![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
118 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
recurrent sinusitis, bronchiectasis, male infertility
genetics? |
Kartagener(dynein microtubule defect)
autosomal recessive |
|
|
Tuberous Sclerosis
|
autosomal dominant
adenoma sebaceum SEIZURES mental retardation CNS hamartomas cardiac rhabdomyomas ash leaf spots renal angiomyolipoma |
|
|
Friedrich's Ataxia
genetics and presentation |
Autosomal Recessive - trinucleotide(GAA) repeat in frataxin gene
spinal ataxia - staggering gait, hammer toes, etc. kyphoscoliosis in child |
|
|
Neural input to adrenals
|
one neuron -- ACh
|
|
|
neural input to sweat glands
|
2 neurons -- ACh
|
|
|
20% ether is effective at destroying?
|
enveloped viruses
|
|
|
How do you destroy non-enveloped viruses
|
boil in water 1 minute
|
|
|
snRNP
|
small nuclear ribonucleoproteins
participate in the formation of spliceosomes |
|
|
what is the resistance of a vessel determined by?
|
viscosity*length/radius^4
|
|
|
how do you calculate flow in a blood vessel?
|
change in pressure / Resistance
|
|
|
pemphigus vulgaris
|
IgG antibody vs desmosomes(anti-epithelial cell antibody)
"Nikolsky's Sign" positive -- skin peels off light rubbing |
|
|
acantholysis
|
loss of intercellular connections
a/w pemphigus vulgaris |
|
|
bullous pemphigoid
|
IgG antibody against HEMIdesmosomes(epidermal basement membrane..."bullow" the membrane)
eosinophils with tense blisters |
|
|
spares oral mucosa
Nikolsky's sign? bullous pemphigoid vs pemphigus vulgaris |
bullous pemphigoid
negative |
|
|
Dermatitis herpetiformis a/w
|
celiac disease
|
|
|
Deposits of IgA at tips of dermal papillae leading to pruritic papules and vesicles
|
Dermatitis herpetiformis
|
|
|
anti-desmoglein antibodies
Nikolsky sign? |
pemphigus vulgaris
positive |
|
|
pemphigus vulgaris hypersensitivity
|
Type II
|
|
|
Calcium dependent adhesion molecules
|
Cadherins
|
|
|
Epithelial Junctions
types and associated protein |
Zona Occludens(tight) - claudins/occludins
Zona adherens - actin/cadherins Macula adherens(desmosome) - IMF/cadherins Hemidesmosome - integrins bind laminin in BM |
|
|
sensory nerve to pinky area
|
C8
|
|
|
sensory nerve to deltoid area
|
C4
|
|
|
sensory nerve to middle finger area
|
C7
|
|
|
sensory nerve to thumb area
|
C8
|
|
|
sensory nerve to proximal arm(humerus) area
|
C5
|
|
|
draw brachial plexus
|
draw
|
|
|
long thoracic nerve innervates
|
serratus anterior
|
|
|
rotator cuff muscles
|
SItS
Supraspinatus Infraspinatus teres minor Subscapularis |
|
|
pudendal nerve landmark
|
ischial spine
|
|
|
lumbar puncture landmark
|
iliac crest
|
|
|
promotes migration and proliferation of smooth muscle cells into intima of blood vessels
|
PDGF
|
|
|
promotes migration of smooth muscle cells
|
TGF-Beta
|
|
|
men who engage in anal intercourse are at risk for urethritis by what organism?
|
E. coli
|
|
|
purulent, yellow-green urethral discharge from a male
|
gonorrhea
|
|
|
Describe process of Type IV hypersensitivity
|
Dendritic cells process antigen and present it on MHC II receptors to Th1 cells which secrete IFN-gamma to recruit macrophages
|
|
|
What cells produce factors that cause atheroma production?
|
monocytes and platelets
|
|
|
where are pericytes most populated in the vasculature?
|
post capillary venules
|
|
|
What antibiotic fights chlamydia?
|
Azithromycin(Macrolide)
or Doxycycline(Tetracycline) |
|
|
Alternative treatment for gonorrhea?
|
Fluoroquinolone
|
|
|
What type of hypersensitivity is granulomatous inflammation?
|
Type IV
|
|
|
What cytokine important for Type IV hypersensitivity?
|
IFN-gamma released by Th1
|
|
|
Octreotide
|
Somatostatin analog
|
|
|
What MOA does octreotide treat diarrhea?
|
decreases secretions
|
|
|
diphenoxylate
|
opiate related to meperidine that reduces gastric motility
|
|
|
Cri-du-chat syndrome
|
5p deletion
|
|
|
Paternal vs Maternal inheritance of Huntington's Disease
|
Maternal inheritance will not exhibit anticipation. This is because the expansion of trinucleotide repeats occurs during spermatogenesis.
|
|
|
neuraminidase cleaves what molecule?
|
Sialic Acid
|
|
|
What is necessary to be mindful of for nitrate administration
|
tolerance development in repeated usage
|
|
|
"Monday disease" or heart palpitations and flushing in an industrial worker
|
Nitrate occupational exposure
Develops tolerance over the week and then upon rexposure experiences reflex symptoms to the vasodilatory effects of the nitrate. |
|
|
Nitroglycerin MOA
|
NO release in smooth muscle causing increase in cGMP.
Venodilatory |
|
|
Phase 1 vs Phase 2 metabolism
old people lose what first? |
Phase 1 - P-450
Phase 2 - Glucuronidation, Acetylation, Sulfation(GAS) OLD PEOPLE HAVE GAS geriatrics lose Phase 1 |
|
|
P-450 inducers
|
Quinidine
Barbiturates St. John's Wart Phenytoin Rifampin Griseofulvin Carbamazepine Chronic Alcohol Use |
|
|
P-450 inhibitors
|
MAGIC RACKS
Macrolides Amiodarone Grapefruit Juice Isoniazid Cimetidine Ritonavir Acute Alcohol Abuse Ciprofloxacin Ketoconazole Sulfonamides |
|
|
Carbamazepine
|
Anti-epileptic for partial seizures
Mood stabilizer for bipolar disorder |
|
|
Describe an instance of pharmacodynamic drug antagonism
|
A non-selective beta blocker(labetalol, carvedilol) will block the effects of catecholamines by preventing them from binding
|
|
|
What do you coadminister with nitrates?
|
Beta blockers to try to prevent reflex tachycardia
|
|
|
Marker for immunity vs Hep B
|
Anti-HBsAg
|
|
|
Window period of Hep B infection
|
period between loss of HBs Ag in blood and appearance of Anti-HBsAg in bloodI
|
|
|
IgM Anti-HBc
|
important SPECIFIC marker for acute Hep B infection
Will be present during window period. |
|
|
IgG Anti-HBc
|
will be present in resolved infection as well as chronic infection but be ABSENT in vaccinated individuals.
|
|
|
Marker of acute infection of Hepatitis A
|
Anti-HAV IgM
|
|
|
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
|
Emphysema
Chronic Bronchitis |
|
|
Cystic fibrosis patients classically have what lung disorder
|
COPD - bronchiectasis
|
|
|
QRS complex corresponds to...?
|
ventricular depolarization
|
|
|
Which phases do anti-arrhythmics not work on?
|
1 and 4
|
|
|
Which class are K+ modulators anti-arrhythmics? What phase do they work on?
|
Class III
Phase 3 |
|
|
Which class are Ca+2 modulators anti-arrhythmics? What phase do they mostly work on?
|
Class IV
Phase 2 |
|
|
Ventricular repolarization correlates to what phase?
|
Phase 0, the immediate incline
Phase 4 is the flat plateau before the next AP Phase 2 is the depolarized plateau. |
|
|
What substance is neither secreted nor absorbed in kidney?
|
Inulin
100% of inulin is excreted |
|
|
What substance is almost completely excreted in kidneys?
|
Paraaminohippuric Acid(PAH)
90% of filtered PAH is EXCRETED |
|
|
What substance is almost completely reabsorbed in kidneys?
|
Sodium
99% of filtered sodium is reabsorbed |
|
|
Describe absorption/secretion of urea in kidney...
|
About 55% of filtered urea is excreted
|
|
|
GFR is dependent on what factors?
|
oncotic pressure difference and hydrostatic pressure difference between Bowman's Capsule and Renal Arteriole.
|
|
|
How does a bladder neck obstruction influence FF?
|
It increases Bowman's Space Hydrostatic Pressure pushing fluid back into arteriole, thereby decreasing GFR.
Doesn't change RPF, so net decrease in FF |
|
|
How does constriction of afferent arteriole change FF?
|
It doesn't change FF
|
|
|
How does dilation of efferent arteriole change FF?
|
It decreases FF via increase in RPF and decrease in GFR(decreased renal capillary hydrostatic pressure)
|
|
|
aseptic meningitis with oral ulcers on the back of the mouth
|
coxsackie A
|
|
|
Slow progression of hemiparesis, visual field defects(hemianopsia), cognitive impairment.
|
JC Virus
progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy |
|
|
Infectious causes of Hydrops Fetalis
|
CMV, Syphilis, Parvovirus B19
|
|
|
Rheumatic heart disease - which valves affected?
|
80% only mitral valve
20% mitral and aortic valve |
|
|
endocarditis a/w colonic malignancy
|
strep bovis
|
|
|
endocarditis a/w genitourinary procedures
|
e. faecium, faecalis
|
|
|
What does anergy to cutaneously applied candida antigen imply?
|
decreased cell-mediated immunity(T-cell dependent)
|
|
|
Which hypersensitivity is associated with a decrease in complement?
|
Type III
|
|
|
fever, urticaria, arthralgias, glomerulonephritis, lymphadenopathy, low C3 serum level
|
serum sickness - Type III hypersensitivity
|
|
|
watershed stroke
|
most common in ant/middle
presents with upper arm/leg weakness, higher order visual processing |
|
|
Possible method of drug resistance by tumor cells
|
ATP dependent pump similar to bacteria
|
|
|
MDR1 is a protein expressed by cancer cells that provides drug resistance. A protein similar to MDR1 is normally expressed in what tissue?
|
intestinal, renal tubular cells, and vessels of blood brain barrier.
|
|
|
Why is carbidopa administered with levidopa?
|
When levidopa is converted to dopamine in peripheral tissues, it activates nausea/vomiting centers.
Carbidopa is a DDCI(Dopamine decarboxylase inhibitor) and it inhibits production of dopamine(from L-DOPA) in peripheral tissues(Carbidopa can't cross BBB), but not the brain. |
|
|
What electrolyte imbalance usually causes parasthesias?
|
Calcium
|
|
|
What kind of gene is VHL? What disease is it associated with?
|
Tumor Suppressor
Renal Cell Carcinoma |
|
|
Where does intron splicing occur?
|
nucleus
also, 5' cap and poly A tail 5' cap occurs in two steps--GTP added then methylated |
|
|
describe process of adding poly A tail
|
recognition of AAUAAA sequence, cleavage few residues downstream, addition of 20-250 Adenosine residues
|
|
|
describe process of adding 5' cap
|
5' cap occurs in two steps--GTP added then methylated
guanylyltransferase and guanine-7-methyltransferase |
|
|
muscle provides support for abdominal contents
|
transversus abdominus - it is not attached to ribcage, so supporting the abdominal viscera doesn't interfere with breathing
|
|
|
atrophy/demyelination of posterior column of spinal cord and medial roots
|
Tabes Dorsalis -- Tertiary Syphilis
|
|
|
lupus anticoagulant prolongues what?
|
PTT
|
|
|
How do ACE inhibitors predispose to Acute Renal Failure?
|
In Renal Artery stenosis, Renal perfusion is maintained via efferent arteriole constriction by Angiotensin II.
|
|
|
Increased Afterload
|

Increases Aortic Pressure
Decreases Stroke Volume Increases End Systolic Volume |
|
|
Increased Preload
|

Increased Preload
Increases Stroke Volume |
|
|
Increased Contractility
|

Increased Contractility
Increases Stroke Volume Increases Ejection Fraction Decreases End Systolic Volume |
|
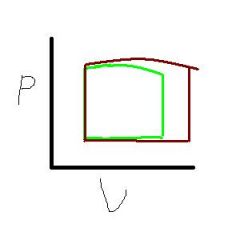
|
Increased Preload
|
|

|
Increased Contractility
|
|

|
Increased Afterload
|
|
|
Heart sound a/w atrial kick is a/w what?
|
S4
a/w ventricular hypertrophy |
|
|
Wide Splitting
|
Pulmonic stenosis, right bundle branch block
|
|
|
Fixed splitting
|
ASD
|
|
|
Paradoxical Splitting
|
Aortic stenosis, left bundle branch block
|
|
|
Tetralogy of Falot caused by
|
Anterior Superior displacement of infundibular septum
|
|
|
Transposition of great vessels caused by
|
failure of aorticopulmonary septum to spiral
|
|
|
Mental retardation, mousy odor, eczema
|
Phenylketonuria
|
|
|
Thrombocytopenia, Eczema, recurrent infections
|
Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome
|
|
|
Von-Hippel Lindau triad
|
hemangioblastomas, clear cell renal carcinomas, pheochromocytomas
|
|
|
Presents in childhood with kyphoscoliosis
|
Friedrich's Ataxia
|
|
|
tennis elbow
|
lateral epicondylitis
|
|
|
golf elbow
|
medial epicondylitis
|
|
|
What predisposes to winged scapula?
|
mastectomy
|
|
|
what cell associated with bullous pemphigoid?
|
eosinophils
|

