![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
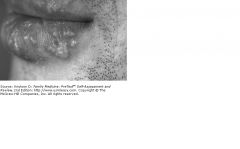
You are seeing a 21-year-old man with a skin infection on his lip. It is the first time he has ever had this type of infection. It began with a burning at the site of the infection, then an eruption of vesicles. The rash is shown below: Which of the following is true of this infection?
This is a primary infection, and future infections are likely to be more severe. B. Based on the picture shown, distinguishing features indicate it to be a herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) infection. C. Fever, malaise, and adenopathy are likely to be present. D. Triggers for this rash include fever, infection, or exposure to ultraviolet light. E. If the lesions are pustular, antibiotics are indicated. |
Triggers for this rash include fever, infection, or exposure to ultraviolet light.
|
The description and picture are consistent with a recurrence of HSV infection. Symptomatic primary infections are characterized by gingivostomatitis with or without cutaneous or perioral lesions. Fever, malaise, and tender adenopathy are common with primary infections. Recurrences are usually less severe. The episode shown above is a recurrence because it appears as grouped vesicles as opposed to gingivostomatitis. There is no way to differentiate HSV-1 from HSV-2 simply by looking at the lesions. Lesions are sometimes mistaken for bacterial processes because they can be pustular. Triggers for recurrences are ultraviolet light exposure or illness.
|
|
|
A 36-year-old woman is being evaluated in the sleep laboratory. She is noted to have a decreased latency of REM. Which of the following disorders is this woman most likely to be suffering from?
|
Major Depression
|
A decreased latency of REM sleep is seen in major depression. Depression is the psychiatric disorder that has been most associated with disruptions in biological rhythms. Besides the decreased latency of REM sleep, early morning awakening and other neuroendocrine perturbations are often found with major depression.
|
|
|
A 52-year-old woman is brought to the emergency room after her husband finds her unresponsive at home. The patient left behind a suicide note, and two empty bottles of pills (sertraline and lorazepam) plus an empty bottle of vodka were found next to the patient. In the emergency room the patient's vital signs are: blood pressure 90/60 mm Hg, pulse 60 beats/min, respirations 6 breaths/min. Which of the following medications is most likely to be helpful in the emergency room setting in this situation?
|
Flumazenil
|
This patient's respiration is very depressed, and it is likely that the benzodiazepines are playing a role. Flumazenil can be used in the emergency room setting to counteract the effects of benzodiazepine overdose. LAAM is an opioid agonist that suppresses opioid withdrawal. It is no longer used, because patients developed prolonged QT intervals associated with potentially fatal arrhythmias. Disulfiram is used as an aversive treatment to maintain sobriety in those with alcohol dependence, and acamprosate is also used to improve treatment outcomes in those with alcoholism, though the exact treatment mechanism is not known
|
|
|
A patient at 17 weeks gestation is diagnosed as having an intrauterine fetal demise. She returns to your office 5 weeks later and her vital signs are: blood pressure 110/72 mm Hg, pulse 93 beats per minute, temperature 36.38°C, respiratory rate 16 breaths per minute. She has not had a miscarriage, although she has had some occasional spotting. Her cervix is closed on examination. This patient is at increased risk for which of the following?
Septic Abortion, Recurrent Abortion, Consumptive Coagulopathy, Ectopic Pregnancy |
Consumptive Coagulopathy
|
A patient at 17 weeks gestation is diagnosed as having an intrauterine fetal demise. She returns to your office 5 weeks later and her vital signs are: blood pressure 110/72 mm Hg, pulse 93 beats per minute, temperature 36.38°C, respiratory rate 16 breaths per minute. She has not had a miscarriage, although she has had some occasional spotting. Her cervix is closed on examination. This patient is at increased risk for which of the following?
|
|
|
A 72-year-old woman presents with the acute onset of double vision. The second image disappears if she covers either eye. Which of the following ocular motor nerves is most likely to be impaired in this patient?
|
Abducens
|
Remember, 6th nerve issues are 3 times more common than 3rd nerve and 6 times more common than 4th nerve
|
|
|
A patient at 17 weeks gestation is diagnosed as having an intrauterine fetal demise. She returns to your office 5 weeks later and her vital signs are: blood pressure 110/72 mm Hg, pulse 93 beats per minute, temperature 36.38°C, respiratory rate 16 breaths per minute. She has not had a miscarriage, although she has had some occasional spotting. Her cervix is closed on examination. This patient is at increased risk for which of the following?
Septic Abortion, Recurrent Abortion, Consumptive Coagulopathy, Ectopic Pregnancy |
Consumptive Coagulopathy
|
A patient at 17 weeks gestation is diagnosed as having an intrauterine fetal demise. She returns to your office 5 weeks later and her vital signs are: blood pressure 110/72 mm Hg, pulse 93 beats per minute, temperature 36.38°C, respiratory rate 16 breaths per minute. She has not had a miscarriage, although she has had some occasional spotting. Her cervix is closed on examination. This patient is at increased risk for which of the following?
|
|
|
A 72-year-old woman presents with the acute onset of double vision. The second image disappears if she covers either eye. Which of the following ocular motor nerves is most likely to be impaired in this patient?
|
Abducens
|
Remember, 6th nerve issues are 3 times more common than 3rd nerve and 6 times more common than 4th nerve
|
|
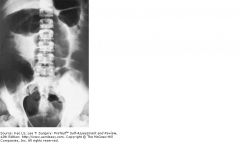
A 50-year-old man presents to the emergency room with a 6-hour history of excruciating abdominal pain and distention. The abdominal film shown here is obtained. Which of the following is the most appropriate next diagnostic maneuver?
|
Proctosigmoidoscopy
|
The film shows a markedly distended colon. The differential diagnosis includes tumor, foreign body, and colitis, but far more likely is either cecal or sigmoid volvulus. Sigmoid volvulus may be ruled out quickly by proctosigmoidoscopy, which is preferable to barium enema, since sigmoid volvulus may be treated successfully by rectal tube decompression via the sigmoidoscope. If sigmoidoscopy is negative, the working diagnosis, based on this classic film, must be cecal volvulus; barium enema would clinch the diagnosis, but the colon might rupture in the intervening 1 to 2 hours. Emergency celiotomy should be done.
|

