![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
150 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
achalasia
|
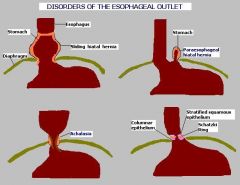
-a/w scleroderma
-decrease in VIP -nocturnal regurg of food -dysphagia for solids and liquids -chest pain and heart burn, hiccups, nocturnal cough, difficulty belching |
|
|
Tx for achalasia?
|
pneumatic dilation, esophagomyotomy, long acting nitrates, Calcium channel blockers, botulinum toxin injection
|
|
|
gold standard diagnosis for GERD?
|
24-48 hr PH monitoring
|
|
|
Esophageal varices
|
-painless bleeding of submucosal veins in lower 1/3 of esophagus
-L. gastric vein, portal HTN |
|
|
Esophagitis
|
a/w reflux, infection (HSV-1, CMV, Candida), or chemical ingestion
|
|
|
Plummer-Vinson syndrome
|
traid of: Dysphagia, Glossitis, Iron deficiency anemia
|
|
|
Barrett's esophagus
|
replacement of nonkeratinized (stratified) squamous epithelium with intestinal (columnar) epithelium
|
|
|
risk factors for esophageal cancer?
|
ABCDEF
Alchohol/Achalasia Barrett's esophagus Cigarettes Diverticuli Esophageal web, esophagitis Familial |
|
|
Where does squamous cell carcinoma present vs Adenocarcinoma in esophagus?
|
Squamous cell--upper and middle
Adenocarcinoma--lower 1/3 |
|
|
Where does celiac's dz present?
|
proximal small bowel
|
|
|
What is celiac's dz a/w?
|
dermatatis herpatiformi (vesicular lesions on elbow)
|
|
|
Tropical sprue
|
probably infection; responds to antibiotics. Similar to celiac sprue, but can affect entire small bowel
|
|
|
Whipple's disease
|
-tropheryma whippeli (can't culture, gram (+);
-PAS positive (stains with glycoprotein) in intestinal lamina propria -mesenteric nodules -Arthlagias, cardiac and neurologic symptoms are common -commin in older men "andy Whipple becomes and old man who has a big heart but is slightly crazy bc he lives in the PASt when his medical school years were good. |
|
|
disaccharidase deficiency
|
-MC= lactase defieciency--> milk intolerance. Normal-appearing villi.
-Since lactase is located at tips of intestinal villi, self-limited lactase deficiency can occur following injury (viral diarrhea) - |
|
|
What kind of diarrhea is disaccharidase deficiency?
|
osmotic diarrhea
|
|
|
PH of stool in disaccharidase deficiency?
|
Low, acid stool
|
|
|
mechaninsm of disaccharidase deficiency
|
-lactose--> glucose and galactose
-Goes to colon and anearobic bacteria eat it |
|
|
Pancreatic insufficiency
|
-Due to cystic fibrosis, obstructing cancer, and chronic pancreatitis
-Causes malabsorption of fat and fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) |
|
|
Abeta-lipoprotinemia
|
-decrease synthesis of apo B --> inability to generate chylomicrons --> decreased secretion of cholesterol, VLDL into blood stream --> fat accumulation in enterocyte. Present in early childhood with malabsorption and neurologic manifestations
|
|
|
Celiacs have antibodies to what?
|
gliadin and tissue transglutaminase
|
|
|
Celiacs dz primarily affects what area?
|
jejunum
|
|
|
What is the screening test for celiacs?
|
serum levels of tissue transglutaminase antibodies
|
|
|
causes of acute gastritis?
|
stress, NSAIDs (decrease PGE2 --> decrease mucosa production), alcohol, uremia, burns (Curlings ulcer) and brain injury (Cushing's ulcer)
-"Burned by the curling iron, always cushion the brain" |
|
|
describe the difference between cushings and curling's ulcer
|
Curlings: decrease plasma volume --> sloughing of gastric mucosa
cushings: increased vagal stimulation --> Increased Ach --> increased H+ production |
|
|
Type A chronic gastritis
|
-nonerosive, fundus/body
-Autimmune disorder characterized by Autoantibodies to parietal cells -pernicious Anemia -Achlorhydira -a/w other autoimmune disorders |
|
|
Type B chronic gastritis
|
-MC
-H. Pylori infection (burrown through mucus) -increased risk of MALT lymphoma "Bacterium affects the Antrum" |
|
|
Menetrier's dz
|
-Gastric hypertrophy with protein loss, parietal cell atrophy and increase mucous cells. Precancerous.
-Rugae of stomach are so hypertrophied that they look like brain gyri -Mostly males |
|
|
What type of cancer is stomach cancer usually?
|
-adenocarcinoma
-early aggressive local spread and node/liver mets (supraclavicular node) |
|
|
What is adenocarcinoma of the stomach a/w?
|
nitrosamines (smoked foods), achlorhydria, chronic gastritis type A blood.
|
|
|
features of adenocarcinoma of the stomach?
|
-Signet ring cells
-acanthosis nigricans -linitis plastica (diffusely infiltrative, thickened rigid appearance "leather bottle) |
|
|
MC location for adenocarcinoma of the stomach?
|
lesser curvature
|
|
|
Virchow's node
|
involvement of left supraclavicular node by mets from stomach
|
|
|
Krukenberg's tumor
|
bilateral mets to ovaries. Abundant mucus, signet ring cells
|
|
|
Sister Mary Joseph's nodules
|
subcutaneous periumbilical metastasis
|
|
|
gastric uclers
|
-pain if Greater with meals (weight loss)
-often older pts -H. pylori if 70% -NSAIDs -due to decrease mucosal protection |
|
|
MCC of duoenal ulcers?
|
-almost 100% h. pylori
- |
|
|
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
|
increase gastric acid secretion causes duodenal ulcers
|
|
|
Hypertrophy of Brunner's glands?
|
-Cause of duodenal ulcers. Decrease mucosal protection
|
|
|
What do the ulcers look like in the duodenum?
|
clean, punched out margins unlike the raised margins of carcinoma.
|
|
|
Complications of duodenal ulcer?
|
-bleeding, penetration into pancrease, perofration, and obstruction
|
|
|
Presentation of Duodenal ulcer?
|
-pain Decreases with meal (weight gain)
-black tarry stool (acid works on hemaglobin to make hematin = black pigment) -can present as shoulder pain do flat plate |
|
|
What does ischemic colitis of the splenic flexure present as vs Small bowel?
|
-ischemia of splenic flexure= specific pain and bloody stool
-small bowel= entire abdomen + bloody diarrhea -pain after eating --> weight loss |
|
|
extraintestinal manifestations of chrons?
|
Migratory polyarthritis, eythrma nodosum, ankylosing spondylitis, uveitis, immunologic disorders
|
|
|
extraintestinal manifestations of Ulcative colitis?
|
pyoderma gangrenosum, primary sclerosing cholangitis
|
|
|
treatment of chrons?
|
Corticosteroids, infliximab
"Inflict the Crohn with steroids" |
|
|
treatment of Ulcerative colitis?
|
ASA preparations (sulfasalazine), ifliximab, colectomy
|
|
|
IBS
|
Recurrent abdominal pain a/w >2 of the following:
1) Pain improves with defecation 2) Change in stool frequency 3) Change in appearance of stool No structual abnormalities. May present with diarrhea, constipation, or alternating. Tx symptoms |
|
|
MCC of appendicitis in children?
|
-mumps or adenovirus
-Lymphoid tissue in appendix. -Hyperplasia of lymphoid tissue in appenix |
|
|
MCC of appendicitis in adults?
|
stool impaction= produces ischemia and e. coli gets in
|
|
|
MC indication for abdominal surgery in children?
|
appendicitis
|
|
|
False diverticula
|
-most common
-lack or have an attenuated muscularis externa -only mucosa and submucosa outpouch (vs true which has all three) |
|
|
MC place for a false diverticula?
|
where vasa recta perforate muscularix externa
|
|
|
What causes diverticulosis?
|
increased intraluminal pressure and focal weakness in colonic wall. A/w low fiber diets.
|
|
|
Symptoms of diverticulosis?
|
often aymptomatic or a/w vague discomfort and/or painless rectal bleeding
|
|
|
MC place for diverticulosis?
|
sigmoid colon
|
|
|
Diverticulitis
|
-inflammation of diverticula
-may perforate--> peritonitis, abcess formation or bowel stenosis. -Give antibiotics |
|
|
symptoms of diverticulitis
|
-LLQ pain, fever, leukocytosis
-bright red bleeding -"left sided appendicitis" |
|
|
pneumaturia
|
-caused by diverticulitits
-colovesicle fistula (fistula with bladder) |
|
|
Zenker's diverticulum
|
-False diverticulum
-herniation of mucosal tissue at junction of pharynx and esophagus. -symptoms: halitosis, dysphagia, obstruction |
|
|
Where does meckel's diverticulum arise from?
|
-vitelline duct or yolk stalk
|
|
|
What may be contained in a meckel's diverticulum?
|
-ectopic acid--secreting gastric mucosa and/or pancreatic tissue
|
|
|
MC congenital anomaly of the GI tract?
|
meckel's diverticulum
|
|
|
What can meckel's diverticulum cause?
|
PAINLESS bleeding, intrussusception, volvulus or obstruction near the terminal ileum.
|
|
|
omphalomesenteric cyst
|
-cystic dilation of vitelline duct
-feces coming out of umbilicus -connects midgut with the yolk sac |
|
|
intussusception
|
-can comprimise blood supply
-usually in kids (adenovirus) -Abdominal emergency in early childhood -coil spring appearance on barium enema on ultrasound |
|
|
Volvulus
|
-twisting of portion of bowel around its mesentery; can lead to obstruction and infarction
-may occur at cecum and sigmoid colon, where ther is redundant mesentery -usually in elderly |
|
|
What is Hirschsprungs dz due to?
|
-failure of neural crest migration (lose Auerbach's and Meissner's plexuses)
-lose sympathetic neuons -problem in RET signalling pathway |
|
|
Symptoms of Hirschsprungs dz?
|
-no bowel movement, chronic constipation early in life
-abdominal pain, small stools -no stool on examining finger, no stool in rectal vault -failure to pass meconium -dilated portion of colon proximal to the aganglionic segment (dilated megacolon) |
|
|
What bug can cause Hirschsprungs dz?
|
Chaga's dz (trypanosoma cruzi)
|
|
|
MC place for Hirschsprungs dz?
|
-distal sigmoid colon and rectum
|
|
|
duodenal atresia
|
-Causes early bilious vomiting with proximal stomach distention (double bubble) due to failure of recanalization of small bowel.
-a/w down syndrome |
|
|
Meconium ileus
|
in cystic fibrosis, meconium plug obstructs intestine, preventing stool passage at birth
|
|
|
Necrotizing enterocolitis
|
-Necrosis of intestinal mucosa and possible perforation.
-Colon is usually involved, but can involve entire GI tract -In neonates, MC in premies -blood in stool, biliary distention, air in bowel |
|
|
Angiodysplasia
|
-Tortuous dilation of vessels--> bleeding
-most often found in cecum, terminal ileum and ascending colon -MC in older pts -confirmed by angiography |
|
|
What makes a polyp more malignant?
|
the more villous it is
VILLous = VILLainOUS |
|
|
MC non-neoplastic polyp in colon?
|
Hyperplastic (>50 % found in rectosigmoid colon
|
|
|
Juvenile polyposis syndrome
|
-if just one = not pre-cancerious
-if mutlople increase risk for adenocarcinoma |
|
|
Puetz-Jeghers syndrome
|
-AD
-multiple nonmaligant hamartomas throughout GI tract -hyperpigmented mouth, lips, hands, and genitalia -increase risk of CRC and other malignancies |
|
|
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP)
|
-AD mutation of APC gene (uncontrolled cell proliferation) on chromosome 5q
-Two-hit hypothesis. 100% progress to CRC -Thousands of polypsl pancolonic, always involves the rectum |
|
|
Gardner's syndrome
|
FAP + osseus and soft tissue tumors, retinal hyperplasia
"The FAMILY GARDNER was a SOFT man with nice EYEs, and had BONEY hands |
|
|
Turcot's syndrome
|
AR, FAP + malignant CNS tumor
"Turcot = Turban" |
|
|
Hereditary nonpolyposis colerectal cancer (HNPCC/Lynch syndrome)
|
AD mutation of DNA mismatch repair genes (80% progress to CRC)
-proximal colon is always involved |
|
|
Risk factors to CRC?
|
IDB, streptococcus bovis, tobacco use, large villous adenomas, juvanile polyposis syndrome, Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, decreased fiber intake (decreased ability to get rid of lithcolic acid)
|
|
|
Presentation of distal vs proximal colon in CRC
|
Distal (L)-obstruction, colicky pain, hematochezia (smaller diameter, forms anular polyp bc theres not enough room.
Proximal colon (R)- dull pain, iron deficiency anemia, fatigue (bleeds, bigger diameter, better chance of forming a polyp) |
|
|
Apple core lesion seen on barium enema x-ray?
|
colorectal cancer
|
|
|
Villous adenoma
|
-sessile. Looks like villous surface of small intestine. Have increase Malignant potential
-Mucus coating of the stool |
|
|
most common place for carcinoid tumor?
|
small intestine
|
|
|
EM of carcinoid tumor?
|
dense core bodies
|
|
|
Symptoms of carcinoid tumor?
|
wheezing, right-sided heart murmurs, diarrhea, flushing
|
|
|
Serum markers of viral hepatitis?
|
ALT> AST
(ALT means diffuse liver necrosis) |
|
|
Serum markers of alcoholic hepatitis?
|
AST>ALT also GGT
"wASTed" could also be fatty change. Increased AST means mitochondria are uncoupled |
|
|
MI Serum markers from liver?
|
AST
|
|
|
Obstructive liver dz
|
increased gamma glutamyl transferase and increased Alkaline phosphatase
|
|
|
best tests for liver severity?
|
-albumin levels and PT (these are made in the liver so if there is a severe problem they will be low)
|
|
|
Mechanism of Reye's syndrome
|
asprin metabolites decreases beta oxidation by reversible inhibition of mitochondrial enzyme.
|
|
|
Findings in Reye's syndome?
|
-mitochondrial abnormalities, fatty liver (microvesicular fatty change), hypoglycemia, coma
-a/w viral infections (VZV and influenza B) |
|
|
Hepatic steatosis?
|
short-term change with moderate alcohol intake. Macrovesicular fatty change that may be reversible with alcohol cessation
|
|
|
Alcoholic hepatitis
|
-Requires sustained, long-term consumption.
-swollen and necrotic hepatocytes with neutrophilic inflitration. -Mallory bodies (intracytoplasmic eosinophils |
|
|
alcoholic cirrhosis
|
-irreversible
-micronodular -irregular and shrunken liver -"honail" appearance -sclerosis around central vein |
|
|
risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma/hepatoma
|
-Hep B and Hep C
-Wilson's dz -hemochromatosis -alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency -alcoholic cirrhosis -carcinogens (aflatoxin in peanuts) |
|
|
important serum marker for hepatocellular carcinoma?
|
-alpha-fetoprotein
|
|
|
Findings in hepatocellular carcinoma?
|
jaundice, tender hepatomegaly, ascites, polycythemia, and hypoglycemia
|
|
|
Nutmeg liver
|
-back-up of blood into liver.
-Commonly caused by right sides heart failure and Budd-Chiari syndrome. -liver appears mottled like nutmeg -centrilobular congestion and necrosis can result in cardiac cirrhosis |
|
|
Budd-Chiari syndrome
|
occlusion of IVE or hepatic veins with centrilobular congestion and necrosis, leading to congestive liver disease (hepatomegaly, ascites, abdominal pain and eventual liver failure)
-varices, visible abdominal and back veins -Absent JVD |
|
|
what is Budd-Chiari syndrome a/w?
|
polycythemia vera, pregnancy and hepatocellular carcinoma
|
|
|
alpha-1 antitrypsin in hepatic carcinoma?
|
-decreased
-can be seen as PAS (period acid-schiff) positive globules |
|
|
Gilbert's syndrome
|
-mildly decreased UDP-glucuronyl transferase or decrease bilirubin uptake.
-asymptomatic. Elevated unconjugated bilirubin w/o overt hemolysis |
|
|
What is wilson's disease characterized by?
|
-Asterixis
-Basal ganglia degeneration (parkinsonian) -Ceruloplasmin, Cirrhosis, Corneal deposits (Kayser-Fleischer rings), Copper accumulation, Carcinoma, Choreiform movements -Dementia -Hemolytic anemia -Renal dz (fanconi's syndrome) |
|
|
Tx for wilson's dz
|
Penicillamine (copper chelator), zinc (inhibits copper reabsorption in intestine), ammonium tetrthiomolydate (amonium competes for copper reabsorption in bowel, increase excretion in urine)
|
|
|
Pathology behind wilson's dz?
|
-failure of copper to enter circulation as ceruloplasm (binding protein for copper)
-increased unbound copper in blood -toxic effects |
|
|
gold standard diagnosis for wilson's dz?
|
liver biopsy for copper
|
|
|
Hemochromatosis
|
-iron deposition.
-classic triad= Cirrhosis, Diabetes mellitus, and skin pigmentation --> bronze diabetes -CHF, increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma -May be AR or due to chronic infusion therapy (high ferritin, iron and decreased TIBC= increased transferrin saturation) |
|
|
serum marker in Primary biliary Cirrhosis
|
-increased serum mitochondrial antibodies
-a/w other autoimmune conditions |
|
|
serum marker for primary sclerosing cholangitis
|
Hypergammaglobuinemia (IgM). Associated with ulcerative colitis. Can lead to secondary biliary cirrhosis
|
|
|
Cholesterol stones
|
-MC, radiolucent with 10-20% opaque due to calcifications
-obesity, Crohn's dz, cysitc fibrosis, advanced age, clofibrate, estrogens, multiparity, rapid weight loss and native american "The Fat Old Native American Chron, who had Many Babies and was on Estrogen meds refused to eat Cholesterol and only ate Fiber so she had Rapid Weight Loss" |
|
|
Pigment stone
|
-radioopaque
-seen in pts with chronic hemolysis, alcoholic cirrhosis, advanced age and biliary infection -jet black stones. |
|
|
Cholestasis
|
-Stone in common bile duct -deep green colored liver.
-Bile is blocked, which has conj bilirubin in it and is backed up into the liver. -conj bilirubin will eventually reflux into the sinusoids, and leads to bilirubin in the urine and light color stools, with NO urobilinogen in the urine. The yellow urine is due to water soluble conj bilirubin in the urine. -Alk phos and gamma glutamyl transferase are elevated What is the mech for getting rid of cholesterol? Bile. So, you reflux cholesterol, bilirubin and bile salts (they are all recycled). -No hypercholesterolemia b/c it is recycled. -bile salts deposit in the skin, leading to itching. |
|
|
Hemosiderosis
|
ACQUIRED Fe overload – from alcohol.
|
|
|
MCC’s hepatocellular carcinoma
|
pigment cirrhosis: hemochromatosis; hepatitis B and C.
|
|
|
pt with underlying cirrhosis, and is stable. But suddenly the pt begins to lose wt and ascites is getting worse. Do a peritoneal tap and it is hemorrhagic. Dx?
|
hepatocellular carcinoma (get alpha feto protein)
|
|
|
MCC small bowel obstruction?
|
adhesion from previous surgery if no surgery than indirect inguinal hernia.
|
|
|
25 y/o female, RUQ crampy pain, fever, point tenderness, neutrophilic leukocytosis, stones revealed on ultrasound. CBC showed a mild normocytic anemia and a corrected reticulocyte ct of 8%. Splenomegaly on PE and family hx of splenectomy. Dx?
|
Congenital spherocytosis; b/c she has been hemolyzing RBC’s all her life, she puts a lot of bilirubin into conj bilirubin and therefore has supersaturated bile with bilirubin, and forms Ca bilirubinate stones that are jet black. Seen with ultrasound.
|
|
|
screening test of choice for stones?
|
Ultrasound
|
|
|
Screening test of choice for anything in the pancreas
|
CT
|
|
|
What can be seen on x-ray if stone obstructs ileocecal valve?
|
air in the biliary tree
|
|
|
Cholecystitis
|
-Inflammation of gallbladder. -Usually from gallstones; rarely ischemia or infections
-increase alkaline phosphatase if bile duct becomes involved |
|
|
Causes of acute pancreatitis?
|
-Gallstones
-Ethanolol -Trauma -Steroids -Mumps -Autoimmune -Scorpion string -Hypercalcemia/Hyperlipidemia -ERCP -Drugs (sulfa drugs) "GET SMASHED" |
|
|
clinical presentation of acute pancreatitis?
|
-epigastric abdominal pain radiating to back
-anorexia -nausea |
|
|
labs in acute pancreatitis?
|
elevated amylase lipase
|
|
|
MCC of acute pancreatitis?
|
alcohol
|
|
|
2nd MCC of acute pancreatitis?
|
stone caught in accessory ducts of the pancreas
|
|
|
Pancreatic pseudocyst
|
-Hx of acute pancreatitis
-a lot of fluid accumulates around an inflamed pancreas and forms a false capsule and has a potential to rupture (not good to have amylase in peritoneal cavity). |
|
|
MCC of pancreatic cancer in the head of the pancreas? 2nd MCC?
|
MCC = smoker, 2nd MCC = chronic pancreatitis, painless jaundice (mainly conjugated bilirubin), light colored stools, palpable GB (Courvoisier’s sign).
|
|
|
Sentinel sign
|
Duodenum next to inflammed pancreas stops peristalsing (Whenever the bowel lacks peristalsis, will see air accumulate and will get distension)
|
|
|
Chronic pancreatitis?
|
-can lead to pancreatic insufficiency --> steatorrhea, fat -soluble vitamin deficiency
-Chronic calcifying pancreatitis is stongly associated with alcoholism, increase risk of pancreatic cancer |
|
|
Where are tumors more common in the pancreas?
|
pancreatic head
|
|
|
PPl at risk for pancreatic adenocarcinoma?
|
Jewish and African-American males
|
|
|
tumor markers for pancreatic adenocarcinoma?
|
CEA and CA-19-9 tumor markers
|
|
|
how does pancreatic adenocarcinoma present?
|
1) abdominal pain radiating to back
2) weight loss (due to malabsoprtion and anorexia) 3) Migratory thrombophlebitis (redness and tenderness on palpation of extremities (trousseau's syndrome) 4) Obstructive jaundice with palpable gallbladder (Courvoisier's sign) |
|
|
I-hyperchylomicronemia labs
|
-increased chylomicrons
-elevated TG, Cholesterol |
|
|
pathophysiology of I-hyperchylomicronemia
|
-lipoprotein lipase deficiency or altered apolipoprotein C-II.
-Causes pancreatitits, hepatosplenomegaly, and eruptive/pruritic xanthomas (no increased risk for atherosclerosis) "hyperCYLomicronemia causes the pancreas to CRY" |
|
|
IIa-familial hypercholesterolemia labs
|
increased LDL, increased Cholesterol
|
|
|
IIa-familial hypercholesterolemia pathophys
|
AD, adsent LDL receptors, Causes accelerated atherosclerosis, tendon (achilles) xanthomas, and corneal arcus
"Achilles LoveD cholesterol so he turned yellow and got athersclerosis" |
|
|
IV-hypertriglyceridemia labs
|
increased VLDL, increased TG
|
|
|
IV-hypertriglyceridemia pathophys
|
-hepatic overproduction of VLDL
-causes pancreatitis "the liver TRIs too hard to produce VLDL" |
|
|
the left gastro-omental artery branches off of what artery?
|
-splenic
-supplies greater curvature of stomach |
|
|
the right gastro-omental artery branches off of what artery?
|
Gastroduodenal artery
|
|
|
Gastroduodenal artery branches off of what?
|
common Hepatic artery
|
|
|
Right gastric artery branches off of what artery?
|
proper hepatic
|
|
|
The left gastric artery branches off of what artery?
|
Celiac trunk
|

