrosis
|
1. Halothane: [Inhaled General Anesthetic]
2. Amanita Phalloides: [death cap mushroom] 3. Valproic Acid: [General Myoclonic seizure] 4. Acetaminophen |
Liver HAVAc
|
|
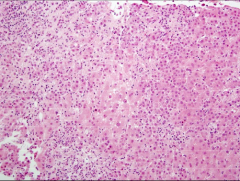
Hepatitis
|
INH
|
|
|
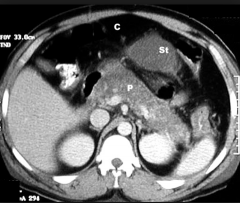
Pancreatitis
|
1. Didanosine: [HIV-reverse transcriptase inhibitor]
2. Cortiscosteroids 3. Alcahol 4. Valproic Acid: [General Myoclonic Siezure] 5. Azathioprine: [Organ Transplant mercaptopurine pro-drug] 6. Diuretics: [Furosimide, HCTZ] |
Drugs Causing A Violent Abdominal Distress
|
|
|
Pseudomembranous Colitis
|
1. Clindamycin
2. Ampicillin 3. Cephalosporins |
|
|
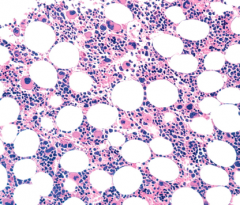
Agranulocytosis
|
1. Dapsone: [Antibacterial]
2. Clozapine: [Schizophrenia] 3. Carbamazepine: [Partial Siezures+ Tonic Clonic] 4. Colchicine: [Gout, Med Fever- binds microtubules] 5. Methimazole: [Hypothyroid Graves] 6. Propylthiouricil: [Hypothyroid Graves] |
Drugs CCCrush Meylobalsts and Premyelocites
Presents: Low White Count |
|
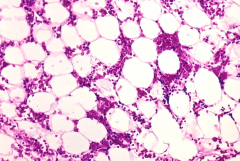
Aplastic Anemia
|
1. Carbamazepine: [Partial siezure + Tonic Clonic]
2. Methimazole: [Hyperthyroid Graves] 3. NSAIDS 4. Benzene 5. Chloramphenicol: [Antibacterial gram- gram+ anaerobic] 6. Propylthiouracil: [Hypothyroid Graves] |
Can't Make New Blood Cells Properly
Presents: Deficiency in all three blood cell types: Red(anemia), Platelets(Thrombocytopenia), White(Leukopenia) |
|
|
Gray Baby Syndrome
|
Chloramphenicol: [Antibacterial]
|
|
|
|
Hemolysis in G6PD deficiency
|
1. INH
2. Sulfonamides 3. Dapsone: [Antibacerial] 4. Primaquine: [Malaria, Pneumocystic Pneumonia] 5. Aspirin 6. Ibuprofen 7. Nitrofurantoin: [Antibacterial] |
Hemolysis IS D PAIN
Non-Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia during Increased oxidative stress[decreased glutathione] X-Linked recessive |
|
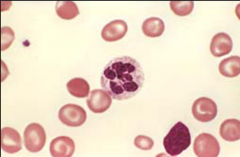
Megalobastic Anemia
|
1. Phenytoin: [ General Tonic Clonic Seizure
2. Methotrexate: [Cancer Rheumatoid Artheritis] 3. Sulfa Drugs |
Having a blast with PMS
|
|
|
Thrombocytopenia
|
1. Heparin
2. Cimetidine: [Peptic Ulcer Histamine H2 receptor antagonist] |
|
|
|
Thrombotic Complications
|
OCP's e.g. Estrogens
|
|
|
|
Fat Redistribution
|
1. Protease Inhibitors: [HIV Hep C Antiviral]
2. Glucocorticoids: [Cushings] |
Fat PiG
|
|
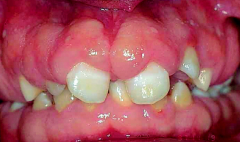
Gingival Hyperplasia
|
1. Phenytoin: [General Tonic Clonic Siezure]
2. Verapamil: [Calcium Channel Blocker] 3. Cyclopsorine: [Organ transplant immunosepressant] 4. Nifedipine: [Calcium Channel Blocker] |
|
|
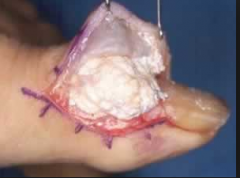
Hyperuricemia (gout)
|
1. Pyrazinamide: [TB]
2. Thiazides 3. Furosemide 4. Niacin 5. Cyclosporine: [Organ transplant Immunosuppresant] |
Painful Tophi and Feet Need Care
|
|
|
Myopathy
|
1. Fibrates
2. Niacin 3. Colchicine 4. Hydroxychloroquine 5. Inteferon Alpha 6. Penicillamine 7. Satins 8. Glucocorticoids |
FINCH PeGS
|
|
|
Osteoperosis
|
1. Corticosteroids
2. Heparin |
|
|
|
Photosensitivity
|
1. Sulfonamides
2. Amioderone: [Arrhythmias] 3. Tetracyclines: [Antibacterial] 4. 5-FU: [Inhibit thymidilate synthase] |
SAT For Photo
|
|
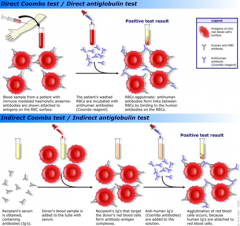
Direct Coombs- Positive Hemolytic Anemia
|
1. Methyldopa
2. Penicillin |
HAMP
Autoimmune: Anitbodies Against Red Blood Cells Lyse them |
|
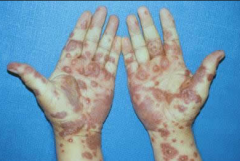
Rash (Stevens-Johnson Syndrome)
|
1. Anti-epileptic (ethosuximide, carbamazepine, lamotrigine, Phenytoin, Phenobarbital)
2. Allopurinol 3. Sulfa Drugs 4. Penicillin |
Steven Johnson has EPILEPTIC ALLergy to SULFA DRUGS and PENICILLIN
Milder form of Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis epidermis seperates from dermis. Weave-basket patttern on histology |
|
|
SLE-like syndrome
|
1. Sulfa Drugs
2. Haydralazine: [HTN/HF vasodilator] 3. INH 4. Procainamide: [Ia anti-arrhythmic] 5. Phenytoin 6. Etanercept: [autoimmune diseases TNF Inhibitor] |
Having Lupus is "SHIPP-E"
|
|
|
Teeth Discoloration
|
Tetracylcines
|
|
|
|
Tendonitis, Tendon Rupture, and Cartilage Damage
|
1. Fluoroquinolones: [antibiotic]
|
|
|
|
Cinchonism
|
1. Quinidine: [arrythmia/malaria]
2. Quinine: [Malaria] |
skin rashes, deafness (reversible), somnolence, diminished visual acuity or blindness, anaphylactic shock, cardiotoxicity
|
|
|
Parkinson-like syndrome
|
1. Antypsychotics
2. Reserpine 3. Metoclopramide |
Cogwheel rigidity of ARM
|
|
|
Siezures
|
1. INH (vitamin B6 deficinecy)
2. Bupropion: [Antidepressant/Smoking aid] 3. Imipenem/Cilastatin: [Beta Lactam Antibiotic] 4. Tramadol: [Analgesic Opiod] 5. Enflurane: [Anesthesia] 6. Metoclopramide: [GERD antiemetic] |
with siezures, I BITE My tongue
|
|
|
Tardive Dyskanesia
|
1. Antipsychotics
2. Metoclopramide |
|
|
|
Diabetes Insipidus
|
1. Lithium
2. Demeclyocycline |
|
|
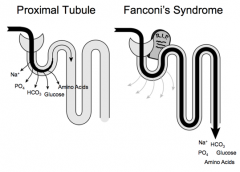
Fanconi Syndrome
|
1. Expired Tetraclycline
|
Disease of the proximal renal tubules of the kidney where glucose, amino acids, uric acid, phosphate and bicarbonate pass into urine, instead of being reabsorbed. Drug induced or Genetic
|
|
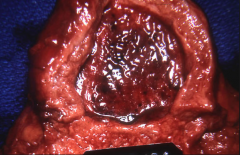
Hemorrhagic cystitis
|
1. Cyclophosphamide: [Cancer Autoimmune]
2. Ifosfomide: [Sex Cancers] |
Prevent by co-administering with mensa
lower urinary tract symptoms that include dysuria, hematuria, and hemorrhage originating from Urinary Bladder |
|
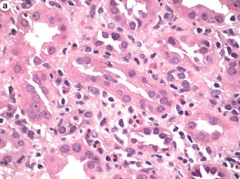
Interstitial Nephritis
|
1. Methicillin
2. NSAIDS 3. Furosamide |
|
|
|
SIADH
|
1. Carbamazepine
2. Cyclophosphamide: [Cancer Anutoimmune] 3. SSRI's |
Can't Concentrate Serum Sodium
|
|
|
Dry Cough
|
1. ACE Inhibitors
|
|
|
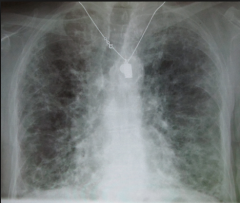
Pulmonary Fibrosis
|
1. Bleomycin
2. Amioderone: [Annti-Arrythmic] 3. Busulfan: [Leukemia] 4. Methotrexate: [Cancer Autoimmune] |
Breathing Air Badly from Medications
|
|
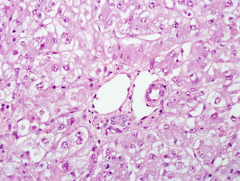
Toxin: Acetominophen
|
Antidote: N-acetylcystiene (replenishes glutathione)
|

|
|

Toxin: AChE inhibitors, Organophosphates
|
Antidote: Atropine followed by pralidoxime
|
1. Atropine blocks achetylcholine action at nerve junction but is not an actual antidote.
2. AChE normally binds ACh at 2 sites. The toxin binds at only 1 of these sites and inhibits the enzyme. Praladoxine binds at the other end, attaches to the toxin, changes its conformation, and then toxin-antidote both leave the enzymatic site together. |
|
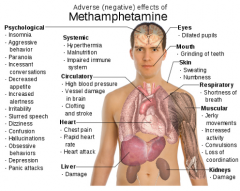
Toxin: Amphetamines (basic)
|
Antidote: NH4Cl (acidify urine)
|
|
|

Toxin: Antimuscarinic, Anticholinergic Agents
i.e Atropine, Scopalamine, Hyoscyamine |
Antidote: Physostigmine Salicylate, Control Hypothermia
|

Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor indirectly increases the amount of acetylcholine in cleft.
|
|
|
Toxin: Benzodiazepines
|
Antidote: Flumazenil
|
Most patients with pure benzodiazepine overdose will usually only exhibit these mild CNS symptoms
Can reverse CNS depression but not Respiratory depression. Only indicated in 10% of cases becasue of side effects |
|
|
Toxin: B-Blockers
|
Antidote: Glucagon
|
|
|
Toxin: Carbon Monoxide
|
Antidote: 100% O2, Hyperbaric O2
|
|
|
Toxin: Copper, Arsenic, Gold
|
Antidote: Penicillamine
|
Chelating Agent: Binds to copper, arsenic and gold and eliminates it through urine.
|
|

Toxin: Cyanide
|
Antidote: Nitrite+thiosulfate, Hydroxocobalamin
|
1. Hydroxocobalamin reacts with cyanide to form cyanocobalamin, which can be safely eliminated by the kidneys.
2. The nitrites oxidize hemoglobin to methemoglobin, which competes with cytochrome oxidase for cyanide ion. Cyanmethemoglobin is formed and the cytochrome oxidase enzyme is restored. The major mechanism to remove the cyanide from the body is by enzymatic conversion to thiocyanate by the mitochondrial enzyme rhodanese. Thiocyanate is a relatively non-toxic molecule and is excreted by the kidneys |
|

Toxin: Digitalis
|
Antidote: Anti-Dig Fab Fragments
|

|
|
|
Toxin: Heparin
|
Antidote: Protamine sulfate
|
|
|
|
Toxin: Iron
|
Antidote: Deferoxamine, deferasirox
|
|
|
Toxin: Lead
|
Antidote: EDTA, dimercaprol, succimer, penicillamine
|
|
|
|
Toxin: Mercury, Arsenic, Gold
|
Antidote: Dimercaprol (BAL), succimer
|
|
|
|
Toxin: Methanol, Ethylene Glycol
|
Antidote: Fomepizole > Alcahol, Dialysis
|
|
|
|
Toxin: Methemoglobin
|
Antidote: Methylene Blue, Vitamin C
|
|
|
|
Toxin: Opioids
|
Antidote: Naloxone
|
|
|
|
Toxin: Salicylates
|
Antidote: NaHCO3 (alkalinize urine), Dialysis
|
|
|
|
Toxin: TCA's
|
Antidote: NaHCO3 (plasma alkalinization)
|
|
|
|
Toxin: tPA, Streptokinase, Urokinase
|
Antidote: Aminocaproic Acid
|
|
|
|
Toxin: Warfarin
|
Anitdote: Vitamin K, Plasma (if active bleeding)
|
|
|
|
Anti-muscarinic
|
1. Atropine
2. TCA 3. Anit-psychotics 4. H1 Blockers |
|
|

Disulfiram Like Reaction
|
1. Metronidazole
2. Cephalosporins 3. Griseofulvin 4. Procarbazine 5. 1st Generation Sulfonyureas |
|
|
|
Nephrotoxicity/Ototoxicity
|
1. Vancomycin
2. Aminoglycosides 3. Furosimide-Loop Diuretics 4. Cisplatin |
|
|
|
Cytochrome p450 Inducers +
|
1. Chronic Alcohol Use
2. Modafinil 3. St. Johns Wart 4. Phenytoin 5. Phenobarbitol 6. Nevirapine NNRTI 7. Rifampin 8. Grisofulvan 9. Carbamazipine |
Chronic Alcaholic Mona Steals Phen-Phen and Never Refuses Greasy Carbs
|
|
|
Substrates
|
1. Anti-epileptics
2. Anti depressants 3. Antipsychotics 4. Anesthetics 5. Theophyline 6. Warfarin 7. Statins 8. OCPs |
Always Always Always Always Think When Starting Others
|
|
|
Cytochrome P450 Inhibitors -
|
1. Acute Alcahol abuse
2. Gemfibrozil 3. Ciprofloxacin 4. Isoniazid 5. Grapefruit Juice 6. Quinidine 7. Amioderone 8. Ketoconazole 9. Macrolides 10. Sulfonamides 11. Cimetidine 12. Ritanovir |
A Cute Gentleman Cippied Iced Grapefruit Juice Quickly And Kept Munching on Soft Cinnamon Rolls
|
|
|
Sulfa Drugs
|
1. Probenecid
2. Furosimide 3. Acetazolamide 4. Celecoxib 5. Thiazides 6. Sulfonamide Antibiotics 7. Sulfsalazine 8. Sulfonylureas |
Popular FACTSSS
|

