![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
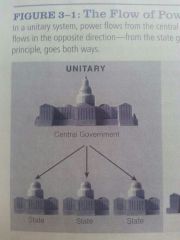
Unitary system
|
A centralized governmental system in which ultimate governmental authority rest in the hands of the National or central government.
|
|
|
|
Confederal system
|
A system consisting of a league of Independent States, in which the central government created by the league has only limited powers over the states.
|

|
|
|
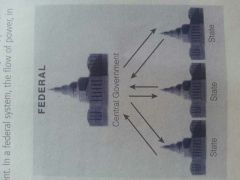
Federal system
|
A federal system lies between the unitary and confederal forms of government. In a federal system of thority is divided usually by a written constitution between a central government and regional or subdivisional governments. ( often called Constituent governments).
|
|
|
|
Note: Why Federalism?
|
The result of federalism was a compromise. The supporters of the new constitution realized that without a federal G arrangement, there would be no ratification of the new constitution. The appeal of federalism was that it retained state traditions and local power while establishing a strong national government capable of handling common problems.
|
|
|
|
Enumerated powers
|
Powers specifically granted to the national government by the Constitution. The first 17 clauses of article 1, section 8, specify most of the enumerated or expressed, powers of the national government.
|
|
|
|
Elastic clause, or Necessary and Proper Clause
|
The clause in article 1, section 8, that grants Congress the power to do whatever is necessary to execute it's specifically delegated powers.
|
|
|
|
Concurrent powers
|
Powers held jointly by the National and State Governments.
|
|
|
|
Supremacy Clause
|
The constitutional provision that makes the Constitution and federal laws superior to all conflicting state and local laws.
|
|
|
|
Commerce Clause
|
The section of the Constitution in which Congress is given the power to regulate trade among the states and with foreign countries.
|
|
|
|
Dual federalism
|
A model of federalism that looks on national and state governments as co-equal sovereign powers. Neither the state government nor the national government should interfere in the others sphere.
|
|
|
|
Cooperative federalism
|
A model of federalism in which the state and the national government cooperate in solving problems.
|
|
|
|
Devolution
|
The transfer of power is from a national or central government to a state or local government.
|
|
|
|
Categorical grant
|
A federal grant to a state or local government for a specific program or project.
|
|
|
|
Block grant
|
A federal grant that provides funds to a state or local government for a general functional area, such as criminal justice or mental health programs.
|
|
|
|
Fiscal
|
Having to do with government revenues and expenditures.
|
|
|
|
Fiscal Federalism
|
A process by which funds raised through taxation or barring by one level of government ( usually the national government) are spent by another level( typically, state or local governments)
|
|
|
|
Federal mandate
|
A requirement in federal legislation that forces States and municipalities to comply with certain rules.
|
|

