![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
1110 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Deficiency in homocystinuria
|
cystathionine synthase
|
|
|
Can't make in homocystinuria
|
met
|
|
|
Vitamin that can help homocystinuria
|
pyridoxine
|
|
|
Pathway for methionine --> cystine or THF, methionine
|
Methionine (S-adenosylmethionine synthase)→ SAM → SA-homocysteine → adenosine + homocystine.
Homocysteine an go to make cystine using B6 or make methionine + THF using B12 → ↓ THF, methionine |
|
|
Inducer or inhibitor? Quinidine
|
Inducer
|
|
|
Inducer or inhibitor? Barbiturates, phenobartial
|
Inducer
|
|
|
Inducer or inhibitor? St. John's wort
|
Inducer
|
|
|
Inducer or inhibitor? Phenytoin
|
Inducer
|
|
|
Inducer or inhibitor? Griseofulvin
|
Inducer
|
|
|
Inducer or inhibitor? Chronic alcohol sue
|
Inducer
|
|
|
Inducer or inhibitor? Macrolides
|
Inhibitor
|
|
|
Inducer or inhibitor? Amiodarone
|
Inhibitor
|
|
|
Inducer or inhibitor? Isoniazid
|
Inhibitor
|
|
|
Inducer or inhibitor? Protease inhibitors
|
Inhibitor
|
|
|
Inducer or inhibitor? Acute alcohol use
|
Inhibitor
|
|
|
Inducer or inhibitor? Ciprofloxain
|
Inhibitor
|
|
|
Inducer or inhibitor? Ketoconazole
|
Inhibitor
|
|
|
Inducer or inhibitor? Sulfonamides
|
Inhibitor
|
|
|
What drugs cause agranulocytosis?
|
Clozapine, carbamazepine, colchicines, propylthiouracil, methimazole, dapsone
|
|
|
What drugs cause hyperglycemia?
|
Niacin, tacrolimus, protease inhibitors
|
|
|
What drugs cause gout?
|
Furosemide, thiazides, niacin, cyclosporine, pyrazinamide
|
|
|
What drugs cause myopathy?
|
Fibrates, niacin, colchicines, hydroxychlorquine, IFN alpha, penicillamine, glucocorticoids
|
|
|
MOA of bacitracin
|
Inhibits phosphorylation/dephosphorylation of the lipid carrier required to transfer peptidoglycan to the cell wall
|
|
|
MOA of sulfonamides
|
PABA analogs --> inhibition of dihydropteroic acid synthase (PABA + dihydropterine --> dihydropteroic acid --> --> THF
|
|
|
Sulfonamides bactericidal or static?
|
Bacteriostatic
|
|
|
Sulfonamide side effects
|
GI, phototoxic, Stevens Johnson, especially if immunocompromised
|
|
|
Why are sulfonamides contraindicated in neonates?
|
Displace bili from albumin --> kernicterus
|
|
|
MOA of trimethoprim
|
Competitively inhibits dihydrofolic acid reductase (DHF--> THF)
|
|
|
Side effects of trimethoprim
|
Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia
|
|
|
Sulfonamide mechanism of resistance?
|
Increasing PABA, decreased target affinity, uptake of exogenous folic acid
|
|
|
Side effects of fluoroquinolones
|
GI is common. Dizziness, insomnia, photosensitivity, QT interval prolongation. Gatifloxacin can cause hyperglycemia but hypoglycemia with oral hypoglycemics - this is mainly only for ophthalmic use
|
|
|
Mechanism of fluoroquinolone resistance
|
Efflux pumps, gyrase mutations
|
|
|
First generation cephalosporins? Spectrum?
|
Cefazolin, cephalexin - gram positive cocci, Proteus mirabilis, E. coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae
|
|
|
Second generation cephalosporins? Spectrum?
|
cefoxitin, cefaclor, cefprozil, cefuroxime (crosses BBB) - Gram positive cocci, H. flu, Enterobacter aerogenes, Neisseria, Proteus mirabilis, E. coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Serratia marcescens
|
|
|
Third generation cephalosporins? spectrum?
|
ceftriaxone, cefotaxime (pseudomonas), cefdinir (ear infections), ceftazidime, cefoperazone (disulfram-like reaction)- serious gram negative infections resistant to other beta lactams, S. pneumo.
• Cefdinir can be used for resistant ear infections • Cefoperazone not good for meningitis (doesn’t cross BB, lipophilic – highly protein bound, eliminated in bile, remember - disulfram) |
|
|
What amino acids are localization signals (out of the nucleus) rich in?
|
lysine, arginine, proline
|
|
|
How to ribosomes attach to the RER?
|
Riboporins - recognize large subunit
|
|
|
The N-oligosarccharides on what amino acid are modified in the golgi?
|
Aspargine
|
|
|
O-oligosaccharides are added to what amino acids in the golgi?
|
Serine, threonin
|
|
|
Describe some trafficking proteins
|
COP I (golgi to ER), COP II (RER to cis golgi), clathrin
|
|
|
How does clathrin work in endocytosis
|
Thing bind the membrane receptor, this binds to adaptin, which lets the receptor interact with clathrin, clathrins interact with each other, and the membrane folds inward. Dynamin pinches it off.
|
|
|
Vimentin stains for what cancers?
|
Sarcoma (is important in connective tissue)
|
|
|
What intermediate filaments would you stain for in neuroblastoma?
|
Neurofilament
|
|
|
What step is defective in collagen synthesis in Ehler's Danlos
|
Cleaving the C and N terminal ends
|
|
|
What amino acids is elastin rich in?
|
Proline, glycine
|
|
|
Where does ketogenesis take place?
|
Mitochondria
|
|
|
Where does the pentose phosphate pathway take place?
|
Cytoplasm
|
|
|
Where does the HMP shunt take place?
|
Cytoplasm
|
|
|
What does adenine deaminate to?
|
Guanine
|
|
|
What does cytosine deaminate to?
|
Uracil
|
|
|
Uracil can be methylated to what?
|
Thymine (involved thymidilate synthase, targeted by 5FU)
|
|
|
What amino acids is DNA methylated on?
|
Cytosine, adenine
|
|
|
What DNA polymerases are used in eukaryotes?
|
Alpha lagging, delta leading, beta and epsilone filll gapas in the lagging strand.
|
|
|
What is nucleotide excision repair used for?
|
Bulky adducts like thymine dimers
|
|
|
What is base excision repair used for?
|
An abnormal base, like in spontanous deamination. Glycosylase forms the AP site, endonuclase cuts the 5' end, lase cuts the 3' end
|
|
|
What is the MOA for alpha amantin (death cap mushroom)?
|
Inhibits RNA polymerase II
|
|
|
What is a P body?
|
An entity in eukaryotic cells involved in mRNA regulation, repression
|
|
|
What sequence is an amino acid loaded on in the tRNA?
|
CCA on the 3' end
|
|
|
Whats a defining sequence on the T arm of a tRNA?
|
thymidine psi (pseudouracil) cytadine sequence
|
|
|
What antineoplastic targets the G2 stage?
|
Bleomycin
|
|
|
What cyclin/CDK rleases Rb from TF-E2F?
|
Cyclin D/CDK 4. This activates cyclin E
|
|
|
What cyclin/CDK allows progression into S phase?
|
Cyclin E/CDK2
|
|
|
What cyclin/CDK complex allows progression to mitosis?
|
Cyclin A/CDK2
|
|
|
What cyclin/CDK is inovlved in initiating mitosis?
|
Cyclin B/CDK1, activated by CDC 25. Breaks down nuclear laminin, etc
|
|
|
What is lyonization?
|
Random X inactivation
|
|
|
What inheritence pattern is hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia?
|
AD (Osler-Weber-Rendu)
|
|
|
What inheritence pattern is hereditary spherocytosis?
|
ADCGG
|
|
|
What trinucleotide repeat is present in fragile X?
|
CGG
|
|
|
What trinucleotide repeat is present in Freidrich's ataxia
|
GAA
|
|
|
What trinucleotide repeat is present in myotonic dystrophy?
|
CTG
|
|
|
What does a Southern blot do?
|
DNA with a DNA probe
|
|
|
What does a Northern blot do?
|
RNA using a DNA probe
|
|
|
What does a Southwestern blot do?
|
DNA binding proteins/TFs with an oligonucleotide probe
|
|
|
What does a Western blot do?
|
Protein with an antibody probe
|
|
|
What is the Shine Delgarno sequence?
|
RNA sequence ribosomes recognize
|
|
|
Rate limiting step for de novo pyrimidine synthesis?
|
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II
|
|
|
Rate limiting step for de novo purine synthesis?
|
Glutamine PRPP amidotransferase
|
|
|
Rate limiting step for urea cycle?
|
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I
|
|
|
Rate limiting step for fatty acid oxidation?
|
Carnitine acyltransferase I
|
|
|
How much ATP is generated in the heart and liver?
|
32 ATP (malate-aspartate shuttle)
|
|
|
Hexokinase/glucokinase (glucose --> G6P) characteristics
|
Glucokinase is in the liver and pancreas. Step uses 1 ATP
|
|
|
What is PFK 1 regulated by (F6P-->F1,6BP)
|
Inhibited by ATP, citrate. Activated by AMP, F-2,6-BP
|
|
|
What is fexodenadine?
|
2nd/3rd generation H1 blocker
|
|
|
What neurocutaneous disorder is associated with angiomyolipoma?
|
Tuberous sclerosis, especially bilateral renal angiomyolipomas.
|
|
|
If you see someone with ash leaf spots, you might suspect what other problems?
|
Angiomyolipomas, cortical tubers, subependymal hamartomas, seizures, MR, cardiac rhabdomyoma, facial angiofibromas
|
|
|
What comes from the ventral pancreatic bud?
|
Uncinate process, part of the head (inferior), and the proximal main pancreatic duct.
|
|
|
What are the two ducts of the pancreas (fail to fuse in pancreas divisum)?
|
Dorsal duct of Santorini drains most of it, drains into the minor papilla. Ventral duct of Wirsung opens into the major papilla, drains the uncinate process
|
|
|
Side effects of carbamazepine?
|
Bone marrow suppression, hepatotoxicity, SIADH, p450 induction
|
|
|
Spectrum for ampcillin, amoxicillin
|
Gram positive cocci, but not staph, listeria. H. pylori, H. flu, E. coli, borreila
|
|
|
What is amikacin?
|
Aminoglycoside
|
|
|
What do you use for bubonic plague and tularemia?
|
Streptomycin. Also works against TB
|
|
|
What are the side effects of aminoglycosides?
|
Nephrotoxic, ototoxic, contact dermatitis (neomycin). Neuromuscular blockade due to decreased acetyl CoA release (like botulinism toxin)
|
|
|
What is terbenafine?
|
Blocks squalene epoxidase and thus ergosterol synthesis. For dematophytes. Can cause hepatotoxicity
|
|
|
What antibiotics inhibit formation of the initiation complex?
|
Aminoglycosides (30s), linezolid (50s)
|
|
|
What antibiotics inhibit amino acid incorporation?
|
Tetracyclines (30s), dalfopristin, quinupristin (50s) - block the attachment of the tRNA to the acceptor site
|
|
|
What antibiotics block peptide bond formation?
|
Chloramphenicol. Inhibits the activity of peptidyltransferase.
|
|
|
What antibiotics block translocation?
|
Macrolides and clindamycin (50s)
|
|
|
What is varenicline?
|
Nicotine partial agonist to treat nicotine addiction.
|
|
|
What are the high potency neuroleptics?
|
Fluphenazine, thiothixene, haloperidol, trifluoperazine (moderate potency) – extrapyramidal symptoms predominate
|
|
|
What are the low potency neuroleptics?
|
Chlorpromazine, thioridazine – more anticholinergic, antihistamine, and alpha blockade effects
|
|
|
What's an interesting side effect of chlorpromazine?
|
Corneal deposits. A low potency typical neuroleptic
|
|
|
What's an interesting side effect of thioridazine?
|
Retinal deposits. A low potency typical neuroleptic
|
|
|
What is trihexyphenidyl?
|
Anti muscarinic. Used in Parkinson's and neuroleptic drug side effects
|
|
|
What is clozapine? What is an important side effect?
|
Atypical antipsychotic. Agranulocytosis.
|
|
|
What is risperidone?
|
Atypical antipsychotic.
|
|
|
What is ziprasidone?
|
Atypical antipsychotic.
|
|
|
What atypical antipsychotic prolongs the QT interval?
|
Ziprasidone
|
|
|
What are imipramine, desipramine and clomipramine?
|
Tricyclic antidepressants. Desipramine is the least sedating and has a lower seizure threshold of the TCAs.
|
|
|
What are doxepin and amoxapine?
|
Tricyclic antidepressants
|
|
|
What is milnacipran?
|
SNRI, often used for fibromyalgia
|
|
|
What is duloxetine?
|
SNRI, predominant NE effect, can be used in diabetic peripheral neuropathy
|
|
|
What is sibutramine?
|
SNRI used for weight loss
|
|
|
What is tranylcypromine?
|
MAOI
|
|
|
What is isocarboxazid?
|
MAOI
|
|
|
What is selegiline?
|
Selective MAO B inhibitor used in Parkinsons
|
|
|
What is maprotiline?
|
Norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor
|
|
|
What is produced in the reaction 1,3 BPD --> 3 phosphoglycerate by phosphoglycerate kinase?
|
1 ATP via substrate level phosphorylation
|
|
|
What is produced in the reaction PEP --> pyruvate by pyruvate kinase? How is it regulated?
|
1 ATP via substrate level phosphorylation. Inhibited by ATP and alanine. Activated by F1,6,BP
|
|
|
How is the pyruvate dehydrogenate (pyruvate --> acetyl CoA) complex regulated? What are the components of the complex?
|
Inhibited by ATP, NADH, acetyl CoA. Activated by NAD, ADP, and calcium (thus can be activated by muscle contraction).
TPP, FAD, NAD, CoA (from pantothenate), lipoic acid |
|
|
How do you manage a pyruvate dehydrogenase deficiency?
|
They will have low acetyl CoA and thus high lactate, oxaloacetate and alanine. Give ketogenic amino acids and high fat intake.
|
|
|
What are the ketogenic and glucogenic amino acids?
|
Isoleucine, tyrosine, tryptophan, phenylalanine
|
|
|
Where does fructose enter glycolysis?
|
As glyceraldehyde, skips PFK1
|
|
|
What does the citric acid cycle produce?
|
3 NADH, 1 FADH2, 2 CO2, 1 GTP per acetyl coA = 24 ATP per glucose
|
|
|
What is citrate synthase inhibited by (acetyl CoA to citrate)
|
ATP; it is irreversible
|
|
|
What are nalbuphine and pentazocine?
|
Kappa receptor agonists, so cause spinal analgesia, but dysphoria. Mu antagonist, so can precipitate withdrawal
|
|
|
What is methylnaltrexone used for?
|
Used to reverse opiate induced constipation. Mainly stays in the gut.
|
|
|
What could you give to treat opiate withdrawal?
|
Clonidine (alpha 2 blockade)
|
|
|
What is loperamide?
|
Opiate anti-diarrheal
|
|
|
What would you use to prevent cisplatin nephrotoxicity?
|
Amifostine
|
|
|
What inhibits the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex?
|
ATP, acetyl CoA, NADH
|
|
|
What is produced by isocitrate dehydrogenase (isocitrate to alpha ketoglutarate)? What is it regulated by?
|
Produces CO2 and NADH. Inhibited by ATP
|
|
|
What is citrate synthase inhibited by? (acetyl CoA to citrate)
|
ATP
|
|
|
What is alpha ketoglutarate dehydrogenase inhibited by?
|
Inhibited by NADH and ATP
|
|
|
What is produced by succinyl CoA synthetase? (succinyl CoA to succinate)
|
Produces GTP (substrate level phosphorylation) and CoA. The GTP can be used to form PEP in gluconeogenesis to using PEP carboxykinase
|
|
|
What is produced in the reaction from succinate to fumarate?
|
FADH2
|
|
|
What is produced in the reaction of malate to oxaloacetate?
|
NADH
|
|
|
What inhibits complex I of the ETC?
|
Barbiturates (amytal), rotenone (fish poison), 1-methyl-4-phenylpyrimidinum (MPP - from MPTP)
|
|
|
What inhibits complex III of the ETC?
|
antimycin A
|
|
|
What inhibits complex IV of the ETC?
|
CN-, CO, azide (N3), H2S
|
|
|
What is oligomycin?
|
ATP synthase inhibitor
|
|
|
What is the step in gluconeogenesis analogous to PFK1?
|
Fructose 1,6 bisphosphatase (F16BP to F6P). Inhibited by AMP and F26BP
|
|
|
What 2 steps in gluconeogenesis are analogous to pyruvate kinase?
|
Pyruvate carboxylase (pyruvate --> oxoaloacetate) in the mitochondria. Requires biotin (adds CO2) and ATP. Activated by acetyl CoA.
PEP carboxykinase (oxaloacetate --> PEP) in the cytosol. Requires GTP |
|
|
How can odd chain fatty acids be used as a glucose source?
|
Broken down to propionyl CoA, which is a precursor for succinyl CoA.
|
|
|
What acts via cAMP to phosphorylate glycogen phosphorylase kinase which phosphorylates glycogen phosphorylase? Is GP-P active? How else can this happen?
|
Epinephrine and glucagon. Yes. It is also activated by calcium/calmodulin (allosteric) and increased AMP.
|
|
|
What are the basic steps of glycogen synthesis
|
Glucose 6 P → Glucose 1P (UDP glucose phosphorylase) → UDP glucose → straight chain glycogen
|
|
|
What is the enzyme deficiency in Von Gierke's disease?
|
Glucose 6 phosphatase
Glycogen (glycogen phosphorylase) →> G1P (phosphoglucomutase) → G6P (glucose 6 phosphatase)→ glucose |
|
|
What is the enyzme deficiency in Pompe's?
|
Lysosomal alpha 1,4 glycosidase.
Glycogen (lysosomal alpha 1,4 glycosidase) → Glucose + P |
|
|
What are the steps in fatty acid synthesis?
|
Citrate is transferred from the mitochondrial matrix to the cytoplasm using the citrate shuttle. Using ATP and citrate lyase, citrate is converted to acetyl CoA. Acetyl coA is converted to malonyl CoA using acetyl CoA carboxylase (rate limiting), and CO2 from biotin --> Malonyl CoA → palmitate
|
|
|
What does ApoE do?
|
Mediates remnant uptake, present on everything but LDL
|
|
|
What does Apo A-I do?
|
Present on chylomicrons and HDL. Activates LCAT, which catalyzes cholesterol esterification.
|
|
|
What does ApoC-II do?
|
A cofactor for LPL present on chylomicrons and IDL
|
|
|
What does ApoB-48 do?
|
On chylomicrons and chylomicron remnants, mediates chylomicron secretion.
|
|
|
What does ApoB-100 do?
|
Binds LDL receptor. Present on VLDL, IDL, and LDL
|
|
|
What vitamin is needed by transamination reactions?
|
Pyridoxal phosphate (B6)
|
|
|
How does excess NH4 limit the TCA cycle?
|
Depletes alpha ketoglutarate
|
|
|
What can you use benzoate and phenylbutyrate for?
|
Binding amino acids to increase excretion in hyperammonemia
|
|
|
What are the oxidative (irreversible) steps of the HMP shunt?
|
G-6-P + NAD→ phosphogluconolactone + NADPH via G6PD ,
6phospho gluconolactone + NAD+→ ribulose-5-P + NADPH via 6phosphogluconate dehydrogenase |
|
|
What does the non oxidative part of the HMP hunt do?
|
Makes ribose 5P from ribulose 5P, as well as G3P, F6P. Transketolases are used, which require TPP
|
|
|
What are some properties of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II?
|
Involved in pyrimidine synthesis, is in the cytosol, get its N from glutamine
|
|
|
What are some properties of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I?
|
Involved in the urea cycle, is in the mitochondria, gets its N from ammonia.
|
|
|
What is the basic outline of pyrimidine synthesis?
|
Start with orotic acid and add a sugar and phosphate, then modify the orotic acid to the appropriate base. In purine synthesis, a base is just added to ribose and phosphate.
|
|
|
What is an alcohol dehydrogenase inhibitor?
|
Fomepizole
|
|
|
What do you use fomepizole in?
|
Methanol, ethylene glycol poisoning
|
|
|
Why is there hypoglycemia with alcohol intake?
|
Ethanol leads to increased NADH, so more pyruvate is diverted to lactate and more OAA to malate since both of these reactions increase NAD+. At the same time this stimulates fatty acid synthesis because of increased NADPH
|
|
|
What is the translocation in M3 AML?
|
t(15;17)
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of vitamin A toxicity?
|
Alopecia, hyperlipidemia, hepatotoxicity, arthralgia, sore throat
|
|
|
What happens in vitamin A deficiency?
|
Keratinized squamous metaplasia underlies a lot. In the lungs, increases risk for infection. In the eyes, it causes keratomalacia (wrinkling, clouding of the cornea), Bitot spots (drry, silvery plaques on the bulbar conjunctiva). In the skin, it causes follicular hyperkeratosis and thus alopecia.
|
|
|
Thyamine is needed for what 4 enzymes?
|
3 need TLCFN - pyruvate dehydrogenase, alphaketoglutarate dehydrogenase, branched chain amino acid dehydrogenase.
Transketolase only needs thiamine |
|
|
What happens in hereditary transketolase mutation?
|
Decreased affinity for TPP leads to Wernicke Korsakoff without the beriberi.
|
|
|
How do you diagnose thiamine deficiency?
|
See transketolase activity with thiamine addition
|
|
|
What are some reactions riboflavin is important in?
|
Succinate dehydrogenase, fatty acyl CoA dehydrogenase, glycerol phosphate dehydrogenase. It is also important in complex I and II of the ETC
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of riboflavin deficiency?
|
B symptoms + dermatitis, corneal neovascularization
|
|
|
What amino acid is niacin derived from? What does it need?
|
Tryptophan, using B6
|
|
|
What are some causes of niacin deficiency?
|
Hartnup disease (decreased tryptophan absorption), carcinoid (increased tryptophan metabolism), isoniazid (decreased B6), diet
|
|
|
What does pantothenate do?
|
It's part of CoA and fatty acid synthase
|
|
|
How does pantothenate deficiency present?
|
Dermatitis, enteritis, alopecia, adrenal insuffciency
|
|
|
What is pyridoxal phosphate used in?
|
Transamination reactions (e.g. by AST) - this is why alcohol can cause B6 deficiency, decarboxylation reactions, glycogen phosphorylase, cystathione, heme, niacin and GABA synthesis
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of B6 deficiency?
|
Decreased GABA - convulsions, peripheral neuropathy. Impaired heme synthesis causes sideroblastic anemia. Dermatitis, glossitis, cheilosis. Can also be caused by oral contraceptives.
|
|
|
What is propinoyl CoA carboxylase involved in?
|
Breaking down propionyl CoA to methylmalonyl coA. Priopionyl CoA is from the metabolism of Valine, Odd chain fatty acids, Methionine, Isoleucine, Threonine (VOMIT)
|
|
|
What is biotin a cofactor for? What does deficiency cause?
|
The ABC enzymes (need ATP, biotin, CoA) used in carboxylation. Pyruvate carboxylase - fasting hypoglycemia. Acetyl coA carboxylase - decreased fatty acid synthesis. Propinoyl CoA carboxylase - alopecia, bowel inflammation, muscle pain
|
|
|
Where is folic acid absorbed?
|
Distal ileum
|
|
|
What is B12 a cofactor for?
|
Homocysteine methyltransferase converts homocysteine + methylTHF to methionine and THF. Untraps folate from storage form.
Methylmalonyl CoA mutase is involved in VOMIT breakdown (val, odd carbon fattty acids, met, ile, thr). Also a succinyl CoA source |
|
|
What vitamin toxicity could cause a false negative guiac?
|
Vitamin C. Can also cause GI symptoms
|
|
|
What happens in vitamin E deficiency?
|
Erythrocyte gragility, dorsal column, SCT demyelination.
|
|
|
What can vitamin E toxicity cause?
|
Hemorrhagic stroke in adults, necrotizing entercolitis in infants
|
|
|
Gamma carboxylation via vitamin K requires what?
|
Calcium
|
|
|
What worsens vitamin K deficiency in a newborn?
|
Phenobarbital, carbamazepine use during pregnancy
|
|
|
What transporters are involved in iron absorption?
|
Diavalent metal transporter-1 gets it across the luminal membrane. It enters circulation through ferroportin. There it is bound to ferritin.
|
|
|
How does hepcidin work?
|
It binds ferroportin so it degrades it. If there is too much iron or inflammation, increased hepcidin decreases ferroportin so there is less absorption and less release from macrophages.
|
|
|
How are the kidneys involved in iron homeostasis?
|
They release lactoferrin which binds free iron in the urine so it is recovered
|
|
|
What are some enzymes zinc is necessary for?
|
Lactate dehydrogenase, carbonic anhydrase
|
|
|
What are some symptoms of zinc deficiency?
|
Decreased adult hair, hypogonadism, dysgeusia, acrodermatitis enteropathica (rash around eye, mouth, anus, etc), diarrhea, decreased night vision
|
|
|
What does cadmium poisoning cause?
|
Alveolar macrophage necrosis, causing obstructive lung disease. Also a lung cancer risk and calcium loss
|
|
|
What are the gluogenic amino acids?
|
Met, val, arg, his
|
|
|
What is the order of phenylalanine to epinephrine synthesis?
|
Phenylalanine (by phenylalanine hydroxylase)→ tyrosine (tyrosine hydroxylase)→ Dopa (dopa decarboxylase; inhibited by carbodopa)→ dopamine → NE (facilitated by cortisol) → epinephrine. Dopa can form melanin.
|
|
|
What can tryptophan make?
|
Niacian via pyridoxine. Serotonin and melatonin via tetrahydrobiopterin
|
|
|
What amino acid is porphyrin from?
|
Glycine
|
|
|
What is derived from glutamate?
|
GABA, glutathione
|
|
|
Describe the step deficient in PKU
|
Phenylalanine (phenylalanine hydroxylase; requires tetrahydrobiopterin – BH4) → tyrosine.
BH4 is regenerated using dihydrobiopterin reductase |
|
|
What enzyme converts NE to epi?
|
Norepinephrine (phenylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase – PNMT; requires SAM)→ epinephrine
|
|
|
What step of collagen synthesis is defective in Ehler's Danlos?
|
Cleaving of C and N terminal ends from procollagen forming tropocollagen. This uses collagen peptidases.
|
|
|
What is Leigh syndreom?
|
A mitochondrial myopathy subacute sclerosing encephalopathy. Leber's hereditary neuropathy is also one, cause an acute loss of central vision.
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of cytochrome C oxidase deficiency?
|
Weakness, hypotonia, encephalopathy. (autosomal recessive)
|
|
|
What enzyme is missing in homocystinuria?
|
Cystathionin synthetase - error of methionine metabolism
|
|
|
What is the pathway of methionine metabolism
|
Methionine (S-adenosylmethionine synthase)→ SAM → SA-homocystine → adenosine + homocystine;
1. Homocysteine (cystathionine synthase, B6) → cystathionine (cystathionase, B6) → cysteine 2. Or, homocysteine + N5-methyl THF (B12) → methionine + THF |
|
|
How does homocystinuria present?
|
MR, vision problems, thrombosis. Can look like Marfan's.
|
|
|
What vitamin is helpful in homocystinuria?
|
B6, a cofactor for cystathionine synthase
|
|
|
What happens in arginase deficiency?
|
Converts arginine to urea + ornithine. Spasticity. Treat with low protein diet, supplementing essential amino acids.
|
|
|
What enzyme is deficient in orotic aciduria?
|
Orotic acid phosphoribosyl transferase or orotidine 5' phosphate decarboxylase. Thus orotic acid cannot be converted to UMP. Causes megaloblastic anemia, no hyperammonemia. Treat with oral uridine
|
|
|
What kind of acid base abnormality occurs in propionyl coA carboxylase deficiency?
|
Anion gap acidosis
|
|
|
What does HGPRT deficiency cause?
|
↓ conversion of hypoxanthine → IMP; guanine → GMP
The pathway is shunted towards uric acid and denovo production (thus ↑ uric acid AND PRPP – which would ↑ PRPP amidotransferase activity by mass effect) |
|
|
What are the symptoms of fructose intolerance?
|
Hypoglycemia, jaundice, cirrhosis, vomiting
|
|
|
What is missing in classic galactosemia?
|
Absence of galactose 1-P uridyl transferase, thus G1P and galactilol accumulate.
|
|
|
How does classic galactosemia present?
|
Jaundice, hepatomegaly, infantile cataracts, MR, vomiting, hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis, aminoaciduria
|
|
|
What are some lab abnormalities of Von Gierke's?
|
Increased blood lactate and uric acid
|
|
|
What is deficient in Pompe's (type II)?
|
↓ lysosomal alpha 1,4 glucosidase (acid maltase) – mnemonic 2x2=4
|
|
|
What is deficient in Cori's (type III)?
|
↓ debranching enzyme (alpha 1,6 glucosidase) – mnemonic 2x3=6
Normal blood lactate levels, hypoglycemia is mild. Abnormal glycogen. |
|
|
What is deficiency in Andersen's (type IV)
|
Branching enzyme, abnormal glycogen
|
|
|
What is a tetrahydrobiopterin reductase deficiency?
|
Malignant PKU. Used for both phenylalanine and tyrosine hydroxylase. Supplementation in tyrosine will still cause dopamine deficiency. BH4 deficiency will present similarly
|
|
|
What is deficient in McArdles (type IV)?
|
↓ skeletal muscle glycogen phosphorylase
|
|
|
What is deficient in Hers (type V)
|
Hepatic glycogen phosphorylase (like McArdles for liver)
|
|
|
How does PKU present?
|
Seizures, fair skin (↓ melanin from phenylalanine), eczema, musty odor (↑ aromatic amino acids)
|
|
|
What is homogentisic acid oxidase involved in?
|
Tyrosine to fumarate
|
|
|
What can cause atherosclerosis in childhood?
|
Homocystinuria
|
|
|
How do you treat cystathionine synthase deficiency?
|
Homocystinuria - ↓ Met, ↑ Cys, B12, serine and folate
|
|
|
How do you treat homocysteine methyl transferase deficiency? This enzyme requires B12.
|
Homocystinuria - ↑ methionine
|
|
|
What causes cystinuria?
|
Defect of renal tubular amino acid transporter for cystine, ornithine, lysine, arginine in the PCT. Treat with acetazolamide to alkalinize urine and prevent stones.
|
|
|
What vitamin supplementation could help maple syrup urine disease?
|
Thiamine
|
|
|
Describe Hartnup disease
|
↓ neutral amino acids absorbed in gut, ↑ excreted → pellagra (tryptophan → niacin) with symptoms that wax and wane.
Tryptophan is a precursor for nicotinic acid, serotonin and melatonin. Nicotinic acid, nicotinamide, ↑ protein in diet Proline and hydroxyproline will be normal. |
|
|
How does I cell disease present (failure of addition of mannose 6 phosphate to lysosome proteins)
|
Coarse facial features, corneal clouding, restricted joint movement, lysosomal enzymes in the plasma, skeletal abnormalities, hepatosplenomegaly
|
|
|
What is deficient in Fabry's?
|
Alpha galactosidase A deficiency → ↑ ceramide trihexose
|
|
|
How does Fabry's present?
|
Peripheral neuropathy, angiokeratomas (dark red, non blanching macules and papules), CV/renal disease.
Death is usually due to renal failure |
|
|
What is deficiency in Gaucher's? (Hint, starts with a G)
|
Glucocerebrosidase deficiency → ↑ glucocerebroside
|
|
|
How does Gaucher's present?
|
Hepatosplenomegaly, aseptic necrosis of femur, Gaucher cells
|
|
|
What is deficient in Neimann Pick?
|
Sphingomyelinase deficiency – ↑ sphingomyelin
|
|
|
How does Neimann Pick present?
|
Sphingomyelin accumulates → foamy histocytes that accumulate in the liver, spleen, and CNS. Retina deposition → blindness. Hepatosplenomegaly, progressive hypotonia. Normal initial development.
|
|
|
What is deficient in Tay Sachs?
|
Deficiency of hexosaminidase A → ↑ GM2 ganglioside
|
|
|
How does Tay Sachs present?
|
Neurodegeneration, lysosomes with onion skin. No hepatomegaly vs Neimann Pick.
|
|
|
What is the X linked lysosomal storage disease?
|
Fabry's
|
|
|
What is deficient in Krabbes?
|
Galactocerebrosidase --> build up of galactocerebroside
|
|
|
How does Krabbes present?
|
Peripheral neuropathy, developmental delay, optic atrophy, globoid cells (giant, mononucleate)
|
|
|
What is deficient in metachromatic leukodystrophy?
|
Deficiency of arylsulfatase A, ↑ cerebroside sulfate
|
|
|
How does metachromatic leukodystrophy present?
|
Central and peripheral demyelination, ataxia, dementia
|
|
|
What is deficient in Hurler's and Hunter's?
|
Deficiency of alpha L iduronidase → ↑ heparan sulfate, dermatan sulfate
|
|
|
What is type Ia dyslipidemia?
|
↑ chylomicrons → ↑ TG, cholesterol. Lipoprotein lipase deficiency or altered apo C-II
|
|
|
What is deficient in abetalipoproteinemia?
|
↓ apo B-100 (VLDL, LDL) and apo B-48 (chylomicrons) → inability to synthesize lipoproteins
|
|
|
How does abetalipoproteinemia present?
|
Within first few months – steatorrhea, acanthocytosis, ataxia, night blindness
|
|
|
What is the quad screen in Downs like?
|
↓AFP, estriol; ↑ hCG, inhibin A
|
|
|
How does Edwards present?
|
Trisomy 18: severe mental retardation, rocker bottom feet, micrognathia (small jaw), low set ears, clenched hands, prominent occiput, heart defects
|
|
|
What is the quad screen in Edwards like?
|
↓ AFP, hCG, estriol; normal inhibin A
|
|
|
How does Patau's present?
|
Trisomy 13: Rocker bottom feet, microphthalmia, microcephaly, cleft lip, cleft palate, holoproencephaly – cyclopia, polydactyly, heart defects, hole in the iris, deafness, etc
|
|
|
How is the quad screen like in Pataus?
|
Normal
|
|
|
What is the nasal transepithelial potential difference like in CF?
|
More negative due to increased sodium reabsorption
|
|
|
How does Cri-du-chat present (microdeletion at 5p)?
|
Microcephaly, MR, high pitched cry, epitcanthal folds, heart defects – esp VSD
|
|
|
How does William's syndrome present (microdeletion at 7q)?
|
Elastin is deleted. Elvin facies, MR, hypercalcemia (↑ sensitive to vitamin D), good verbal skills, extremely friendly, cardiovascular problems
|
|
|
What does sonic hedgehog do?
|
Produced at limb bases in the zone of polarizing activity, involved in anterior-posterior axis. Mediates ectodermal function.
Deficiency: holoprosencephaly |
|
|
What does Wnt-7 do?
|
Produced at apical ectodermal ridge (at the disal end of each limb). Involved in the dorsal-ventral axis
|
|
|
What does homeobox do?
|
Involved in craniocaudal segmental organization. Mutation can cause appendages in the wrong direction (e.g. synpolydactyly – an extra fused digit)
|
|
|
What structures in development become the ligaments in the abdomen?
|
Umbilical vein – ligamentum teres of the liver, which is in the falciform ligament.
Umbilical arteries – medial umbilical ligaments. Ductus venosus – ligamentum venosum. Allantois/urachus – median umbilical ligament |
|
|
What part of the placenta secretes hCG? What makes cells?
|
Syncitiotrophoblast makes hcg. CYTOtrophoblast makes cells
|
|
|
What is a malformation vs deformation? Aplasia?
|
Malformation is an intrinsic disruption in the embryonic period. Deformation is extrinsic and is later. Aplasia is an absent organ despite present primordial tissue
|
|
|
What embryonic layer is the lens from?
|
Surface ectoderm
|
|
|
What embryonic layer is the oral cavity lining from?
|
Surface ectoderm
|
|
|
What embryonic layer are the salivary, sweat and mammary glands from?
|
Surface ectoderm
|
|
|
What embryonic layer is the adenohypophysis from?
|
Surface ectoderm
|
|
|
What embryonic layer is neurohypophysis from?
|
Neuroectoderm
|
|
|
What embryonic layer are oligodendroglia and astrocytes from?
|
Neuroectoderm
|
|
|
What embryonic layer are ependymal cells from?
|
Neuroectoderm
|
|
|
What embryonic layer is the pineal gland from?
|
Neuroectoderm
|
|
|
What embryonic layer is the retina from?
|
Neuroectoderm
|
|
|
What embryonic layer is the spinal cord from?
|
Neuroectoderm
|
|
|
What embryonic layer is the ANS from?
|
Neural crest
|
|
|
What embryonic layer are the cranial nerves from?
|
Neural crest
|
|
|
What embryonic layer is the pia/arachnoid from?
|
Neural crest
|
|
|
What embryonic layer are the inner ear bones from?
|
Neural crest
|
|
|
What embryonic layer are the sensory organs of the ear from?
|
Surface ectoderm
|
|
|
What embryonic layer are schwann cells from?
|
Neural crest
|
|
|
What embryonic layer are chromaffin cells from?
|
Neural crest
|
|
|
What embryonic layer are parathyroids from?
|
Endoderm
|
|
|
What embryonic layer is the urethra and vagina from?
|
Mesoderm
|
|
|
What embryonic layer are serosal linings from?
|
Mesoderm
|
|
|
What embryonic layer are the testes and ovaries from?
|
Mesoderm
|
|
|
What embryonic layer is the eustachian tube from?
|
Mesoderm
|
|
|
What embryonic layer is the adrenal cortex from?
|
Mesoderm
|
|
|
What embryonic layer is the dermis from?
|
Mesoderm
|
|
|
What forms from the first aortic arch?
|
part of the maxillary artery, a branch of the external carotid
|
|
|
What forms from the second aortic arch?
|
Stapedial and hyoid artery?
|
|
|
What forms from the third aortic arch?
|
Common carotid, proximal internal carotid
|
|
|
What forms from the fourth aortic arch?
|
L: aortic arch, R: proximal subclavian
|
|
|
What forms from the sixth aortic arch?
|
Proximal pulmonary arteries
|
|
|
What kind of tissue are the branchial arches?
|
Mesoderm, neural crest. Nerves grow in.
|
|
|
What is the innervation of the first branchial arch?
|
CN V2, V3
|
|
|
What is the innervation of the second branchial arch?
|
CN VII
|
|
|
What is the innervation of the third branchial arch?
|
CN IV
|
|
|
What is the innervation of the fourth branchial arch?
|
CN X - superior laryngeal
|
|
|
What is the innervation of the sixth branchial arch?
|
CN X - recurrent laryngeal
|
|
|
What are the muscles, bones and cartilage of the first arch?
|
Innervation:, CN V2 – maxillary, CN V3 – mandibular
Muscles: muscles of mastication, digastric anterior belly, mylohyoid, tensor tympani, tensor veli palatini Bones: malleus, incus, maxilla, mandible Cartilage: Meckel’s cartilage – mandible, sphenomandibular ligament Anterior 2/3 of the tongue |
|
|
What are the muscles, bones and cartilage of the second arch?
|
Innervation: CN seven
Muscles: muscles of facial expression, digastric posterior belly, stylohyoid, stapedius Bones: stapes, styloid process, lesser horn and upper body of hyoid Cartilage: Reichert’s cartilage – stylohyoid ligement |
|
|
What are the muscles, bones and cartilage of the third arch?
|
Innervation: CN IX
Artery: common carotids Muscle: stylopharyngeus (thus the only muscle innervated by CN IX) Bones: greater horn and lower body of hyoid 3rd and 4th form the posterior 2/3 of the tongue |
|
|
What are the muscles, bones and cartilage of the fourth arch?
|
Innervation: CN X (superior laryngeal n)
Artery: Right subclavian, aortic arch Muscles: Muscle of pharynx, soft palate, cricothyoid |
|
|
What are the muscles and arteries from the 6th branchial arch?
|
Innervation: CN X (recurrent laryngeal)
Artery: pulmonary arteries, ductus arteriosus Muscles: Intrinsic muscles of larynx except the cricothyroid |
|
|
What is Treacher Collins syndrome?
|
Failure of neural crest migration --> mandibular hypoplasia, facial abnormalities
|
|
|
What does the first cleft become?
|
External auditory meatus
|
|
|
What comes from the first pharyngeal pouch?
|
Middle ear cavity, eustachian tube, mastoid air cells
|
|
|
What comes from the second pharyngeal pouch?
|
Palatine tonsil epithelium
|
|
|
What comes from the third pharyngeal pouch?
|
Dorsal wing: inferior parathyroids; ventral wing: thymus
|
|
|
What comes from the fourth pharyngeal pouch?
|
Superior parathyroids
|
|
|
Prosencephalon --> telencephalon --> diencephalon. What are the derivatives?
|
The telencephalon becomes the hemispheres and the lateral ventricles. It also includes the basal ganglia and hippocampus.
The diencephalons becomes the thalamus and third ventricle, as well as the hypothalamus and the optic tract. |
|
|
Rhombencephalon ---> metencephalon, myelencephalon. What are the derivatives
|
The metencephalon becomes the pons and has the upper part of the 4th ventricle
The myelencephalon becomes the medulla and has the lower 4th ventricles |
|
|
What are the derivatives from the bulbus cordis and right horn of the sinus venousus?
|
Smooth parts of ventricles, smooth right atrium.
|
|
|
What are the derivatives from the left horn of the sinus venosus?
|
Coronary sinus
|
|
|
What are the derivatives from the right cardinal veins?
|
SVC
|
|
|
What causes an annular pancreas?
|
The dorsal bud cleaves in two
|
|
|
What occurs with a defect in the caudal fold of the anterior gut wall?
|
Bladder exstrophy?
|
|
|
What occurs with a defect in the lateral fold of the anterior gut wall?
|
Gastrochisis, Omphalmocele
|
|
|
What happens in atresia of the ileum?
|
Atresia distal to the duodenum is due to vascular accident (apple peel lesion - bowel spirals)
|
|
|
What is the analog to the corpus spongiosum and cavernosum in the female?
|
Vestibular bulbs (from the genital tubercle
|
|
|
What is the female analog to the Cowper (bulbourethral) glands?
|
Bartholins (greater vestibular) glands
|
|
|
What does the gubernaculum become?
|
Ovarian/round ligament; anchors testes in scrotum.
|
|
|
Why are alkalating agents teratogenic?
|
Absence of digits
|
|
|
Why is carbamazepine teratogenic?
|
NTDs, craniofacial defects, nail hypoplasia, growth retardation
|
|
|
Why is phenytoin teratogenic?
|
Fetal hydantoin syndrome - microcephaly, craniofacial anomalies, nail/finger defects, cardiac defects
|
|
|
What are 4 obligate aerobes?
|
Nocardia, P. aeruginosa, M. tuberculosis, Bacillis
|
|
|
What are 3 obligate anaerobes?
|
Clostridium, actinomyces, bacteriodes (ABC)
|
|
|
What are 8 facultative intracellulars?
|
• Salmonella, neisseria, brucella, mycobacteria, listeria, francisella, legionella, Y. pestis
|
|
|
What are some urease positives?
|
Nocardia, cryptococcus, klebsiella
|
|
|
What toxins are related to lysogenic phages?
|
Shiga-like toxin, botulinum toxin, cholera toxin, diphtheria toxin, erythrogenic toxin of S. pyogenes
|
|
|
What gram negative makes sports?
|
Coxiella burnetti
|
|
|
How do you tell apart coag negative staph?
|
Novobiocin sensitive – S. epidermidis. Novobiocin resistant – S. saprophiticus
|
|
|
How do you differentiate alpha hemolytic strep?
|
Optochin and bile sensitive – s. pneumo. Optochin and bile resistant – S. mutans
|
|
|
How do you tell apart beta hemolytic strep?
|
Bacitracin sensitive – S. pyogenes. Bacitracin resistant – S. agalactiae
|
|
|
What are some properties of S. aureus?
|
Beta hemolytic, ferments mannitol, salt tolerant.
|
|
|
What are the S. aureus virulence factors and toxins?
|
Protein A – binds the Fc region of Ig to prevent opsonization, complement fixation and phagocytosis
TSST-1 (binds MHC II). Can cause desquamation on the palms and soles weeks later Alpha toxin (hemolysis), enterotoxins (food poisoning), exfoliative/epidermolytic toxin (scalded skin syndrome), beta toxin - sphingomyelinase, Gamma toxin – proteins a&B → hemolysin, proteins B&C → leukocidin |
|
|
What are some properties of staph epidermidis?
|
Gamma hemolytic cocci in clusters. Sensitive to novobiocin.
|
|
|
How do you treat S. epidermidis?
|
Usually resistant to methicillin. Treat with vancomyin and rifampin or gentamicin
|
|
|
What are some properties of staph saprophyticus?
|
Gamma hemolytic, resistant to novobiocin
|
|
|
What are some properties of strep pneumo?
|
Alpha hemolytic diplococcus sensitive to optochin.
|
|
|
What are step pneumo's virulence factors?
|
Capsule - necessary (acquired by transformation).
Pneumolysin - kills epithelial cells and reduces oxidative burst. |
|
|
Pyruvate carboxylase, required to make glucose out of pyruvate forming substances is increased by what?
|
Acetyl CoA
|
|
|
What is the antidote for arsenic poisoning?
|
Dimercaprol (though this is nephrotoxic and can cause hypertension)
|
|
|
What is the MOA for selegilline?
|
MAO-B inhibitor used in Parkinsons.
|
|
|
What medicine can cause generalized lymphadenopathy without a seum sickness like syndrome?
|
Phenytoin. Also causes acne, hirsuitism, gingival hypertrophy
|
|
|
What is recombination?
|
A host cell is coinfected with segmented viruses that exchagnge whole segments.
|
|
|
What is phenotypic mixing?
|
A host cell is coinfected by 2 stains, and a virion is made with the genome of one and the capsid of another
|
|
|
What occurs in iron poisoning?
|
Cells die due to lipid peroxidation. There are acute GI bleeds and erosions. Chronically, there is metabolic acidosis, scarring, and GI obstruction
|
|
|
When do brown pigment stones form in the gallbladder?
|
Infection, which results in the release of beta glucuonidase by injured hepatocytes and bacteria. They increase the amount of unconjugated bilirubin in the bile.
|
|
|
How do bases attach to the sugar in DNA?
|
Glycosidic bonds
|
|
|
What is mismatch repair used for?
|
Corrects errors in replication. Uses hMSH2 and hMLH, which are mutated in Lynch syndrome.
|
|
|
What disease is caused by a defect in nonhomologous end joining?
|
Ataxia telangiectasia (autosomal recessive mutation of ATM)
|
|
|
How does ataxia telangiectasia present?
|
Cerebella atrophy and ataxia, blanching telangiectasias, sinopulmonary infections (B&T cells involved, btu mainly IgA), skin discolorations, AVMs, epistaxis, poor smooth pursuit, increased AFP after 8 months, increased risk of hemotologic malignancies
|
|
|
What do BRCA 1 and 2 do?
|
Double strand break repair
|
|
|
What is wrong in bloom syndrome?
|
Usually due to helicase deficiency leading to genommic instability.
|
|
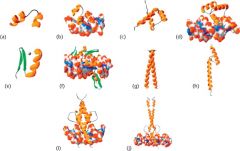
Which are the helix-loop-helix, leucine zipper, helix-turn-helix, and zinc finger structural motifs for transcription factors?
|
A. Helix turn helix
E. Zinc finger G. Leucine zipper H. Helix loop helix |
|
|
Can a subdural hematoma cross the falx or tentorium?
|
No
|
|
|
Can an epidural hematoma cross the falx or tentorium?
|
Yes
|
|
|
Why can a lumbar puncture in a subarachnoid hemorrhage be yellow?
|
Bilirubin
|
|
|
How do you treat vasospasm due to blood breakdown after a subarachnoid hemorrhage?
|
Nimodipine
|
|
|
What is an alternative to aspirin in angina?
|
Clopidogrel - irreversible ADP receptor blocker
|
|
|
What neurotransmitter may be involved in narcolepsy?
|
Orexin (hypocretin)
|
|
|
What's the treatment for beta blocker overdose?
|
Glucagon
|
|
|
What is pergolide?
|
Dopamine agonist
|
|
|
What is chlorpromazine?
|
Typical neuroleptic. Can cause corneal deposits.
|
|
|
What is fluphenazine?
|
Typical neuroleptic. High potency. EPS common.
|
|
|
What is thioridazine?
|
Typical neuroleptic. Strongly muscarinic and alpha blocking. Can cause retinal deposits
|
|
|
What is haloperiodol.
|
Typical neuroleptic. High potency. EPS common.
|
|
|
What is clozapine?
|
Aypical neuroleptic. Has muscarinic and alpha blocking properties as well as 5HT2, D2c. Causes agranulocytosis, seizures and increased salivation. No risk of tardive dyskinesia
|
|
|
What is olanzapine?
|
Aypical neuroleptic. Blocks D2c and 5HT2. Blocks D2c, not A so less EPS risk
|
|
|
What is risperidone?
|
Aypical neuroleptic. Blocks D2c and 5HT2.
|
|
|
What is apaprazole?
|
Aypical neuroleptic. Partial agonist of dopamine D2 receptors. Also blocks 5HT2
|
|
|
|
|
|
Where does the lateral corticospinal tract go through the thalamus?
|
VA
|
|
|
What diseases affect the anterior horn?
|
West nile, polio, ALS (and UMN), Werdnig Hoffman (autosomal recessive)
|
|
|
What gene defect is associated with ALS
|
SOD1
|
|
|
What is the treatment for ALS?
|
Riluzole (↓ glutamate release)
|
|
|
What's the difference versus the anterior and lateral STT?
|
Anterior: crude touch, pressure. Lateral: pain and temperature.
|
|
|
What is mutated in Freidrichs ataxia?
|
trinucleotide repeat (GAA) in the gene that endcodes fraxatin, impairing mitochondrial functioning
|
|
|
What are the symptoms of Freidrichs ataxia?
|
Ataxia, nystagmus, pes cavus, hammer toes, HOCM (cause of death), kyphoscoliosis.
|
|
|
Why is there ptosis in Horner's?
|
Superior tarsal
|
|
|
Where does the biceps reflex test?
|
C5
|
|
|
Where does the triceps reflex test?
|
C7
|
|
|
Where does the patellar reflex test?
|
L4
|
|
|
Where does the achilles reflex test?
|
S1
|
|
|
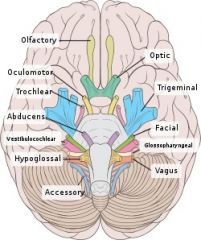
|
|
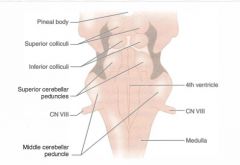
|
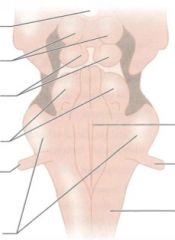
|
|
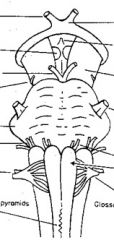
|
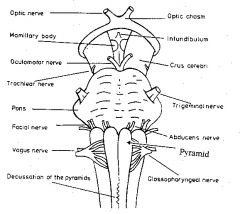
|
|
|
What is the Gallant reflex?
|
Stroking one side of the spine with the baby held prone causes lateral flexion of the begs towards the stimulated side
|
|
|
What CN is responsible for salviation of the submandibular and sublingual glads, lacrimation, and the stapedius?
|
CN VII
|
|
|
What CN is responsible for salivation from the carotid, the carotid body and sinus, and stylopharyngeal?
|
CN IX
|
|
|
What CN is responsible for palate elevation, the uvula, and monitoring the aortic chemo and baroreceptors?
|
CN X
|
|
|
What are the cranial nerve nuclei of the midbrain?
|
III, IV
|
|
|
What are the cranial nerve nuclei of the pons?
|
V, VI, VII, VIII
|
|
|
What are the cranial nerve nuclei of the medulla?
|
IX, X, XI, XII
|
|
|
What does the dorsal motor nucleus do?
|
Parasympathetics to the heart, lungs, GI
|
|
|
What goes through the optic canal?
|
CN II, ophthalmic artery, central rentinal vein
|
|
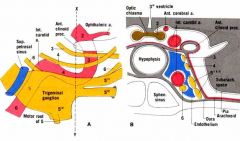
|
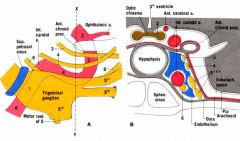
|
|
|
What goes through the superior orbital fissure?
|
CN III, IV, V1, VI, ophthalmic vein, sympathetics
|
|
|
What goes through the foramen rotundum?
|
V2
|
|
|
What goes through the foramen ovale?
|
V3
|
|
|
What goes through the foramen spinosum?
|
MMA
|
|
|
What goes through the internal auditory meatus?
|
VII, VIII
|
|
|
What goes through the jugular foramen?
|
IX, X, XI, jugular vein
|
|
|
What does a CN V motor lesion do?
|
Jaw deviation toward the lesion do the unopposed opposite pterygoid.
|
|
|
What are the signs of conductive heading loss?
|
Abnormal Rinne (bone>air), Weber localizes to the affected ear.
|
|
|
What are the signs of sensorineural heading loss?
|
Normal Rinne (air>bone), Weber localizes to the unaffected ear.
|
|
|
What are the branches of CN VII?
|
To Zanzibar by motor car:
Temporal, zygomatic, buccal, mandibular, cervical |
|
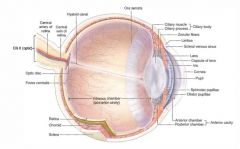
|
|
|
|
What diseases do you see Bell's palsy in?
|
AIDS, lyme, herpes, sarcoidosis, tumors, diabetes. Bilateral - lyme, Guillain Barre.
|
|
|
What goes through the cavernous sinus?
|
III, IV, V1, V2, VI, post ganglionic sympathetics, ICA
|
|
|
What conditions are associated with anterior uveitis?
|
HLA B 27 - Reiters, ankylosing spondylitis, sarcoidosis. Iritis is a form.
|
|
|
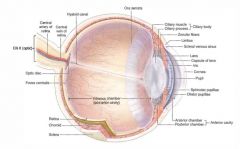
Where is aqueous humor produced?
|
Ciliary epithelium. Under beta adrenergic stimulation.
|
|
|
What are some properties of S. viridans (S. mutans, sanguis)
|
Alpha hemolytic, optochin resistant
|
|
|
What are some properties of group A strep (S. pyogenes)?
|
Beta hemolytic, bacitracin sensitive, PYR +
|
|
|
What are GAS virulence factors?
|
M protein prevents phagocytosis, streptolysin O (oxygen labile), streptolysin S (oxygen stable), erythrogenic, pyrogenic, exotoxin A (TSS-like)
|
|
|
What's the rash in scarlet fever called?
|
Erythema marginatum
|
|
|
What are some properties of GBS (S. agalactiae)?
|
Beta hemolytic, bacitracin resistant
|
|
|
What are some properties of S. bovis?
|
Any hemolysis, PYR+, can hydrolyze esculin (black), do not grow in hypertonic saline, do grow in bile salts. Remember they can cause urinary and biliary infections
|
|
|
What are some properties of enterococci?
|
Cocci in chains, can grow in hypertonic saline or bile. Can cause biliary infections, endocarditis after GU procedures.
|
|
|
What is the treatment for enterococci?
|
Vancomycin (or penicillin) + aminoglycoside
|
|
|
What are some properties of Corynebacterium diphtheriae?
|
Catalase +, club shaped rod. Grows in cysteine tellurite agar – black, iridescent colonies or Loffler’s – cytoplasmic metachromatic granules. Elek test for toxin – metachromatic (blue and red) granules
|
|
|
What are some properties of diphtheria toxin?
|
Coded for by a beta prophage. Inhibits protein synthesis by ADP ribosylating EF-2
|
|
|
How do you treat diphtheria?
|
Antitoxin, then antibiotics (penicillin, erythromycin), then vaccinate
|
|
|
How does diphtheria present?
|
Bluish skin coloration, sore throat, hoarseness, cough, headache, difficulty swallowing, painful swallowing, difficulty breathing, rapid breathing, foul-smelling bloodstained nasal discharge, grey pseudomembranes
|
|
|
What are some properties of listeria?
|
Beta hemolytic rod with tumbling motility, V or L formations. Forms actin rockets to move between cells. DOES have LPS. Has a narrow zone of beta hemolysis, multiplies at 4c
|
|
|
How do you treat listeria?
|
Ampcillin. Remember it is engulfed by macrophages but can survive intracellularly.
|
|
|
What are C. dificile's toxins?
|
Toxin A: enterotoxin. Binds to the brush border of the gut. Neutrophil chemoattractant → inflammation, loss of water, and mucosal death
Toxin B: cytotoxin. Depolymerizes actin → loss of cytoskeleton integrity → cell death. Stimulates fibrin deposition |
|
|
What is C. perfringen's toxin?
|
Produces alpha toxin (lecithinase), a phospholipase. Causes myonecrosis and hemolysis. Remmber it's spores can cause watery diarrhea.
|
|
|
What does B. anthracis look like on a plate?
|
“medusa head” colonies in long chains
|
|
|
What does B. anthracis's edema factor do?
|
calmodulin dependent adenylate cyclase that causes cAMP ↑. It suppresses neutrophil function and leads to edema (similar to Bordetella pertussis’s extracellular adenylate cyclase)
|
|
|
What gram positive is weakly acid fast?
|
N. asteroides. Treat with sulfonamides.
|
|
|
How do you treat actinomyces israelli?
|
Penicillin
|
|
|
What are the oxidase negative rods that don't ferment lactose?
|
shigella, salmonella, proteus. pseudomonas is oxidase positive
|
|
|
What are the fast lactose fermenting rods?
|
Klebsiella, E. coli, enterobacter
|
|
|
What are the slow lactose fermenting rods?
|
Citrobacteri, serratia
|
|
|
How do you treat H. flu meningitis?
|
Ceftriaxone, prophylaxis with rifampin.
|
|
|
What is the Hib vaccine?
|
Vaccine is a polysaccharide conjugated with diphtheria toxin. Other carriers include N. meningitides outer membrane protein complex, tetanus toxoid
|
|
|
How do you treat legionella?
|
Fluoroquinolones, newer macrolides.
|
|
|
What are some properties of pseudomonas aeruginosa?
|
Aerobic, non lactose fermenting, oxidase positive, encapsulated, catalase positive
|
|
|
What is pseudomonas's toxins?
|
Produces exotoxin A – inactivates EF-2 by ribosylation. Also makes collagenase, elastase, fibrinolysin, phospholipase C, DNAse
|
|
|
What can cause sepsis with black skin lesions (ecthyma gangrenosum - less edematous than anthrax), malignant otitis externa in diabetics, osteomyelitis from shoes, corneal infections in contact lens wearers.
|
Pseudomonas
|
|
|
How do you treat pseudomonas?
|
aminoglycoside + extended spectrum penicillin (e.g. piperacillin, ticaricillin)
Often sensitive to fluroquinolones, cefepime, aztreonam, aminoglycosides, extended spectrum penicllins, polymyxins |
|
|
Describe E. coli EIEC
|
Invasive, causes dysentery. Necrosis and inflammation, similar presentation to shigella. Does not produce toxin
|
|
|
Describe E. coli EPEC
|
Causes diarrhea in children. No toxins. Adheres to villi and flattens them, prevents absorption.
|
|
|
Describe E. coli EHEC
|
Produces shiga-like toxin (verotoxin – inhibits 60s ribosome). Causes dysentery, HUS. Unlike other strains, does not ferment sorbitol
|
|
|
What are some properties of C. jejuni?
|
Comma shaped, oxidase positive, grows at 42 degrees C. Can occur prior to Guillain Barre
|
|
|
How do you treat C. jejuni?
|
Erythromycin or fluroquinolones, but self limiting.
|
|
|
Describe Vibrio chorerae
|
Comma shaped, oxidase positive, grows in alkaline media. Very acid sensitive → increased risk with PPIs, even with food due to buffering capacity
|
|
|
How does Yersenia entercolitica present?
|
Diarrhea. Can cause mesenteric adenitis that looks like Crohns or appenditicits. (via pet feces, milk, pork)
|
|
|
What does CN XII not innervate?
|
Palatoglossus
|
|
|
What are common etiologies of otitis media?
|
S. pneumo, non Hib H. flu, M. catarrhalis
|
|
|
How does Sturge Weber present?
|
Port wine stains, ipsilateral leptomeningeal angioma, pheochromocytoma. Calcification of skull causes tram track appearance on xray. Can cause glaucoma, seizures, hemiparesis, MR. Sporadic, NOT genetic
|
|
|
What causes granuloma inguinale
|
Klebsiella granulomatus. Papules that ulcerate can become exophytic, soft painless mass with indurated borders, scarring and stricture. Tropical. Treat with erythromycin.
|
|
|
How does tuberous sclerosis pressent?
|
CNS/retinal and skin hamartomas, Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma, Adenoma sebaceum (cutaneous angiofibromas), Mitral regurgitation, Ash leaf spots, Rhabdomyomas, MR, Renal angiomyolipoma, Seizures
|
|
|
How does neurofibromatosis I present?
|
• Café au lait spots, inguinal/axillary freckles
• Lisch nodules (pigmented iris hamartomas) • Neural tumors (meningiomas, etc) • Cutaneous lesions are skin colored/pink, rubbery, “buttonholing” – looks like goes into the skin with gentle pressure • Optic nerve glioma • Skeletal disorders (e.g. scoliosis, sphenoid dysplasia, congential pseudoarthritis) • Pheochromocytoma |
|
|
What does meningioma look like on histology?
|
Histology shows spindle cells concentrically arranged in a whorled pattern, psammoma bodies
|
|
|
What tumor marker is positive in a schwannoma?
|
S-100
|
|
|
What is diphenoxylate?
|
Opioid analgesic, used for diarrhea
|
|
|
What are the short acting benzodiazepines?
|
triazolam, oxazepam, midazolam
|
|
|
What is treatment for H. pylori?
|
o PPI, clarithromycin, amoxicillin or metronidazole
o Or bismuth, metronidazole, tetracycline, PPI |
|
|
What are some P. mirabilis characteristics?
|
Oxidase negative, nonlactose fermenting, catalase +, nitrase +, makes urease. Characteristic swarming pattern; motile
|
|
|
What can cause bacillary angiomatosis?
|
Bartonella (cat-scratch)
|
|
|
How is brucella transmitted?
|
Unpasteurized dairy, animals (undulant fever)
|
|
|
What causes yaws?
|
T. pertenue. Causes keloids, nasal/cartilage destruction
|
|
|
What causes condyloma lata?
|
Syphilis
|
|
|
How does leptospirosis present?
|
A question marked shape spirochete. Causes flu-like illness, jaundice, photophobia, abdominal pain. Can also cause Weil's disease - azotemia, jaundice, hemorrhage, anemia.
|
|
|
What do you call the rash in lyme disease?
|
Erythema chronicum migrans
|
|
|
How do you treat borrelia?
|
Doxycycline, ceftriaxone for later stages
|
|
|
What are TB's virulence factors?
|
• Sulfatides – allow for intracellular proliferation (by preventing lysosome fusion)
• Cord factor – blocks macrophage activation by IFN gamma, induces TNF alpha secretion. It blocks neutrophils and damages mitochondria. In vitro, it allows cord formation. It is the main drug resistance factor. It is a mycoside – 2 mycolic acids bound to the disaccharide trehalose. |
|
|
What are cold agglutinins seen in?
|
M. pneumoniae, EBV, hematologic malignancies
|
|
|
How do you treat M. pneumoniae?
|
Tetracycline, erythromycine, azithromycin
|
|
|
How does coxiella burnetti present?
|
Interstitial pneumonia
|
|
|
What is a Weil-Felix reaction?
|
o Serum mixed with Proteus antigens; antirickettsial antibodies react with O antigen and agglutinate
|
|
|
How does lymphogranuloma venerum prestent (C. trachomatis L1, L2, L3)
|
Acute lymphadenitis, primary ulcers, rectal disease mimicking IBD, papule → several draining ulcers weeks later, red eyes, inclusion bodies and granulomatous inflammation with stellate abscesses. Can cause anogenital fibrosis
|
|
|
How does legionella pneumonia cause?
|
High fever, reltive bradycardia, headache, confusion, watery diarrhea, hyponatremia - specific. Unlike other atypical pneumonias CXR shows unilobar infiltration → consolidation
|
|
|
Where do you find histoplasma?
|
Midwest. Associated with bird and bat droppings
|
|
|
What does histoplasma look like on a smear?
|
Dimorphic. Macrophages filled with it, where it multiples. Culture shows hyphae
|
|
|
How does disseminated histoplasmosis present?
|
Hepatosplenomegaly, tongue ulcers, diffuse pulmonary infiltrate, hilar lymphadenopathy
|
|
|
Where do you find bastomyces?
|
Eastern US. Found in the soil, mold form predominates (transmitted through aerosols)
|
|
|
Where does alpha 1 act?
|
Gq. Arterioles (increases diastolic BP), veins (increases systolic BP), vas defrens, liver (glycogenolysis), decreases renin release from the kidney
|
|
|
What tissues does alpha 2 act on?
|
Pancreas (decreases insulin secretion), platelets (promotes aggregation)
|
|
|
What does beta 1 act on?
|
Heart (SA, AV, atria, ventricles), kidneys (increase renin release - usually more sensitive than alpha receptors)
|
|
|
What does beta 2 act on?
|
Mostly not innervated, so less effect from norepinephrine.
Blood vessels (vasodilation, more sensitive than alpha 1). Relaxes uterus, bronchioles. Increases glycogenolysis in muscles. Liver (increases gluconeogenesis, glycogenosysis), increases insulin secretion (beta is more sensitive). |
|
|
What do D1 receptors do?
|
Increase RBP and GFR, dilates coronaries. At higher doses, it acts more like norepinephrine, so you add adrenergic actions.
|
|
|
What is fenoldopam?
|
D1 partial agonist, used as an antihypertensive (can be used in hypertensive crisis)
Relaxes renal vascular smooth muscle, also mesenteric anc coronary beds. Increases sodium and water excretion |
|
|
ow do you treat endometritis?
|
cefoxitin, ticarcillin-clavulanate, ampicillin-sulbactam
|
|
|
How does disseminated blastomycosis present?
|
Papules, pustules, ulcer, verrucous lesions, bone pain (lytic lesions), granulomatous nodules (cauliflower lesion). Remember it is dimorphic.
|
|
|
How does coccidiodes present?
|
Causes pneumonia (acute is most common, can be chronic progressive), pulmonary nodules/cavities, extrapulmonary disease and meningitis that can disseminate to bone and skin (erythema nodosum). Can cause a thin walled cavity in the lung leading to hemoptysis
|
|
|
How does paracoccidiodes present?
|
Granulomas in the mucus membranes and skin.
|
|
|
How does paracoccidiodes look microscopically?
|
Buds with captains wheel formation. Large
|
|
|
How does malassezia furfur cause tinea versicolor?
|
Degrades lipids that produce acids → damage melanocytes
Hyper/hypopigmented patches, usually on trunk, begin as nonpruritic macules → scaling plaque |
|
|
What does M. furfur look like on KOH?
|
Spaghetti and meatballs
|
|
|
Are dermatophytes dimorphic?
|
No, just mold form. Treat with turbenafine or azoles
|
|
|
How do you treat systemic candidiasis?
|
Fluconazole, caspofungin, or amphoterecin B
|
|
|
How does aflatoxin cause HCC?
|
G to T mutation in p53. Remember aspergillus is a mold only
|
|
|
What does N. neoformans look like on a slide?
|
Yeast form only, round or oval encapsulated cells with narrow based buds, wide capsular halos and unequal budding
|
|
|
How do you treat cryptococcus?
|
Amphoterecin B and flucytosine, prophylaxis with fluconazole
|
|
|
What mold (no yeast form) is related to increased susceptibility with iron overload, especially with deferoxamine?
|
Mucor and rhizopus
|
|
|
What do mucor and rhizopus look like?
|
irregular, broad, nonseptate hyphae branching at wide angles
|
|
|
What does pneumocystis look like?
|
disk shaped yeasts (no mold form) on methenamine silver stain
|
|
|
How do you treat sporothrix?
|
itraconazole or potassium iodide
|
|
|
What does sporothrix look like?
|
Cigar shaped budding yeast (dimorphic)
Histology shows a granuloma made of histiocytes, giant cells, neutrophils, surrounded by plasma cells. |
|
|
How do you treat enamoeba histolytica?
|
metronidazole or tinidazole, followed by iodoquinol to eliminate cysts
|
|
|
How do you diagnose cryptosporidium?
|
Cysts on acid fast stain. Resistant to chlorination
|
|
|
How do you treat T. gondii?
|
sulfadiazine + pyrimethamine and folinic acid
|
|
|
What does congenital toxoplasmosis look like?
|
o Hydrocephalus
o Intracranial calcification o Chorioretinitis – white/yellow scars on retina o Hepatosplenomegaly, rash, seizures, altered muscle tone, ocular movement defects |
|
|
What disease does Naegleria fowleri cause?
|
Rapidly fatal meningoencephalitis, from freshwater
|
|
|
How do you treat T. brucei?
|
Suramin if early, melarsoprol if CNS involvement
|
|
|
How do you treat T. cruzi?
|
Nifurtimox
|
|
|
What does babesia present like?
|
Fever, hemolytic anemia, worse if asplenic (remember it is transmitted by the ixodes tick so common in eastern US)
|
|
|
What does babesia look like on a smear?
|
maltese cross (merozoite) and ring form (trophozoite - looks like P. falciparum) in RBCs
|
|
|
How do you treat babesia?
|
Quinine, clindamyclin
|
|
|
How do you treat Leishmania?
|
cutaneous with stibogluconate, visceral with liposomal amphoterecin B
|
|
|
How does visceral Leishmanias presents (kala-azar)?
|
spiking fever, hepatosplenomegaly, pancytopenia
|
|
|
What are the nematodes (roundworms?
|
Enterobius vermicularis, ascaris lumbricoides, trichenella spiralis, strongyloides steroralis, ancytlostoma duodenale, necator americanus, dracunculus medinesis, onchocerca voluvus, loa loa, wuchereria bancrofti, toxocara canis - most are treated with bendazoles, some with pyrantel pamoate, a couple with niridazole or diethylcarbamazine
|
|
|
How does trichenella spiralis present?
|
A nematode, found in undercooked meat. Causes muscle inflammation, periorbital edema, fever.
|
|
|
What are the hookworms?
|
A nematode. Ancyclostoma duodenale, necator americanus. Sucks blood from the inestinal walls and causes anemia. Burrows into the skin
|
|
|
How is drancunculus medinensis spread?
|
A nematode. Spread through drinking water. Causes skin inflammation and ulceration. Treat with niridazole
|
|
|
How does onchocera volvulus present?
|
A nematode. Hyperpigmented skin, river blindless. Can cause an allergic reaction. Transmitted by female blackflies. Treat with ivermectin.
|
|
|
What is loa loa?
|
A nematode. Spread by flies. Causes swelling in the skin, worms can be seen in the conjunctiva. Treat with diethylcarbamazine.
|
|
|
What does wuchereria bancrofti cause?
|
A nematode. Elephantiasis. Spread by mosquitos. Treat with diethylcarbamazine.
|
|
|
How does toxocara canis infection present?
|
granulomas, if in retina, can cause blindness. Visceral larva migrans (skin disease). Treat with diethyl carbamazine
|
|
|
How do you treat T. solium?
|
Praziquantel and dexamethasone (dying larvae can cause an immune response. Treat cystercercosis with bendazoles.
|
|
|
How does Echinococcus granulosus present?
|
A cestode (tapeworm). Eggs in dog feces are ingested → hydatid cysts in liver. They are encapsulated with eggshell calcification, fluid, budding cells.
Treat with albendazole |
|
|
What can Schistosoma mansoni cause?
|
A trematode (fluke). Spleen and liver inflammation → portal hypertension and splenmegaly. Can also cause swimmer's itching with granulomas
|
|
|
What can Schistosoma hamatobium cause?
|
Squamous cell carcinoma of the bladder. Treat schistosoma with praziquantel
|
|
|
What is clonorchis sinensis associated with?
|
Cholangiocarcinoma, causes biliary tract inflammation and pigmented gallstones. Treat infection with praziquantel or albendazole
|
|
|
How does paragonimus westermani present?
|
A trematode. From cooking undercooked crab. Causes inflammation of the lung, secondary bacterial infection, hemoptysis.
|
|
|
What microbes have IgA protease?
|
S. pnuemo, Hib, Neisseria, all of which cause meningitis
|
|
|
What bacteria have type III secretion systems?
|
E. coli, Salmonella, Yersinia, P. aeruginosa, Chlamydia
|
|
|
What are some exotoxins inhibiting protein synthesis?
|
C. diphtheriae – diphtheria toxin
o Inactivates elongation factor EF-2 P. aeruginosa – exotoxin A Inactivates elongation factor EF-2 Shigella – shiga toxin Inactivates 60s ribosome by cleaving rRNA EHEC – shiga-like toxin Inactivates 60s ribosome by cleaving rRNA |
|
|
How does diphteria toxin work?
|
Inactivates EF-2, was transferred via a lysogenic phage
|
|
|
How does Pseudomona's exotoxin A work?
|
Elongates EF-2
|
|
|
How does shiga toxin work?
|
Inactivates 60s ribosome by cleaving rRNA
|
|
|
How does shiga-like toxin work?
|
In EHEC, but does not invade. Inactivates 60s ribosome by cleaving rRNA
|
|
|
How does ETEC heat labile toxin work?
|
Overactivates adenylate cyclase and increases Cl secretion
|
|
|
What endotoxins increase fluid secretion?
|
ETEC
o Heat labile toxin – overactivates adenylate cycline → ↑ Cl- secretion o Heat stabile toxin – overactivates guanylate cyclase → ↓ NaCl reabsorption Yersenia entercolitica – heat stable toxin o Overactivates guanylate cyclase → ↓ NaCl reabsorption. Bacillus anthracis – edema factor o Mimics adenylate cyclase to ↑ camp. Vibrio cholerae – cholera toxin o Permanently activates Gs |
|
|
How does ETEC heat stabile toxin work?
|
Overactivates guanylate cycles to decrease NaCl reabsorption
|
|
|
How does yersenia entercolitica heat stable toxin work?
|
Like ETEC's - overactivates guanylate cyclase
|
|
|
How does B. anthracis edema factor work?
|
Mimics adenylate cycline
|
|
|
How does cholera toxin work?
|
Permanently activates Gs
|
|
|
What are pertussis's toxins?
|
o Pertussis toxin - disables Gi to overactivate adenylate cyclase
o Adenylate cyclase toxin ↓ leukocyte chemotaxis o Tracheal cyctotoxin kills epithelial cells |
|
|
What S. pyogenes toxin causes shock?
|
Exotoxin A
|
|
|
How does C. perfringens alpha toxin work?
|
A phospholipase that degrades tissue and cell membranes
|
|
|
How does streptolysin O work?
|
Degrades cell membranes, lyses RBCs, oxygen labile
|
|
|
What microbes need cysteine to culture?
|
Francisella, brucella, legionella, pasteurella
|
|
|
What do you culture N. gonorrhoeae on?
|
Thayer martin (VPN) - vancomycin, polymyxin, nystatin
|
|
|
What do you culture D. diphtheriae on?
|
Tellurite, Lofflers
|
|
|
What do you stain with Giemsa?
|
Borrelia, plasmodium, trypanosomes, chlamydia
|
|
|
What do you use a silver stain for?
|
Fungi, legionella
|
|
|
What toxins are associated with lysogenic phages?
|
Shiga-like toxin, botulinum toxin, cholera toxin, diphtheria toxin, erythrogenic toxin (S. pyogenes)
|
|
|
What are the naked viruses?
|
Mnemonic: naked CPR (RNA) and PAPP (DNA, including HPV) smears
• Calcivirus, picornavirus, reovirus, hepevirus • Parvovirus, adenovirus, papillomavirus, polyomavirus |
|
|
What virus's envelope is from the nuclear membrane?
|
Herpes
|
|
|
What viruses naked genomes are infective?
|
Naked genome of dsDNA (except pox and HBV) and + ssRNA are infectious
|
|
|
What are the nonlinear DNA viruses?
|
All are linear except papilloma, polyoma (circular) and hepadna (partially circular)
|
|
|
What DNA virus does not re[licate in the nucleus?
|
Poxvirus, also the only nonicosahedral
|
|
|
What are the DNA viruses?
|
hepadna, herpes, adeno, pox, parvo, papilloma, polyoma
|
|
|
What are complications of VZV?
|
ENcephalitis, giant cell pneumonia
|
|
|
How can reactivation CMV present?
|
Interstitial pneumonitis, retinitis (full thickness necrosis and edema), hepatitis, colitis. Treat with ganciclovir, foscarnet, or cidofovir.
|
|
|
How do you treat kaposi sarcoma?
|
allotretinoin, vinblastin, danorubicin
|
|
|
What order do HBV antigens present in?
|
SECES. Remember HBV has reverse transcriptase
|
|
|
What HBV serologic marker is present in the window phase?
|
Anti-HBcAg IgM
|
|
|
How does adenovirus infection present?
|
• Hemorrhagic cystitis, especially in males and children; resolves spontaneously
• Pharyngoconjunctival fever - low grade fever, throat pain, red eyes, cervical lymphadenopathy– self limited. • Pneumonia • Conjunctivitis – watery pink eye |
|
|
What is parvovirus's genome?
|
Unenveloped linear negative sense DNA
|
|
|
What is molluscum contagiosum caused by?
|
Poxvirus
|
|
|
What is the only dsRNA virus?
|
Reoviruses (reovirus, rotavirus)
|
|
|
What kind of virus is HBV?
|
Hepadnavirus
|
|
|
What are the positive stranded RNA viruses?
|
Retro, toga, flavi, corona, hepe, calci, picorna
|
|
|
What are the segmented RNA viruses?
|
Bunya, orthomyxo, arena, reo (BOAR)
|
|
|
What RNA viruses don't replicate in the cytoplasma?
|
Influenza, retroviruses
|
|
|
What are RNA viruses that start with an H, A or P?
|
hepevirus, picornavirus, paramyxovirus, arenavirus
|
|
|
What are some reoviruses?
|
Icosahedral DS linear RNA.
Coltivirus - colorado tick fever (self limited) Rotavirus - URI, then diarrhea, especially in the winter. Villous atrophy decreases Na absorption. |
|
|
What are some picornaviruses?
|
Icosahedral + linear RNA
Poliovirus, echovirus, rhinovirus, coxsackievirus, HAV. Enteroviruses are the most common cause of asceptic meningitis |
|
|
How does echovirus present?
|
Picornavirus. Asceptic meningitis, myocarditis, and URI in the summer
|
|
|
What does coxsackie virus cause?
|
Picornavirus. Asceptic meningitis, herpangina (febrile pharyngitis, sores in mouth, odynophagia), hand-foot-mouth (vesicles, papules), myocarditis
|
|
|
What do you do for hepatitis A prophylaxis?
|
Picornavirus. Give Ig
|
|
|
What is a hepevirus?
|
HEV. Icosahedral + linear RNA
|
|
|
What are some symptoms for yellow fever?
|
Flavivirus: icosahedral + linear RNA.
Causes jaundice, black vomitus, bleeding, increased LFTs, flaccid paralysis |
|
|
What are some togaviruses?
|
Icosahedral + linear RNA.
Rubella (German measles), equine encephalitis (arbovirus) |
|
|
How does rubella present?
|
Toga virus.
Post auricular tenderness, rash with face first. Congenital rubella causes PDA, pulmonic stenosis (pulmonary artery hypoplasia), cataracts, sensorineural deafness, blueberry muffin rash, microcephaly |
|
|
What gene is HIV's gp120, gp41 from? What do they do?
|
env. gp120 mediates host cell attachment via CD4, gp41 mediates fusion and entry.
|
|
|
What gene encodes HIV's capsid protein?
|
gag (p24)
|
|
|
What gene encodes HIV's reverse transcriptase?
|
pol
|
|
|
What diseases do you start to see at a CD4 count of <100
|
Toxoplasmosis, histoplasma
|
|
|
What do you start seeing at a CD4 of under 200?
|
PCP pneumonia, cryptosporidium, JC virus reactivation
|
|
|
What do you start seeing at a CD4 of under 50?
|
CMV (retinitis, etc), cryptococcus, MAC
|
|
|
What are some properties of coronavirus?
|
Helical, + sense linear RNA
|
|
|
What are some properties of orthomyxoviruses (flu)?
|
Helical, + linear RNA
|
|
|
What are some paroxymyxoviruses?
|
Helical - linear RNA.
Rubeola (only one with a rash), mumps, parainfluenza virus, RSV |
|
|
How does rubeola present?
|
paroxymyxovirus. Cough, coryza, conjunctivitis, Koplic spots, rash (eventually involves hands and feet unlike rubella)
|
|
|
How does the mumps present?
|
paroxymyxovirus. Parotitis, orchitis, asceptic meningitis
|
|
|
What are some filoviruses?
|
Helical - linear RNA.
Ebola, marburg |
|
|
What are some arenaviruses?
|
Helical - circular RNA with 2 segments.
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis and Lassa fever |
|
|
What are some bunyaviruses?
|
Helical - circular RNA with 3 segments. California encephalitis, sandfly/rift valley fever, crimean-congo hemorrhagic fever (all arboviruses, and hantavirus
|
|
|
What is a deltavirus?
|
Helical - circular RNA. Hepatitis D virus. is double shelled. Requires HBsAg as an envelope.
|
|
|
What is an inherited prion disease?
|
Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker syndrome
|
|
|
What 3 bacteria most commonly mimic appendicitis?
|
Y. entercolitica, C. jejuni, slamonella
|
|
|
What bugs cause bloody diarrhea?
|
campylobacter, salmonella, shigella, EHEC, EIEC, Y. entercolitica, E. histolytica
|
|
|
What commonly causes pneumonia COPD patients?
|
H. flu
|
|
|
How does congenital CMV present?
|
Hearing loss, seizures, peticheal rash, blueberry muffin rash
|
|
|
How do you prophylax meningococcus?
|
Ciprofloxacin, rifampin, minocycline, or ceftriaxone
|
|
|
What antibiotics should you avoid in pregnancy?
|
clarythromycin, sulfonamides (kernicterus), aminoglycosides, fluoroquinolones, metronidazole in the first trimester, tetracycline, ribavirin, griseofulvin, chloramphenicol
|
|
|
What are the clinical uses of penicillins?
|
Gram positives (GBS, S. pyogenes, S. pneumo, actinomyces), Syphilis; Can be used for clostridum, listeria, bacillis, neisseria.
Penicillin can cause hemolytic anemia |
|
|
What are the resistance mechanisms for beta lactams?
|
Beta lactamase, PBP changes, changes in porin structure
|
|
|
What are the methicillin, oxacillin, nafcillin, and dicloxacillin?
|
Beta lactamase resistance penicillines
Methichillin causes interstitial nephritis. |
|
|
What is the spectrum of aminopenicllins?
|
Wider spectrum than penicillin – H. flu, E. coli, Listeria monocytogenes, Proteus mirabilis, Salmonella, Shigella, enterococci, borrelia. Can be used for neonatal infections + aminoglycosides and UTIs
|
|
|
What are the carboxypenicillins? What are they used for?
|
Ticarcillin, carbenicillin, piperacillin. Pseudomonas, gram negative rods, anaerobes
|
|
|
What do you use first generation cephalosporins for?
|
UTI, URI, viridans strep endocarditis
|
|
|
What can aztreonam be used for?
|
Only gram negative rods, no anaerobes. Good for renal insufficiency, allergy. Beta lactamase resistant
|
|
|
What does cilastatin inhibit?
|
Renal dihydropeptidase I which inactivates imipenem. Carbapenums are not useful for MRSA
|
|
|
What is tobramycin?
|
Aminoglycoside
|
|
|
What is neomycin?
|
Aminoglycoside
|
|
|
What is the MOA of aminoglycosides
|
Inhibits the formation of the initiation complex, causing mRNA misreading - therefore, the only bactericidal protein synthesis inhibitor. Needs O2 for uptake.
|
|
|
What are some mechanisms of resistance to aminoglycosides?
|
Transferase enzymes inactivate the drug by acetylation, phosphorylation, adenylation
|
|
|
What are the side effects of aminoglycosides?
|
Nephrotoxic (especially with cephalosporin), ototoxic (especially with a loop), congenital deafness
|
|
|
What is minocycline?
|
A tetracycline. Prolonged use can cause blue skin pigmentation
|
|
|
What can tetracyclines be used for?
|
Borrelia burgdorferi, M. pneumoniae, Rickettsia, Chlamydia (accumulates intracellularly). Also, V. cholera, ureaplasma, tularemia, H. pylori
|
|
|
What is the MOA for tetracyclines?
|
Binds to 30S subunit and prevents the attachment of aminoacyl tRNA. Ok in renal failure
|
|
|
What is the MOA of chloramphenicol?
|
Blocks peptide bond formation at 50S subunit. Resistance is due to acetyltransferase activation
|
|
|
What are the streptogramins?
|
Quinupristin, dalfoprisitin
|
|
|
What is the MOA for streptogramins?
|
Streptogramin A – binds peptidyl transferase of 50s (like chloramphenicol)
Streptogramin B – prevents protein chain extension |
|
|
What can streptogramins be used for?
|
MRSA, VRE, Staph and Strep skin infections
Can be hepatotoxic |
|
|
What is the MOA for clindamycin (a lincosamide)?
|
Blocks peptide bond formation at 50s. Is effective against MRSA
|
|
|
What is clarithromycin?
|
A macrolide
|
|
|
What is the MOA for macrolides?
|
Inhibits protein synthesis by blocking translocation (macroslides). Binds 23s rRNA of the 50S subunit like linezolid.
|
|
|
What are macrolides used for?
|
Atypical pneumonias, URIs, STDs, gram positive cocci (Step in penicillin allergies), Neisseria
|
|
|
What are resistance mechanisms to macrolides?
|
Inactivation by enzymes modifying the drug (phosphorylation, adenylation, acetylation, etc). Pseudomonas ↓ entry. Methylation of 23s rRNA binding site.
|
|
|
What are the side effects of macrolides?
|
Prolonged QT (especially erythromycin), GI discomfort, eosinophilia, skin rashes.
Erythromycin – acute cholestatic hepatitis |
|
|
What is the MOA of linezolid?
|
Binds 23s rRNA of the 50s subunit, interacts with bacterial initiation complex
|
|
|
What is the clinical use of linezolid?
|
VRE, MRSA
|
|
|
What is the MOA of sulfonamides.
|
PABA antimetabolite - inhibits dihydropteroate synthesis
|
|
|
What are sulfonamides used for?
|
Gram positives, gram negatives, nocardia, chlamydia
|
|
|
What are the side effects of sulfonamides?
|
Nephrotoxicity (tubulointerstitial nephritis), photosensitivity
Displaces other drugs from albumin → kernicterus if used during pregnancy (displaces billi), ↑ toxicity (e.g. warfarin) |
|
|
What is the MOA of trimethoprim?
|
Inhibits dihydrofolate reductase? (like methotrexate)
|
|
|
What are the uses for trimethoprim?
|
UTIs, Shigella, Salmonella, MRSA skin infection
|
|
|
What is enoxacin?
|
A fluoroquinolone. Nalidixic acid is a quinolon.
|
|
|
What is the MOA for fluoroquinolones?
|
Inhibits DNA gyrase (topoisomerase II) - bactericidal
|
|
|
What is the clinical use of fluoroquinolones?
|
Gram negative rods - urinary and GI, pseudomonas, Neisseria, some gram positives (S. pneumo for later generations)
Antacids inhibit absorption |
|
|
What is the MOA of metronidazole?
|
Form free radical toxic metabolites. Bactericidal
|
|
|
What is the MOA of nitrofurantoin?
|
Reduced to reactive metabolite by bacteria that inactivates the ribosome. Bactericidal. Not useful for proteus.
|
|
|
How can M. avium be treated?
|
azithromycin, rifampin, ethambuton, streptomycin
|
|
|
How can M. leprae be treated?
|
dapsone, rifampin, clofazimine
|
|
|
What is the MOA for isoniazid?
|
Inhibits mycolic acid synthesis. A prodrug that must be converted by catalase peroxidase. Resistance can be due to KatG mutation, target mutation
Acetylated hepatically then excreted in the urine. |
|
|
What are the side effects of isoniazid?
|
o Hepatitis – initial ↑ LFTs, fever, anorexia, nausea → jaundice, ↑ bilirubin
o SLE in slow acetylators (can prevent with B6) o ↓B6 → sideroblastic anemia (microcytic – ↑ iron, ↑ % sat, ↑ ferritin, ↓ TIBC), peripheral neuropathy |
|
|
What is a side effect of rifampin?
|
Hepatitis
|
|
|
What is the MOA of ethambutol?
|
Blocks carbohydrate polymerization of cell walls by blocking arabinogalactan
|
|
|
What are the side effects of pyrazinamide?
|
Hepatitis, hyperuricemia
|
|
|
What are the side effects of amphoterecin B?
|
Renal toxicity → hypokalemia, hypomagnesia due to ↑ distal tubule membrane permeability.
Fever, chills, hypotension, arrythmias, anemia, phlebitis |
|
|
What is the MOA of pyrazinamide?
|
Blocks pyrazinamidase → inhibits mycolic acid production. Good in the acidic phagolysosome
|
|
|
What is the MOA of flucytosine?
|
Antifungal that converts to 5FU by cytosine deaminase. Good for systemic infections + amphoterecin
|
|
|
What are the clincial uses of azoles?
|
o Fluconazole – crosses blood brain barrier → cryptococcal meningitis. Candida
o Ketoconazole – blastomyces, coccidioides, histoplasma, candida, hypercortisolism o Itraconazole – first line for dimorphic fungi (e.g. sporothrix) o Voriconazole – good for aspergillus o Posaconazole – good for refractory infections, like mucor (class can generally be used for mucor) o Clotrimazol, miconazole – topical |
|
|
What are the side effects of azoles?
|
Decreased hormone synthesis, liver dysfunction, fever, chills
|
|
|
What are the side effects of flucytosine?
|
GI, bone marrow suppression
|
|
|
What is the MOA of caspofungins?
|
Inhibits cell wall synthesis (not membrane like ergosterol) by inhibiting beta glucan synthesis. This causes lysis.
|
|
|
What are mycofungin and anidulafungin?
|
Caspofungins
|
|
|
What are caspofungins used for?
|
Invasive aspergilosis, candida
|
|
|
What are the side effects of caspofungins?
|
Flushing, GI
|
|
|
What is the MOA of terbinafine?
|
Inhibits squalene epoxidase, and thus ergosterol synthesis
|
|
|
What is terbinafine used for?
|
Dermatophytes
|
|
|
What are the side effects of terbinafine?
|
Abnormal LFTs, visual disturbances
|
|
|
What is the MOA of griseofulvin
|
Inhibits microtubule function. Used for dermatophytes because it deposits in keratin containing tissure. Induces P450
|
|
|
What do you treat with pyrimethamine?
|
Toxo and P. faciparum
|
|
|
What is the MOA of chloroquine?
|
Blocks plasmodium heme polymerase.
|
|
|
What are the side effects of chloroquine?
|
Retinopathy, cinchonism (vision changes, GI distress) due to alpha/muscarinic antagonism, bad in G6PD deficiency
|
|
|
What is the MOA of mebendazole?
|
↓ glucose uptake, microtubular structure
|
|
|
What is the MOA of pyrantel pamoate?
|
Nicotinic receptor antagonist – causes contraction, then spastic paralysis → worm falls off
|
|
|
What is the MOA of praziquantel?
|
For cestodes and trematodes. ↑ Calcium influx, vacuolization → spasm
|
|
|
What is the MOA of amantadine?
|
Blocks penetration/uncoating (M2 protein – commonly mutated). Causes dopamine release (rimantidine does not cross the BBB).
|
|
|
What is the MOA of ribavirin?
|
Inhibits guanine nucleotide synthesis by competitive inhibition of IMP dehydrogenase.
Can cause hemolytic anemia |
|
|
What is the MOA of acyclovir?
|
o A guanosine analog → causes chain termination
Must be converted to acyclovir monophosphate using thymidine kinase (rate limiting) → active triphosphate form. Can also be used in VZV, but famclovir is better. |
|
|
What are the side effects of acyclovir?
|
renal toxicity (crystal nephropathy), neurotoxicity (delerium, tremor)
|
|
|
What are the side effects of ganciclovir?
|
Neutropenia (do not use with HIV), lekopenia, thrombocytopenia → bone marrow suppression. Renal toxicity
|
|
|
What is the MOA of foscarnet?
|
A pyrophosphate analog → directly inhibits DNA polymerase. Does not requires thymidine kinase activation. Will inhibit reverse transcriptase in HIV.
|
|
|
What are the side effects of foscarnet?
|
Nephrotoxicity (can cause Mg wasting), hypocalcemia (chelates calcium), hypokalemia, anemia
|
|
|
What is the MOA of cidofovir?
|
An antiviral used for refractory CMV/HSV. Inhibits DNA polymerase like foscarnet.
Is nephrotoxic. Give with probenecid. |
|
|
What are the protease inhibitors?
|
indinavir, lopinavir, atazanavir, darunavir, fosamprenavir, saquininavir, ritonavir
|
|
|
What is the MOA of protease inhibitors?
|
Inhibits HIV-1 protease from the pol gene. Not used as monotherapy?
|
|
|
What are the side effects of protease inhibitors?
|
Lipodystrophy, hyperglycemia, P450 inhibition, hypertriglyceridemia, GI upset
|
|
|
What are the side effects of indavir?
|
nephrotoxicity and nephrolithiasis
|
|
|
What are the side effects of ritonavir?
|
rare pancreatitis. Inhibits P450 → can be used to ↑ other drug concentrations
|
|
|
What are the side effects of atazanavir?
|
nephrolithiasis, ↑ billirubin
|
|
|
What are the NRTI HIV drugs?
|
Tenofovir, emtricitabine, abacavir, lamivudine, zidovudine, didanosine, stavudine, zalcitabine
|
|
|
What is tenofovir?
|
NRTI HIV drug
|
|
|
What is abacavir?
|
NRTI HIV drug
|
|
|
What is emtricitabine?
|
NRTI HIV drug
|
|
|
What is didanosine?
|
NRTI HIV drug
|
|
|
What is zalcitabine?
|
NRTI HIV drug
|
|
|
What is the MOA of NRTI HIV drugs?
|
Competitive inhibitory of nucleotide binding to reverse transcriptase. Must be phosphorylated by a thymidine kinase
|
|
|
What are the side effects of NRTI HIV drug?
|
VERY common bone marrow toxicity, use G-CSF or EPO. Peripheral neuropathy, lactic acidosis (except abacavir), rash
|
|
|
What are the side effects of abacavir?
|
NRTI HIV drug. Causes hypersensitivity, but no lactic acidosis
|
|
|
What are the side effects of didanosine and stavudine?
|
NRTI HIV drugs. Pancreatitis, peripheral neuropathy, hepatic steatosis/increased LFTs
|
|
|
What are the side effects of zalcitabine?
|
NRTI HIV drug. Pancreatitis, peripheral neuropathy.
|
|
|
What are the NNRTI HIV drugs?
|
Nevirapine, efavirenz, delviridine. They do not need to be phosphorylated.
|
|
|
What is nevirapine?
|
NNRTI HIV drug
|
|
|
What is delavirdine?
|
NNRTI HIV drug
|
|
|
What are the side effects of NNRTI HIV drug?
|
Like NRTIs. Can cause hepatic failure with encephalopathy in the first 6 weeks, Stevens Johnsons
|
|
|
What are the side effects of efavirenz?
|
Nightmares, dizziness, depression, false positive marijuana test, teratogen
|
|
|
What is raltegravir?
|
Reversible integrase inhibitor?
|
|
|
What are the side effects of raltegravir?
|
Hypercholesteorelmia, lipodystrophy
|
|
|
What is enfurvitide?
|
Binds gp41, and inhibits fusion. Used for refractory treatment. Increases risk of bacterial pneumonia, causes nodules at injection site.
|
|
|
What is maraviroc?
|
A CCR5 antagonist, inhibits gp120 conformation change. Not used in dual tropism
|
|
|
What increases NK cell activity?
|
W↑ activity with IL-12, IFN B and IFN A. Secretes IFN gamma → macrophage activation
|
|
|
What cytokines do TH1 cells make?
|
IL-2, IFN gamma. Inhibited by IL-10
|
|
|
What cytokines do TH2 cells make?
|
IL-4, IL-5. Inhibited by IFN gamma.
|
|
|
What is the second signal for B cell activation?
|
IL-2, IL-5, IL-6 from TH2 cell
|
|
|
What cytokines do T-regs produce?
|
IL-10, TGF beta
|
|
|
What are the steps of leukocyte extravasation?
|
↑ by PAF
Rolling (E-selectin, Sialyl LewisX; L-selectins) Tight binding (ICAM-1, LFA-1 -integrin; abnormal in LAD) Diapedesis (PECAM-1) Migration |
|
|
Where are the high endothelial venules in the lymph nodes?
|
In the paracortex?
|
|
|
Where are the macrophages and reticular cells in the lymph node?
|
Medullary sinuses
|
|
|
How is the thymus divided?
|
The cortex has immature T cells. The medulla is pale with mature T cells, reticular cells.
|
|
|
What are some encapsulated bacteria?
|
E. coli, K. pneumo, P. aeruginosa, C. neoformans, Salmonella, S. pneumo, H. flu, N. meningitides
|
|
|
What HLA subtype is associated with hemochromatosis?
|
A3
|
|
|
What HLA subtype is associated with Graves disease?
|
B8
|
|
|
What diseases are HLA DR2 associated with?
|
MS, hay fever, SLE, Goodpasture’s
|
|
|
What HLA subtype is steroid responsive nephritic syndrome associated with?
|
DR7
|
|
|
What diseases are HLA DR4 assocaited with?
|
RA, DM I (DM also with DR3)
|
|
|
What disease is HLA DR5 associated with?
|
Pernicious anemia, hashimotos thyroditis
|
|
|
What cytokines are secreted by macrophages?
|
IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, TNF-a
|
|
|
What does IL-1 do?
|
Acute phase. Pyrogen, inflammatory. Activates endothelium to express adhesion molecules, ↑ chemokine secretion to recruit leukocytes
|
|
|
What does IL-6 do?
|
It is an acute phase pyrogen
|
|
|
What does IL-8 do?
|
Neutrophil chemotaxis (also with c5a, leukotriene B4)
|
|
|
What does TNF-a do?
|
Fever, causes release of acute phase proteins, cachexia
|
|
|
What does IL-3 do?
|
Stimulates bone marrow. Secreted by activated CD4 cells
|
|
|
What does IFN gamma do?
|
Activated macrophages and TH1, suppresses TH2
|
|
|
What does IL-4 do?
|
Increases TH2 differentiation, B cell growth, IgE class switching, also IgG
|
|
|
What does IL-5 do?
|
Increases B cell differentiation, IgA class switching, eosinophils
|
|
|
What does IL-10 do?
|
Inhibits activated T cells and TH1, activates TH2. Secreted by TH2 cells and Tregs. Similar to TGF-b
|
|
|
What does IFN gamma do?
|
Increase MHC I and II
|
|
|
What cell surface proteins do T cells express?
|
TCR, CD3 (associated with TCR), CD28(binds B7), CD2
|
|
|
What cell surface proteins do B cells express?
|
CD19, CD20, CD21 (EBV receptor), CD40, B7
|
|
|
What cell surface proteins do macrophages express?
|
CD14 (LPS receptor), CD40, B7, Fc receptors, C3b receptors
|
|
|
What cell surface proteins do NK cells express?
|
CD16 (binds Fc of IgG), CD56
|
|
|
What do CD 55 and 59 do?
|
Inhibits complement C9 binding/MAC. Expressed by all cells.
|
|
|
What do C1-C4 do?
|
Neutralize virus
|
|
|
What things inhibit complement?
|
Decay accelerating factor (CD55, 59), C1 esterase inhibitor
|
|
|
How do superantigens work?
|
↑ IFN gamma release from TH1 cells → IL-1, IL-6, TNF alpha from macrophages
|
|
|
What kind of vaccine is the rotavirus vaccine?
|
Live attenuated
|
|
|
What kind of vaccine is the varicella vaccine?
|
Live attenuated
|
|
|
What kind of vaccine is the smallpox vaccine?
|
Live attenuated
|
|
|
What kind of vaccine is the hepatitis A vaccine?
|
Killed
|
|
|
What kind of vaccine is the cholera vaccine?
|
Killed
|
|
|
What are 2 recombinant vaccines?
|
HBV, HPV
|
|
|
What is involved in VDJ/VJ recobination?
|
RAG1 and 2 recognize the recombination activating gene. Nucletides are added by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase.
|
|
|
What autoantibodies are present in CREST syndrome?
|
Anticentromere
|
|
|
What autoantibodies are present in diffuse scleroderma?
|
Anti-scl-70 --> antitopoisomerase
|
|
|
What autoantibodies are present in primary biliary cirrhosis?
|
Antimitochondrial
|
|
|
What autoantibodies are present in pemphigus vulgaris?
|
Antidesmoglein
|
|
|
What are antimicrosomal antibodies seen in?
|
Hashimotos
|
|
|
What autoantibodies are present in polymyositis and dermatomyositis?
|
Anti-Jo-1
|
|
|
What autoantibodies are present in diabetes mellitus I.
|
Antiglutamate decarboxylase, anti glutamic acid
|
|
|
What is anti ribonucleoprotein seen in?
|
Mixed connective tissue disease
|
|
|
What autoantibodies are present in autoimmune hepatitis?
|
Anti smooth muscle, anti liver/kidney microsomal
|
|
|
What autoantibodies are present in pauci immune crescentic glomerulonephritis?
|
MP-ANCA
|
|
|
What kind of hypersensitivity is eczema?
|
Mainly type I
|
|
|
What kinds of hypersensitivity is complement involved in?
|
Type II and III
|
|
|
What is serum sickness and the arthus reaction?
|
Serum sickness - antibodies are produced in about 5 days, IC's fix complement, causing fever, urticaria, arthralgia, proteinuria, lymphadenopathy, vasculitis with vessel wall necrosis.
The arthus reaction is after an injection, causing edema, necrosis and complement activation |
|
|
What kind of hypersensitity is polyarteritis nodosum?
|
Type III
|
|
|
What kind of hypersensitivity is hypersensitivity pneumonitis?
|
Type III
|
|
|
What kind of hypersensitivity is Hashimoto's thyroiditis?
|
Type IV
|
|
|
What type of hypersensitivity is Guillain Barre?
|
Type IV
|
|
|
What kind of hypersensitivity is graft vs host disease?
|
Type IV
|
|
|
What infections do T cell deficiencies cause?
|
Viral, candida, PCP pneumonia, bacterial sepsis
|
|
|
What kind of infections do B cell deficiencies cause?
|
Encapsulated bacteria, enteroviral encephalitis, polio, giardiasis
|
|
|
What kind of infections do granulocyte deficiencies cause?
|
Staph, pseudomonal, candida, aspergillus
|
|
|
What causes hyper IgM syndrome?
|
Defective CD40L on T cells, other mutaitons
|
|
|
What is defective in Bruton's agammaglobulinemia?
|
Defective BTK means pro B cells do not become pre B cells. All Igs low
|
|
|
How does common variable immunodeficiency present?
|
Normal B cell number, but fewer plasma cells and Ig. Defective maturation, increased risk of autoimmune disease and lymphoma
|
|
|
How does IL-12 deficiency present?
|
Increased risk of mycobacterial infections due to reduced TH1 response. Labs show reduced IFN gamma
|
|
|
What causes Job syndrome?
|
TH cells do not produce IFN gamma. They have eczema and 2 rows of teeth. Increased eosinophils and IgE
|
|
|
What are the causes of SCID?
|
X linked --> IL-2 receptor defect
Autosomal recessive --> adenosine deaminase deficiency (thus feedback inhibition of ribonucleotide reductase) |
|
|
What is bare lymphocyte syndrome?
|
A type of SCID with defective expression of HLA II on APCs
|
|
|
What immune cell deficiencies does ataxia telangiectasia cause?
|
B cell and T cell
|
|
|
How does WIskott Aldrich present?
|
Thrombocytopenic purpura, infections, eczema, bloody diarrhea. Low B and T cells. They have increased IgE and IgA, but decreased IgM
|
|
|
What does a defect in LFA-1 integrin (CD18) on phagocytes cause?
|
Leukocyte adhesion deficiency. No pus
|
|
|
What is mutated in Chediak higashi?
|
Lysosomal regulator trafficking gene, microtubule defect
|
|
|
How does Chediak Higashi present?
|
Partial albanism, peripheral neuropathy, nystagmus, seizures, giant cytoplasmic granules
|
|
|
What are patients with chronic granulomatous disease susceptible to?
|
Staph aureus, pseudomonas cepacia, serratia marcescens, norcardia, aspergillus, klebsiella, candida, E. coli
|
|
|
What is deficient in hereditary angioedema?
|
C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency → ↑ C4 breakdown → ↓ serum C4. Don't use ACE inhibitors
|
|
|
How does C3 deficiency present?
|
Recurrent pyogenic infections, increased type III sensitivity reactions.
|
|
|
What does decay accelerating factor deficiency look like?
|
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Mutated PIG-A so CD 55 and 59 don't anchor.
There may also be thrombosis, pancytopenia, Budd-Chiari syndrome. Diagnose with Ham's test (pH). Treat with iron, anticoagulation, marrow transplant. |
|
|
How do cyclosporins work?
|
Binds to cyclophilins, this complex blocks T cells by inhibitng calcineurin → ↓ IL-2 and IL-2R production
|
|
|
What are the side effects of cyclosporine (an immunosuppressant)?
|
Nephrotoxic (prevent with mannitol), gout, lymphoma
|
|
|
What is the MOA of tacrolimus?
|
An immunosuppressant, decreases IL-2 by binding to the FK binding protein. Can be used topically for eczema.
Inhibits calcineurin activation (calcineurin dephosphorylates nuclear factor of activated T cells, which binds an IL-2 promotoe in the nucleus) - same as cyclosporine. |
|
|
What are the side effects of tacrolimus?
|
nephrotoxicity, peripheral neuropathy, hypertension, pleural effusion, hyperglycemia
|
|
|
What is sirolimus?
|
An immmunosuppressant. binds to FK-binding protein. Inhibits mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) → ↓ T cell proliferation in response to IL-2
|
|
|
What is rapamycin?
|
An immunosuppressant. binds to FK-binding protein. Inhibits mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) → ↓ T cell proliferation in response to IL-2
|
|
|
What are the side effects of sirolimus and rapamycin?
|
Immunosuppressants. Cause hyperlipidemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia
|
|
|
What is daclizumab?
|
Monoclonal antibody to the IL-2 receptor on activated T cells - immunosuppressant
|
|
|
What is muronomab?
|
Immunosuppressant. Monoclonal antibody to epsilon chain of CD3
|
|
|
What cytokine does thaliomide effect?
|
TNF alpha
|
|
|
How doe mycophenolate mofetil work?
|
Inhibits IMP dehydrogenase so that less guanine is produced.
|
|
|
How does azathioprine work?
|
Precursor of 6MP
|
|
|
What is Aldesleukin?
|
Recombinant IL-2, used in RCC and metastatic melanoma
|
|
|
What is sargramostim?
|
Recombinant GM-CSF
|
|
|
What is IFN-a used in?
|
Hepatitis B, hepatitis C, Kaposi sarcoma, leukemia, malignant melanoma
|
|
|
What is oprelvekin?
|
Recombinant IL-11, used in thrombocytopenia
|
|
|
What is infliximab?
|
TNF alpha inhibitor, used in Crohns, RA, seronegative arthropathies
|
|
|
What is etanercept?
|
TNF alpha inhibitor
|
|
|
What is abciximab?
|
A glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor
|
|
|
What is omalizumab?
|
IgE inhibitor
|
|
|
What are some things that can cause granulomas?
|
In Bartonella hensleae, syphilis, berylliosis, listeria, etc
IFN gamma from TH1 activates the macrophages → TNF alpha from macrophages is important in maintaining granuloma formation |
|
|
What is the amyloid protein formed in multiple myeloma?
|
Bence Jones proteins --> AL protein
|
|
|
What is the amyloid protein formed in chronic disease?
|
Serum amyloid associated protein --> AA
|
|
|
What is the amyloid protein formed in senile cardiac amyloidosis?
|
Transerythrin --> AF
|
|
|
What is the amyloid protein formed in type II diabetes?
|
Amylin --> AE protein
|
|
|
What is the amyloid protein formed in dialysis associated amylodosis?
|
MHC class I --> beta 2 microglobulin
|
|
|
What is a permissive drug interaction?
|
One drug doesnt have an effect on its own, but increases the effect of another.
|
|
|
What are some noncompetitive inhibitors?
|
Phenoxybenzamine, digoxin, allopurinol, PPIs, aspirin
|
|
|
What are some weak acids?
|
Phenobarbital, methotrexate, penicillins, cephalosporins, loops, thiazides. Treat OD with bicarb. All tend to increase uric acid.
|
|
|
What is the equation for volume of distribution?
|
Volume of distribution = amount of drug in body / plasma drug concentration
|
|
|
How do you calculate clearance using half life?
|
Clearance = 0.7 Vd /t1/2
|
|
|
How do you calculate loading dose?
|
Loading dose = target plasma concentration x Vd
|
|
|
How do you calculate maintenance dose?
|
Maintenence dose = target plasma concentration x clearance
|
|
|
What G receptor mechanism is alpha 1?
|
Gq
|
|
|
What do alpha 1 receptors do?
|
Increase vascular and sphincter tone, cause pupillary dilator contraction
|
|
|
What G receptor mechanism is alpha 2?
|
Gi
|
|
|
What do alpha 2 receptors do?
|
Decrease sympathetic outflow, increase platelet aggregation, decrease insulin release.
|
|
|
What G receptor mechanism is beta 1?
|
Gs
|
|
|
What do beta 1 receptors do?
|
Increase heart rate, contractility, renin, lipolysis
|
|
|
What G receptor mechanism is beta 2?
|
G2
|
|
|
What do beta 2 receptors do?
|
Vasodilate, bronchodilate, icnrease lipolysis, increase insulin and glucagon release, decrease uterine tone
|
|
|
What G receptor mechanism is M1?
|
Gq. Acts on the CNS
|
|
|
What G receptor mechanism is M2?
|
Gi. Acts on the heart.
|
|
|
What G receptor mechanism is M3?
|
Gq.
|
|
|
What do M3 muscarinic receptors do?
|
Increase gland secretions, peristalsis, bladder contraction, bronchoconstrict, pupillary sphincter contraction, ciliary muscle contraction
|
|
|
What G receptor mechanism is D1?
|
Gs. Relaxes renal vasculature.
|
|
|
What G receptor mechanism is D2?
|
Gi. Modulates neurotransmitter release
|
|
|
What G receptor mechanism is histamine H1?
|
G1
|
|
|
What G receptor mechanism is histamine H2?
|
Gs
|
|
|
What G receptor mechanism is vasopressin V1?
|
Gq. Increases vascular tone
|
|
|
What G receptor mechanism is vasopressin V2?
|
Gs. Increases water reasbroption.
|
|
|
What does hemicholinium do at the nerve terminal?
|
Inhibits sodium driving choline into the cell
|
|
|
What does vesimacol do at the nerve terminal?
|
Inhibits Ach packaging into vesicles
|
|
|
What does black widow toxin do at the nerve terminal?
|
Stimulates Ach release
|
|
|
What does reserpine do at the nerve terminal?
|
Inhibits packaging of NE into vesicles (an anithypertensive)
|
|
|
What does guanethedine do at the nerve terminal?
|
Inhibits norepinephrine release (an antihypertensive)
|
|
|
What does bretylium do at the nerve terminal?
|
Blocks NE release from nerve terminals (also a class III antiarrhythmic)
|
|
|
What do ephedrine and tyramine do at the nerve terminal?
|
stimulates NE release
|
|
|
What is carbachol?
|
A direct cholinomimetic. Used for glaucoma
|
|
|
What is pilocarpine?
|
A direct cholinomimetic. Used in glaucomic emergency
|
|
|
What is bethanechol?
|
A direct cholinomimetic resistant to AchE. Used post op
|
|
|
What is tropicamide?
|
A muscarinic antagonist
|
|
|
What is benztropine?
|
A muscarinic antagonist used in Parkinsons
|
|
|
What is scopolamine?
|
A muscarinic antagonist
|
|
|
What is oxybutynin?
|
A muscarinic antagonist for urge incontinence
|
|
|
What are glycopyrrolate and tolterodine?
|
A muscarinic antagonist for urge incontinence
|
|
|
What are darifenacin and solifenacin?
|
A muscarinic antagonist for urge incontinence
|
|
|
What is glycopyrrolate?
|
A muscarinic antagonist that can be used in asthma
|
|
|
What adrenergic receptors are affected by epinephrine?
|
↑↑↑↑ alpha 1, ↑↑↑↑ alpha 2, ↑↑↑↑ beta 1, ↑↑ beta 2, no effect on dopamine
|
|
|
What adrenergic receptors are affected by norepinephrine?
|
↑↑↑↑ alpha 1, ↑↑↑↑ alpha 2, ↑↑ beta 1, no effect on beta 2 or dopamine
|
|
|
What adrenergic receptors are affected by dobutamine?
|
↑ alpha 1 and 2, ↑↑↑↑ beta 1, ↑ beta 2, no effect on D1
|
|
|
What adrenergic receptors are affected by phenylephrine or pseudodphedrine?
|
↑↑↑↑ alpha 1, ↑↑ alpha 2,
|
|
|
What is ritodrine?
|
Beta 2 agonist (< beta 1 than asthmadrugs), used to reduce uterine contractions.
|
|
|
What is terbutaline?
|
A beta 2 agonist, can reduce uterine contractions
|
|
|
What are 3 sympathoplegics (alpha 2 agonists)?
|
Clonidine, alpha methyldopa, guanfacine. Can cause rebound hypertension
|
|
|
What is phentolamine?
|
A reversible nonselective alpha blocker
|
|
|
What are 2 beta partial agonists?
|
Pindolol, acebutolol. Could be better for airway and lipids.
|
|
|
What is femoldopam?
|
A D1 agonist that doesnt affect alpha or beta receptors.
|
|
|
What is the antidote to atropine?
|
Physostigmine
|
|
|
What is the antidote to theophyilline?
|
Beta blocker
|
|
|
What is a side effect of methyldopa?
|
Coombs positive hemolytic anemia
|
|
|
What antibiotic can cause hypothyroidism?
|
Sulfonamides
|
|
|
What are some drugs that can cause hyperglycemia?
|
niacin, tacrolimus, protease inhibitors
|
|
|
What antihypertensive can cause gingival hyperplasia?
|
Verapamil
|
|
|
What drugs can cause gout?
|
furosemide, thizides, niacin, cyclosporine, pyrazinamide
|
|
|
What are some drugs that can cause myopathy?
|
fibrates, niacin, colchicines, hydroxychlorquine, IFN alpha, penicillamine, glucocorticoids
|
|
|
What are some drugs that can cause Stevens Johnson
|
ethosuxamide, penicillin, allopurinol
|
|
|
What are some drugs that can cause lupus?
|
hydralazine, isoniazid, procainamide, phenytoin
|
|
|
What anticancer drug can cause a disulfram like reaction?
|
Procarbazine (for Hodgkins)
|
|
|
What does minimum alveolar concentration measure?
|
Potency, potency is higher in a lipid soluble drug (thus a lower MAC)
|
|
|
What does blood/gas partition coefficient measure?
|
Solubility in the blood (= slow onset). Lipid soluble anesthetics are generally high protein bound in the blood and thus have a high coefficient.
|
|
|
What is a side effect of halothane?
|
Fulminant hepatitis
|
|
|
What inhaled anesthetic is used in brain surgery?
|
Isoflurane
|
|
|
What inhaled anesthetic is nephrotoxic?
|
Methoxyflurane
|
|
|
What are some lab abnormalities seen with succinylcholine?
|
Hypercalcemia, hyperkalemia
|
|
|
What are pramipexole and ropinirole?
|
Dopamine agonists
|
|
|
What do entacapone and tolcapone do?
|
Inhibit COMT, preventing L-dopa breakdown
|
|
|
What does memantine doe?
|
NMDA antagonist. Can cause hallucinations
|
|
|
What are the Z scores for 95% and 99% confidence intervals?
|
95 - 1.96, 99 - 2.58. Use SEM
|
|
|
What are some developmental milestones?
|
Birth – 3 mo
• Social smile 7-9 mo • Stranger anxiety • Object permanent, response to name, simple instructions, uses gestures 12-15 mo • Walks • Separation anxiety, 2 yr • Jumping, standing on one foot • 2 word phrases 3 yr copy shapes, feeds self, kicks ball • Parallel play, gender identity • 4 yr • Dresses self with help, runs, hops on 1 foot, toilet training, imaginary friends |
|
|
What are some drugs used in narcolepsy?
|
o Modafinil (not triplicate!), sodium oxybate helps cataplexy. Venlafaxine, fluoxetine
|
|
|
CO vs venous return
|
|
|
What are normal pressures in the heart?
|
• RA <5
• RV 25/5 • PA <25/10 • LA/PCWP <12 • LV 130/10 • Aorta 130/90 |
|
|
What is Fick's law?
|
CO = O2 consumption / arteriovenous O2 difference
|
|
|
What does acidosis do to contractility?
|
Decreases it. So does hypercapnea, verapamil, etc
|
|
|
What is the equation for MAP?
|
MAP = CO x TRP (P=QR)
|
|
|
What would shift the starling curve left? (preload vs stroke volume)
|
Exercise, because it increases contractility so there is a larger SV for any given preload
|
|
|
What are the JVP tracings?
|
o a wave – atrial contraction
o c wave – starts with systole. Blood is propelled back into the atrium before tricuspid valve closure and RV contraction causes the tricuspid valve to bulge into the atrium. Peaks halfway through isovolumetric contraction. o x descent – the base of the heart moves towards the apex during rapid ejection, reducing pressure o v wave – atrial filling. Peak right before the tricuspid closes o y descent – the ventricles suck blood out of the atrium o a wave – atrial contraction |
|
|
When do you see U waves on an EKG?
|
Hypokalemia, bradycardia
|
|
|
What does a positive QRS in limb lead III suggest?
|
Right axis devation, possible inferior MI
|
|
|
What is metyrapone?
|
Blocks cortisol synthesis by inhibiting 11 beta hydroxylase, which should decrease ACTH from the pituitary.
|
|
|
Zidovudine is an analog of what?
|
Thymidine
|
|
|
What part of the forearm does the musculocutaneous provide sensory innervation to?
|
Lateral forearm
|
|
|
What amino acid and cofactor are needed to start heme synthesis?
|
Succinyl coA and glycine
|
|
|
What modulates the activity of ALA synthase?
|
Inhibited by heme and glucose, activated by alcohol, barbiturates and hypoxia
|
|
|
What is deficient in acute intermittent porphyria?
|
HMB synthase (Uroporphyrinogen I synthase). Porphobilinogen buids up and there is a deficiency of HMB
|
|
|
What can you use a mucicarmine stain for?
|
Cryptococcus neoformans's capsule (appears as red yeasts)
|
|
|
What 2 things are necessary for isoniozide to be effective?
|
Must be processed by mycobacterial catalase-perodidase, must bind to a specific sequence in its target enzyme
|
|
|
What is synaptophysin?
|
A transmembrane protein in the presynaptic vesicles of neurons, neuroectodermal and neuroendocrine cells
|
|
|
What are some tumors that stain GFAP+?
|
Glioblastoma, oligodendrogliomas, ependymomas, and peripheral neural sheath tumors
|
|
|
What do recurrent lobar hemorrhages in an elderly patient suggest?
|
Central amyloid angiopathy
|
|
|
What kind of axis deviation would a left posterior fascicular block look like?
|
Right
|
|
|
What kind of axis deviation would a left anterior fascicular block look like?
|
Left
|
|
|
What is the pathophys behind congenital long QT syndrome?
|
Usually cardiac Na or K channel defects. Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome is associated with sensorineural deafness
|
|
|
What medications can prolong the QT interval?
|
Macrolides, chloroquin, mefloquin, haloperidol, risperidone, methadone, protease inhibitors, class Ia and class III antiarrhythmics. Antimuscarinics!!!!
|
|
|
How do you treat torsades?
|
Magnesium
|
|
|
What is seen on EKG of Wollf Parkinson White?
|
Widened QRS, delta waves (early depolarization)
|
|
|
How do you treat Wolff Parkinson White?
|
Do not use adenosine, use procainamide or amiodarone
|
|
|
What causes Wolff Parkinson White?
|
Accessory conduction pathway, usually the bundle of Kent.
|
|
|
What causes wide splitting of S2?
|
Pulmonic stenosis, RBBB
|
|
|
What causes paradoxical splitting of S2?
|
Aortic stenosis, LBBB
|
|
|
What murmurs are louder on inspiration?
|
Right sided
|
|
|
What murmurs are louder on expiration?
|
Left sided
|
|
|
What does the hand grip maneuver do?
|
↑ afterload
Intensifies: mitral regurg, VSD, aortic regurg, mitral stenosis (↑ HR) ↓ aortic stenosis, HOCM |
|
|
What does the valsalva maneuver do?
|
Decreases preload due to increased chest pressure.
Accentuates HOCM and mitral valve prolapse (click is early) |
|
|
What does the squatting maneuver do?
|
Increases preload and afterload. Decreases mitral valvprolapse and HOCM
|
|
|
What is related to pulsus parvus et tardus?
|
Aortic stenosis
|
|
|
What is the murmur of ASD?
|
Mid systolic pulmonary ejection murmur due to increased flow across the valve
|
|
|
What maternal condition is transposition of the great vessels related to?
|
Diabetes
|
|
|
How do you treat Prinzmetal angina?
|
DHP calcium channel blocker (e.g. nifedipine)
|
|
|
How does a heart 2-4 days post MI look?
|
Gross: mottling/hyperemia
Microscopic : inflammation, neutrophils, loss of nuclei |
|
|
How does a heart 12-24 hours post MI look?
|
Gross: Pale, mottled
Microscopic: Neutrophils, contraction bands |
|
|
How does a heart 5-10 days post MI look?
|
Gross: Hyperemic, central yellow softening
Microscopic: Granulation tissue |
|
|
What lead changes suggest an anterior wall MI (LAD)?
|
V1-V4
|
|
|
What lead changes suggest an anteroseptal MI? (LAD)
|
V1, V2
|
|
|
What lead changes suggest an anterolateral MI? (LCX)
|
V4-V6
|
|
|
What lead changes suggest an lateral wall MI? (LCX)
|
I, aVL, V5, V6
|
|
|
What lead changes suggest an inferior wall MI?
|
II, III, aVF
|
|
|
What does ANP do?
|
Vascular relaxation, constricts efferent arterioles, dilates adderent arterioles to cause diuresis. Inhibits sodium and water reabsorption in the collecting duct.
|
|
|
What mediates smooth muscle proliferation in atherosclerosis?
|
PDGF, TGF beta
|
|
|
What is Monckeberg arteriolosclerosis?
|
Benign medial calcification of the radial/ulnar, etc artery, causing pipestem arteries. Intima unaffected
|
|
|
What can ingestion of B-aminopropionitrile (in sweet peas) cause?
|
Inhibits lysyl oxidase, which crosslinks elastin and colagen to maintain the elastic laminia, cause aortic aneurysms
|
|
|
What causes genetic dilated cardiomyopathy?
|
Defects in cardiac cytoskeleton proteins (e.g. dystrophin) and mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation enzymes
|
|
|
How do you treat HOCM?
|
Non DHP CCBs (verapamil), beta blockers. Increase afterload, increase preload decrease contractility
|
|
|
How does giant cell arteritis look like on histology?
|
Granulomas of media, fragmented internal elastic lamina. Associated with polymyalgia rheymatica
|
|
|
How does polyarteritis nodosa present?
|
Type III hypersensitivity.
Transmural fibrinoid necrosis with different aged lesions Spares the pulmonary vessels, can cause melena, cutaneous deposits, neurologic problems, abdominal pain. Treat with steroids or cyclophosphamide |
|
|
What is the triad of Henoch Schonlein purpura?
|
Purpura, arthralgia, GI (e.g. melena)
|
|
|
How do you treat Wegners?
|
Steroids and cyclophosphamide
|
|
|
How does Churg Strauss present?
|
Asthma, palpable purpura, neuropathy, GI/heart/kidney problems, granulomas, eosinophils
p-ANCA |
|
What is this?
|
Aschoff body in rheumatic fever
|
|
|
What are the immune complexes made of in Henoch Schonlein purpura?
|
IgA (sometimes C3), increased serum IgA.
Is self limiting |
|
|
What is a pyogenic granuloma?
|
Capillary hemangioma that looks like hypertrophic granulation tissue. Associated with pregnancy and trauma
|
|
|
What is a glomus tumor?
|
Made of temperature receptors that shunt blood
|
|
|
What is angiosarcoma related to?
|
VInyl chloride, arsenic, ThO2 (radiocontrast)
|
|
|
What is the rash in rheumatic fever called?
|
Erythema marginatum (annulare)
|
|
|
What is Kussmaul's sign seen in?
|
(Increased JVD with inspiration) Pericarditis
|
|
|
What is pulsus paradoxus seen in?
|
Cardiac tamponade, also in diseases with exaggerated inspiration (e.g. asthma)
|
|
|
How do you treat raynauds?
|
DHP CCB, aspirin
|
|
|
What is dipyridamole?
|
Inhibits thrombus formation when given chronically and causes vasodilation when given at high doses over a short time. Inhibits thromboxane, increases adenosine, etc
|
|
|
What is bepridil?
|
An antianginal CCB
|
|
|
What is the MOA and side effects of hyrdralazine?
|
Increases cGMP.
Causes angina , lupus, edema Contraindicated in angina and CAD |
|
|
What are some side effects of DHP CCBs?
|
Gingival hyperplasia, flushing, dizziness
|
|
|
What are some side effects of non DHP CCBs?
|
AV block (careful with beta blockers), constipation, etc
|
|
|
What is the most cardiac specific CCB?
|
Verapamil > diltiazem
|
|
|
What is diazoxide?
|
K channel opener that hyperpolarizes smooth muscle, can be used in malignant hypertension.
Can cause hyper glycemia (reduces insulin) |
|
|
What is minoxidil?
|
K channel opener that can be used in hypertension. Can cause hypertrichosis and edema.
|
|
|
What is nesiritide?
|
Recombinant ANP
|
|
|
What is the MOA of niacin?
|
Inhibits lipolysis, reduces hepatic VLDL secretion
|
|
|
What are the side effects of niacin?
|
Flushing, pruritis, diarrhea, hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia
|
|
|
What lipid drug can increase triglycerides?
|
Resins (e.g. colestipol)
|
|
|
What is ezetimibe?
|
blocks cholesterol absorption. May ↑ LFTs, but no problems absorbing vitamins
|
|
|
How does bezafibrate work?
|
Fibrates upregulate LPL
Side effects: myositis, hepatotoxicity, cholesterol gallstones |
|
|
What are 3 Ia antiarrhythmics?
|
Quinidine, procainamide, disopyramide (double quarter pounder)
|
|
|
What do Ia antiarrhythmics do?
|
Increase AP duration, effective refractory period, QT interval. Phase 3 is more drawn out
Acts on the activated channel. |
|
|
What is procainamide?
|
A class Ia antiarrhythimic that can cause drug induced lupus, is anti muscarinic, and can be used in Wolff Parkinson White. Like other Ia's, there is increased risk of arrhythmia with hyperkalemia.
|
|
|
What is quinidine?
|
A class Ia antiarrhythmic that is antimuscarinic and anti alpha adrenergic. It can cause cinchonism (headache, tinnitus, flushing, blurred vision, rash, N/V)
|
|
|
What are 4 class Ib antiarrhythmics?
|
Mexiletine, toxainide, phenytoin, lidocaine (lettuce, mayo, tomato, pickles)
|
|
|
What is mexiletine?
|
class Ib antiarrhythmic
|
|
|
What is the MOA of class Ib antiarrhythmics?
|
Acts on the inactivated form of the Na channel and blocks the plateau phase by keeping the channels refractory. This is why these are preferred post-MI, they are also used for digoxin toxicity. May shorten AP duration
|
|
|
What are the class Ic antiarrhythmics?
|
Flecainide, propafenone (fries please). Can block any channel, will not change AP duration
|
|
|
What is Flecainide?
|
class Ic antiarrhythmic
|
|
|
What is propafenone?
|
class Ic antiarrhythmic
|
|
|
What are 5 class III antiarrhythmics?
|
Ibutilide, sotalol, bretylium, amiodarone, dofetilide.
|
|
|
What is ibutilide?
|
class III antiarrhythmic
|
|
|
What is bretylium?
|
class III antiarrhythmic
|
|
|
What is dofetilide?
|
class III antiarrhythmic
|
|
|
What are the side effects of amiodarone?
|
Pulmonary fibrosis, hepatotoxicity, hypo/hyperthyroid, corneal deposits, blue/gray skin – photodermatitis, neuro problems, constipation
|
|
|
What are some EKG changes with digoxin toxicity?
|
↑ PR, ↓QT, ST scooping, T wave inversion
|
|
|
What is adenosine blocked by?
|
Theophylline
|
|
|
What artery runs with the axillary nerve?
|
Posterior circumflex
|
|
|
What artery runs with the radial nerve?
|
Deep brachial
|
|
|
What artery runs with the median nerve?
|
Brachial
|
|
|
What makes up the rotator cuff?
|
Supraspinatus (abducts), infraspinatus (laterally rotates), teres minor (adducts, laterally rotates), subscapularis (medially roates, adducts)
|
|
|
What can happen in an anterior shoulder dislocation?
|
Axillary nerve, pos circumflex artery, supraspinatus tendon injury.
Bankart lesion - lower labrum tear, Hill-Sach's lesion - humeral head defect |
|
|
What artery is most at risk with a femoral neck fracture?
|
Medial circumflex
|
|
|
What injury can damage the axillary nerve?
|
Surgical nerve of the humerus, anterior dislocation
|
|
|
What injury can damage the radial nerve?
|
Midshaft humeral fracture, axillary comrpession, radial subluxation
|
|
|
What can be injured in a supracondylar humeral fracture?
|
Median nerve
|
|
|
What do the gluteus minimus and medius do?
|
Abduct and medially rotate the thigh
|
|
|
What movement does the tibial branch of the sciatic nerve do?
|
Extend the hip, flex the knee
|
|
|
What deficit will a femoral nerve injury cause?
|
Loss of knee jerk, thigh flexion, leg extension. Loss of sensory
|
|
|
What is the genetic deficiency in osteopetrosis?
|
Carbonic anhydrase II --> abnormal osteoclasts. All labs are NORMAL. Causes pancytopenia
|
|
|
locations
|
|
|
Schaumann body in sarcoid
|
|
|
Asteroid body in sarcoid
|
|
|
Where do giant cell tumors affect?
|
Epiphyseal ends of long bones, soap
|
|
|
What is febuxostat?
|
Xanthine oxidase inhibitor
|
|
|
What drugs do you use for acute gout?
|
NSAIDs, colchicine, steroids
|
|
|
What is probenecid?
|
Inhibitor of uric acid reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubule
|
|
|
What other problems can you have with ankylosing spondylitis?
|
Uveitis, aortic regurgitation, cardiac conduction abnormalities
|
|
|
What microbes are associated with Reiter syndriome?
|
Chlamydia trachomatis, salmonella, shigella flexeri, campylobacter jejuni, yersenia
|
|
|
What complement changes can be seen in SLE?
|
Decreased C3 and C4
|
|
|
What does biopsy show in dermatomyositis?
|
Perifascicular atrophy. Labs show increased CK and aldolase. Postive ANA and anti-Jo-1
|
|
|
What cytokine is important in scleroderma?
|
TGF beta
|
|
|
What does scleroderma pulmonary hypertension look like?
|
Intimal thickening of arterioles
|
|
|
What is parakeratosis?
|
Hyperkeratosis (corneum) + retained nuclei
|
|
|
What deposits are at the tips of the dermal papillae in dermatitis herpetiformis?
|
IgA
|
|
|
What disease is lichen planus releated to?
|
HCV
|
|
|
What is erythema nodosum related to?
|
coccidiodes, histo, TB, leprosy, strep, sarcoid
|
|
|
What do prostaglandins do?
|
Vasodilate, bronchodilate, increase uterine tone
|
|
|
What do prostacyclins do?
|
Vasodilate, bronchodilate, DECREASE uterine tone, inhibit platelet aggregation
|
|
|
What do thromboxanes do?
|
Vasoconstrict, bronchoconstrict, promotes platelet aggregation
|
|
|
What do leukotrienes C4, D4, E4 do?
|
Vasoconstrict, bronchospasm, increase vascular permeablity
|
|
|
What do lipoxins do?
|
Vasodilate, inhibit neutrophil chemotaxis, stimulate monocyte adhesion
|
|
|
What does colchicine do?
|
o Stabilizes tubulin, can reduce LTB4 production
o Causes GI side effects, do not use in renal dysfunction |
|
|
What is etanercept?
|
Recombinant TNF alpha receptor
|
|
|
What is adalimumab?
|
Anti TNF antibody
|
|
|
What uses JAK/STAT tyrosine kinases?
|
Prolactin, GH, cytokines (IL-2,6,8)
|
|
|
In which congenital adrenal hyperplasia can no sex steroids be made?
|
17 alpha hydroxylase deficiency
|
|
|
In which congenital adrenal hyperplasia are there ambiguous genitalia in both sexes?
|
3 beta hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
|
|
|
How does cortisol affect alpha 1 adrenergics?
|
Upregulates alpha 1 receptors on arterioles
|
|
|
How does Conn syndrome present on labs?
|
Low K, alkalosis, low renin, normal sodium
|
|
|
What gene are neuroblastomas related to?
|
N-myc, use bombesin for a tumor marker and stain for neurofilaments. Homer-wright pseudorosettes may be seen
|
|
|
What hormones share an alpha subunit?
|
TSH, LH, FSH, hCG
|
|
|
What else does TRH stimulate?
|
prolactin
|
|
|
What does somatostatin inhibit
|
GH, TSH
|
|
|
What does TNF alpha do to glucose uptake?
|
Decreases it, causing insulin resistance. Catecholamines, glucagons, and steroids can do the same thing
|
|
|
What can decrease magnesium?
|
diarrhea, aminoglycosides, diuretics, alcohol abuse
|
|
|
What does the superior laryngeal nerve innervate
|
Cricothyroid, sensory to the vocal cords
|
|
|
What artery runs by the recurrent laryngeal nerve at the thyroid?
|
Inferior thyroid artery
|
|
|
What does thyroid hormone do to beta 1 receptors?
|
Increases beta 1 receptors in the heart
|
|
|
Why should you not use aspirin or ibuprofen in Graves disease?
|
Displaces TH from TBG
|
|
|
How does papillary thyroid cancer look?
|
Orphan annie, psammoma. Associated with RET, BRAF, NTRK1
|
|
|
What does folliciluar thyroid cancer look like?
|
Hurthle cells. Associated with RAS, PPAR gamma/PAX-8
|
|
|
What is chlorpropramide?
|
First generation sulfonylurea (closes K --> depolarization, diazoxide dose the opposite)
|
|
|
What is glimepiride?
|
2nd generation sulfonyl urea
|
|
|
What should you monitor if using thiazolidinediones?
|
LFTs
(Side note: remember they increase adiponectin) |
|
|
What is pramlintide?
|
Amylin analong - decreases glucagon, delays gastric emptying (can be used in DM )
|
|
|
What are exenatide and liraglutide?
|
GLP-1 like analogs - increase insulin, decrease glucagon, delays gastric emptying.
Can cause pancreatitis |
|
|
What are sitagliptin and saxagliptin?
|
Inhibit dipeptidyl peptise IV, normally inactivates incretins. No hypoglycemia risk
|
|
|
Is PTU or methimazole more hepatotoxic?
|
PTU
|
|
|
What is fludrocortisone?
|
Synthetic aldosterone
|
|
|
Where is Meissner's plexus?
|
Submucosa
|
|
|
What plexus is in the muscularis externa?
|
Auerbachs myenteric plexus (motility)
|
|
|
What makes up the celiac trunk?
|
*Common hepatic – courses right, supplies the duodenum
-Hepatic proper -Right gastric (supplies some of the lesser curve) -Anterior superior pancreaticoduodenal -Right gastroomental (gastroepiploic) Splenic - runs over the pancreas, behind the stomach -Short gastrics (poor collaterals) -Left gastroomental (gastroepiploic) Left gastric – supplies the lesser curve -Esophageal branch |
|
|
What does gastrin do?
|
o ↑ gastric H secretion
o ↑ gastric mucosal growth o ↑ gastric motility stimulates ECL cells to release histamine |
|
|
What regulates gastrin?
|
o Increased release with distension, alkalinization, amino acids/peptides (especially phenylalanine, tryptophan), vagal stimulation. Calcium can also stimulate.
o Inhibited by low stomach pH |
|
|
What does CCK do?
|
o Increases pancreatic enzyme secretion by acinar cells, relaxes the sphincter of Oddi
o Increases gallbladder contraction o Decreases gastric emptying |
|
|
What does secretin do?
|
o ↑ release of high bicarb, low Cl secretion of the pancreatic ductal cells. High flow secretions are high in bicarb, low flow are high in Cl.
• Pancreatic enzymes don’t function as well in an acidic environment o ↓ gastric acid secretion o ↑ bile secretion Regulation: ↑ by duodenal pH <5, presence of fatty acids |
|
|
What does GIP do?
|
By K cells in the gut. Exocrine - decreases acid secretion, endocrine - increases insulin release.
o Stimulated by fatty acids, amino acids, oral glucose (which is why an oral glucose load is used more rapidly than IV) |
|
|
What does VIP do?
|
In parasympathetic ganglia, increases water secretion.
Regulated by distension and vagal stimulation (increased) and adrenergics (decreased) |
|
|
How do you treat primary biliary cirrhosis?
|
Ursidiol decreases cholesterol produced by the liver
|
|
|
What is dicyclomine?
|
Anticholinergic
|
|
|
What do you treat tropical sprue with?
|
Sulfonamide or tetracycline
|
|
|
How does Whipples disease looks like on histology
|
PAS positive foamy macrophages in the lamina propria and mesenteric nodes. GIve TMP SMX
|
|
|
What is a side effect of H2 blockers?
|
Antiandrogenic, thrombocytopenia, increase serum creaotine
|
|
|
What is metoclopramide?
|
D2 agonist, increases serotonin receptors. Increases motility - used for post op gastreoparesis. Can cause seizures, diarrhea, N/V. bad with digoxin and anti diabetics
|
|
|
What is sibutramine
|
NT reuptake inhibitor for weightloss. Cannot be used in heart disease
|
|
|
What is a specific marker of mast cell activation?
|
Tryptase
|
|
|
What CDs do dendritic cells express?
|
CD80, CD86, CD40
|
|
|
What is a marker for langerhans cell histiocytosis?
|
S100, CD1a
|
|
|
What do abciximab, eptifibatide, and tirofiban do?
|
Directly inhibit GpIIbIIa
|
|
|
What do ticlodipine and clopidogrel do?
|
Inhibit ADP reception
|
|
|
What is Bernard Soulier?
|
GpIb deficiency (platelets cant bind vWF)
|
|
|
WHat is Glanzmanns thrombastenia?
|
GpIIbIIIa deficiency
|
|
|
What is basophilic stipplnig seen in?
|
thalassemia, anemia of chronic disease, iron deficiency, lead poisoning
|
|
|
What are target cells in?
|
THAL - thalassemia, HbC diease, asplenia, liver disease
|
|
|
What are the anemia labs?
|
• Iron deficiency
o ↓ iron, ↑ transferrin/TIBC, ↓ ferritin, ↓↓ transferring saturation (Fe/TIBC) • Chronic disease o ↓ iron, ↓ transferrin, ↑ ferritin, ↑/normal transferrin saturation • Hemochromatosis o ↑ iron, ↓ transferrin (saturated), ↑ ferritin, ↑↑ transferrin saturation • Pregnancy, OCPs o Normal iron, ↑ transferrin, normal ferritin, ↓ transferrin saturation • Lead poisoning o ↑ iron, ↓ transferrin, normal ferritin, ↑ transferrin saturation |
|
|
What translocation has a better prognosis in ALL?
|
t(12;21)
Remember this is PAS + |
|
|
What is associated with CLL?
|
Smudge ells, warm hemolytic anemia
|
|
|
What does hairy cell leukemia stain positive for?
|
TRAP
|
|
|
How does AML present?
|
Anemia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, sometimes with DIC.
PAS negative M7 (megakaryocytic) is more common in Down syndrome - the only CD13, CD 33 negative (41,61+) |
|
|
What is CML associated with?
|
Philadelphia chromosome t(9;22) bcr-abl
Associated with increase neutrophils, erythrocytes, and megakaryocytes. Associated with defective PDGF receptor |
|
|
What are Reed Sternberg cells positive for?
|
CD 30, 15
|
|
|
What is Burkitt lymphoma associated with
|
t(8;14) c-myc, high ki-67
|
|
|
How does follicular lymphoma present?
|
Painless lymph node enlargements that come and go. t (14;18) causes decreased apoptosis
Expresses CD19, 20, 79a, 21, 10 |
|
|
What directly inhibits thrombin?
|
Lepirudin, bivalrudin, desorudin; argatroban
|
|
|
What directly inhibits factor Xa and won't affect TT?
|
Rivaroxaban, idraparinux, apixaban
|
|
|
What antiplatelet drug causes neutropenia?
|
Ticlodipine
|
|
|
What is cilostazole?
|
Dilates arteries, inhibits platelet aggregation
|
|
|
What inhibits IIb/IIIa?
|
Abciximab, etifibatide, tirofibide
|
|
|
What mediates cachexia?
|
TNF alpha (cachectin), IFN gamma (affects basal metabolic rate), IL-6
|
|
|
What cancers overexpress N-myc?
|
Neuroblastoma (Homer-Wright pseudorosettes), SCLC
|
|
|
What cancers are associated with RAS mutation?
|
o K-RAS – colon, lung, pancreas
o H-RAS – bladder, kidney (hematuria) o N-RAS – melanoma, hematologic |
|
|
What are the paraneoplastic syndromes?
|
• ACTH
o SCLC • ADH o SCLC, intracranial • PTH-rP, TGF-beta, TNF, IL-1 - hypercalcemia o Squamous cell of the lung, other squamous, RCC, breast carcinoma, multiple myeloma • EPO o RCC, hemangioblastoma, HCC, pheo • Lambert Eaton o Antibodies against presynaptic Ca o SCLC • Hyperuricemia o Leukemia, lymphoma |
|
|
What is cytarabine?
|
Pyrimidine analog that inhibits DNA polymerase, used for acute leukemias. Can cause megaloblastic anemia
|
|
|
What is the MOA of dactinomycin?
|
Intercalates in DNA, decreases unwinding
|
|
|
What are the anthracyclines (-rubacin)
|
Make free radicals that intercalate into DNA and cause breaks. Prevent cardiotoxicity with dexrazoxane, an iron chelator.
|
|
|
What drugs are used in testicular cancer?
|
Etoposide, bleomycin, cisplatin
|
|
|
What is teniposide
|
Inhibits topoisomerase II (like etoposide) so it cant seal its double strand breaks
|
|
|
What do ironotecan and topotecan do?
|
Inhibit topoisomerase II
|
|
|
What do cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide do?
|
Covalently links DNA at guanine. bioactivated by P450.
Prevent acrolein hemorrhagic cystitis with mesna |
|
|
How does busulfan work?
|
Alkalates DNA, used in CML and marrow ablation. Cause pulmonary fibrosis and hyperpigmentation
|
|
|
What are side effects of vincristine
|
Neurotoxic
|
|
|
What does cisplatin do?
|
Forms ROS that cross link DNA. Prevent nephrotoxicity with amifostine
|
|
|
What does hydroxyurea do?
|
Inhibit ribonucelotide reductase. used in melanoma and CML
|
|
|
What are the hypothalamic nuclei?
|
o Lateral
• Hunger, inhibited by leptin • Sympathetics o Ventromedial • Satiety, stimulated by leptin o Preoptic/anterior • Parasympathetic • Cooling • Releases GnRH o Posterior • Sympathetic • Heating o Dorsomedial • Stimulation → obesity, savage behavior, stimulates GI system o Arcuate • Releases hormones affecting the adenohypophysis • Regulates hunger, satiety o Paraventricular • Makes oxytocin • Sympathetic • Regulates food intake o Supraoptic • Makes ADH, with input from OVLT |
|
|
What happens in PPRF/FEF lesions?
|
PPFR
• Eyes look away from the lesion FEF • Eyes look towards the lesion superior colliculi - paralysis of upward gaze |
|
|
How does Wallenberg (lateral medullary syndrome) - PICA present?
|
• Lateral medulla
o Vestibular nuclei → vertigo o Lateral STT → contralateral pain/temp loss o Spinal trigeminal nucleus → ipsilateral pain/temp loss o Nucleus ambiguus – ispilateral dysphagia, hoarseness • PICA specific o Sympathetics – ipsilateral horners o Solitary tract – ipsilateral taste o Nucleus of CII – ipsilateral deviation • ICP – ipsilateral ataxia |
|
|
How does Weber syndrome present? - PCA
|
• Oculomotor – ipsilateral ptosis, mydriasis, down and out
• Cerebral peduncle o Corticospinal tract – contralateral spastic paralysis o Corticobulbar tract – (CN XII, VII) contralateral lower facial paralysis, tongue |
|
|
What brain tumor has Homer Wright pseudo rosettes?
|
Medulloblastoma
|
|
|
What happens in the descending limb?
|
Concentrating - impermeable to sodium
|
|
|
What do you see on EM in post strep GN?
|
Subepithelial IC humps (Ig, C3)
|
|
|
What are 3 kinds of RPCGN?
|
Goodpasture, Henoch Schonlein, Wegeners (pauci immune - no Ig deposits)
|
|
|
How does Bergers IgA glomerulopathy present?
|
Related to Henoch Schonlein purpura. Presents after URI, acute gastrointeritis. Hematuria returns every few months. Mesangial IC deposits and prolfieration
|
|
|
What does membraneous GN show on imaging?
|
EM - spike and dome, subepithelial deposits
|
|
|
What is diffuse proliferative GN assocaited with?
|
SLE - wire looping. Subendothelial IgG deposits.
Nephritic/nephrotic |
|
|
What does type I membranoproliferative GN present like?
|
Tram tracking, associated with HBV, HDV
subendothelial ICs |
|
|
What does type II membranoproliferative GN present like?
|
C3 nephritic facotor (IgG antibody)
dense, ribon like deposits |
|
|
What is Aliskiren?
|
Renin inhibitor
|
|
|
How do you calculate physiologic dead space?
|
Vd=VT (PaCO2 – PeCO2)/PaCO2
|
|
|
What's the alveolar gas equation?
|
PAO2 = 150 – (PaCO2/0.8) . Normal A - a is 10-15
Increased: o V/Q mismatch, diffusion limitation, right to left shunt, normal aging, ↑ FiO2 |

