![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
87 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What effect does proximal (Type II) RTA have on serum K levels?
|
hypokalemia: due to high rates of K excretion d/t hyperaldosteronism and inc delivery of bicarb to the collecting duct; Ca excretion is also elevated.
|
|
|
Which of the RTA's is self-limited?
|
Type II (proximal) b/c of equilibration of acid production and excretion at a lower plasma bicarb level. In type I, excretion of titratable acid is impaired d/t impaired secretion of hydrogen ion in collecting ducts. Acidosis is progressive in this case.
|
|
|
Which type of RTA is assoc with nephrolithiasis?
|
RTA describes conditions where defects in renal/urinary acidification lead to metabolic acidosis. Only type I (distal) is characterized by NL, hypoK, hyperCl, and non-anion gap metabolic acidosis. About 70% of adults with distal RTA have renal calculi.
|
|
|
What is the metabolic defect in RTA type I?
|
defective excretion of hydrogen ions by the distal tubule leads to high urinary pH. Urine remains relatively alkaline (pH greater than 6) despite systemic acidosis d/t inability of distal tubule to maintain proton gradient. Systemic acidosis results in hypercalciuria d/t decreased renal reabsorption, inc bone resorption and hypocitraturia.
|
|
|
When do you suspect RTA type I?
|
hypocitraturia, hypoK, systemic acidosis (bicarb less than 23 mEq/L), nephrocalcinosis on x-ray or RUS, recur calcium phos stones and urine pH greater than 6.
|
|
|
How do you diagnose RTA type I?
|
ammonium chloride load test: urine pH greater than 5.5 after 100mg NH4Cl/kg the day prior. However, since the Tx for RTA and hypocitraturia is the same, the need for this test has diminished.
|
|
|
What is the role of suburethral sling for stress UI?
|
Suburethral (pubovaginal) slings prevent urethral descent with stress and improve the urethral washer effect. Therefore, slings are equally effective for urethral hypermobility and ISD. However, there are ince postop risk of retention with detrusor instability.
|
|
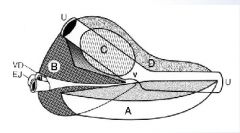
What are the different zones of the prostate?
|
C: transition zone (BPH), B: central zone, A: peripheral zone, D: fibromuscular stroma, U: urethra
|
|
|
What is an example precontrast regimen for a pt with contrast allergy?
|
if alternative imaging is not possible, can give prednisone 50mg at 13, 7, and 1hr prior to the study and 50mg of diphenhydramine 1 hr prior to exam
|
|
|
What are 4 things to look for on a plain film?
|
masses, gasses, bones, and stones
|
|
|
Isotope for measuring GFR?
|
99mTc DTPA
|
|
|
Isotope for measuring RPF?
|
131/123I-Hippuran and 99mTc-MAG3
|
|
|
How is MAG3 cleared?
|
by kidneys primarily by tubular secretion and to a lesser extent by glomerular filtration
|
|
|
why is captopril used in renography for renovascular HTN?
|
it exaggerates the differences b/w the perfused and non-perfused areas of the kidney in pts with renovascular HTN
|
|
|
What is a MIBG scan?
|
Metaiodobenzylguanidine (MIBG): taken up by adrenal neurons; images adrenal medullary tissue and is useful in identifying pheo's of extra-adrenal origin or multiple pheo's; 85-90% sens and nearly 100% spec for pheochromocytomas (false negative rate is 10%) and 100% sens/spec for neuroblastomas
|
|
|
What is used for bone scans for PrCa?
|
99mTc methylenediphosphonate (MDP)
|
|
|
What is a [superscan] in a pt with PrCa?
|
extensive involvement of the bones with mets causing it to light up while the kidneys are not seen
|
|
|
What happens to the vasculature of the kidney in renovascular HTN or obs uropathy?
|
1. release of thromboxane, causing vaso-C of afferent arteriole, causing further dec of RBF; 2. activation of RAS, resulting in angiotensin II, which inc the efferent arteriolar tone to restore and maintain glomerular filtration pressure
|
|
|
What is an indirect radionuclide cystogram (IRC)?
|
99mTc DTPA to detect VUR; caveat: does not provide info aobut he filling phase, so will miss 3% of VUR known to occur during this phase of bladder cycle
|
|
|
What is the advantage of radionuclide cystography (RNC) over VCUG?
|
more sens/spec than VCUG in detecting VUR; lower radiation
|
|
|
What are disadvantages of radionuclide cystography?
|
1. limited ability to GRADE VUR; 2. no additional radiographic data (i.e. constipation or bony abnl, etc)
|
|
|
When is lasix given during a lasix diuretic renogram?
|
when the collecting system has reached its peak level of radioactive counts
|
|
|
What are the indications for renal imaging following blunt trauma?
|
gross hematuria or microhematuria combined with shock (SBP less than 90)
|
|
|
When should you attempt to repair a main renal artery injury?
|
In a HD stable patient with no other assoc major organ system injury, ischemia time less than 8-10hrs, and/or bilateral renal injuries or injury to a solitary kidney
|
|
|
The arterial vascular supply of the ureter comes most commonly from what sources?
|
Upper - renal artery, mid - iliac artery, low - superior vesical artery
|
|
|
what is the ddx of a malignant adrenal mass?
|
adrenocortical carcinoma, pheo, neuroblastoma, mets
|
|
|
what is the most direct and reliable index of glucocorticoid fcn?
|
24 hr excretion of cortisol in urine. Pts with Cushing's often lose diurnal variation or show higher basal levels than healthy subjects
|
|
|
in the dexamethasone suppression test, what serum and urine endpts should change?
|
fall in 17-hydroxycorticosteroid, urinary free cortisol, or plasma cortisol
|
|
|
when using the metyrapone-stimulation test, what result do you look for?
|
metyrapone blocks the conversion of 11-desoxycortisol to cortisol. As plasma cortisol falls, the pituitary secretes more ACTH, thus inc urinary 17-hydroxycorticosteroid levels. Pts with Cushing's dz have a normal or supranormal inc in 17-HCS urinary excretion. Pts with ectopic ACTH secreting tumors will have little or no inc in urinary 17-HCS since it's not influenced by plasma cortisol feedback on the pituitary
|
|
|
what is the shape of cystine stones?
|
hexagonal
|
|
|
what is the shape of calcium oxalate stones?
|
star-box shape
|
|
|
what is the shape of calcium phosphate stones?
|
coffin-shape
|
|
|
what is the radiographic appearance of cystine stones?
|
characteristic ground-glass (less opaque than calcium stones)
|
|
|
what gene is responsible for cystinuria?
|
dibasic amino acid transporter gene SLC3A1
|
|
|
what is first line medical tx for cystine stones?
|
aggressive hydration (3-4 liters of urine per day) and alkalinization to a pH of 7-7.5
|
|
|
what is a potential side effect of alkalinization of urine beyond a pH of 7.5?
|
calcium phosphate crystallization
|
|
|
why does malignancy cause hypercalcemia?
|
osteoclastic bone resorption stimulated by cytokines and other substances released by the tumor, such as PTH-related polypeptide, prostaglandins, TNF, TGF
|
|
|
what are benign incidentalomas of the adrenal gland?
|
adrenal adenomas, myelolipomas, adrenal cysts; less commonly: ectopic tissue, pheo, hyperplasia, aldosteronomas, and adrenal hemorrhage.
|
|
|
why does adrenal hemorrhage during pregnancy affect the R side commonly?
|
inc intraabdominal pressure transmitted through the short R adrenal vein
|
|
|
what is the radiographic appearance of a solitary adrenal adenoma?
|
usually larger than 2cm, assoc with atrophy of opposite gland, and are of low density d/t high lipid concentration
|
|
|
what is the size cutoff for adrenal carcinoma?
|
6cm or larger (5cm on CT)
|
|
|
name 3 agents used to reduce secretion of functional steroids in patients with cushing's:
|
aminoglutethimide blocks conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone; metyrapone blocks conversion of 11-desoxycortisol to cortisone; ketoconazole blocks cytochrome p-450 mediated side-chain cleavage and hydroxylation at both the early and late steps of steroid biosynthesis
|
|
|
what is Nelson's syndrome?
|
occurred in 10-20% pts s/p bilateral adrenalectomy for cushing's dz, deelope pituitary chromophobe adenomas d/t lack of feedback of ACTH production; treated with pituitary radiation
|
|
|
what is the contrast washout test for adrenal tumors?
|
IV contrast given and CT performed after 80sec delay. another scan done 10mins later and 2 scans compared. dec in contrast enhancement of 50% or more is indicative of benign dz, less than 50% is specific for malignance
|
|
|
what is sens/spec of contrast washout test?
|
98% sensitivity; 100% specificity
|
|
|
what primary cancers met to the adrenal?
|
most common: melanoma, breast and lung carcinoma
|
|
|
man with functional adrenocortical tumor with gynecomastia, testis atrophy, and ED, what is the presumed diagnosis?
|
estrogen-secreting tumor that secretes androstenedione, which is converted peripherally to estrogens; 80% malignant, 3-yr survival less than 20%
|
|
|
what syndromes are assoc with adrenocortical Ca in children?
|
beckwith-wiedemann syndrome, isolated hemihypertrophy, Li-Fraumeni syndrome
|
|
|
adrenal tumor in kid younger than 5 is most likely what?
|
wilm's tumor or neuroblastoma
|
|
|
what is 5yr survival of adrenocortical Ca?
|
about 45%; mets commonly lung, liver, LN
|
|
|
how often does adrenal Ca present with mets?
|
about 32%; 19% will have IVC involvement
|
|
|
what drugs are available for medical management of advanced adrenal Ca?
|
mitotane shown to induce tumor response in 35% of pts; ketoconazole has adrenolytic effect; none shown to improve long-term survival
|
|
|
what findings constitute primary hyperaldonsteronism?
|
hypoK with metabolic alkalosis, suppressed peripheral renin activity, elevated urinary and plasma aldosterone levels in HTN pts
|
|
|
what is most sensitive test for hyperaldosteronism?
|
24hr urine for aldosterone and Na under conditions of prolonged Na loading (greater than 10g/day x 5-7days); urinary aldosterone greater than 14 micrograms and urinary Na greater than 250 mEq confirms dx
|
|
|
what plasma aldosterone to renin ration is suggestive for primary aldosteronism?
|
greater than 50 (aldosterone ng/dl to PRA ng/mL/hr)
|
|
|
in pts with primary aldosteronism d/t bilateral adrenal hyperplasia, what is the medical management of choice and how does it work?
|
spironolactone: competitive antagonist of the aldosterone R
|
|
|
is it possible to have a pheo in a normotensive pt?
|
yes, 10% of pheos
|
|
|
how do pheo's in kids vary from adults?
|
higher incidence of familial pheo (10%), and bilaterality (25%), 15-30% incidence of multiple pheo's and incidence of extra-adrenal location
|
|
|
what % of pheo's are malignant?
|
10%
|
|
|
what are the common locations for extra-adrenal pheo?
|
organ of zuckerkandl (close to the origin of IMA), bladder wall, heart, mediastinum, carotid and glomus jugulare bodies
|
|
|
what is the characteristic appearance of pheo's on MRI?
|
bright on T2; considered the best scanning procedure for pts with biochem findings suggestive of pheo
|
|
|
what is preop prep for pt with pheo?
|
vigorous hydration (elev catecholamines lead to significant dehydration), alpha blocker (phenoxybenzamine) with divided dose of 20-30mg PO, inc to 40-100mg PRN. beta blocker added to protect vs arrhythmias and permit reduction in alpha blocker requirement
|
|
|
in surgery for pheo, what drugs should be available intraoperatively?
|
phentolamine, short-acting alpha blocker (50mg/500cc LR); or sodium nitroprusside (50mg per 250cc of 5% dextrose in water); esmolol or propranolol should be available for persistent tachycardias or arrhythmias
|
|
|
following surgical exposure of pheo, what needs to be addressed first?
|
adrenal vein should be divided first to avoid systemic release of catecholamines during manipulation of the gland
|
|
|
what can you use in refractory pheochromocytoma crisis (refractory to sodium nitroprusside, alpha blockers, and beta blockers)?
|
magnesium sulfate: lowers catecholamine release and acts as a very effective alpha adrenergic blocker and arterial dilator
|
|
|
what is the 10% rule with pheochromocytoma?
|
10% malignant, 10% bilateral, 10% pediatric, 10% extra-adrenal, 10% assoc with MEN syndrome
|
|
|
what medical problem is seen postop after pheo removal?
|
hypotension d/t lack of catecholamine vaso-C; also hypoglycemia may also appear. best treated with volume replacement; avoid vaso-C meds if possible
|
|
|
what cells in the juxtaglomerular apparatus controls renin secretion?
|
macula densa cells
|
|
|
how do ACE-I decrease GFR?
|
they cause dilation of both afferent and efferent arterioles, but the efferent arteriolar dilation is more than afferent arteriolar dilation, so results in drop in hydrostatic P at the glomerulus and reduces GFR
|
|
|
renal autoregulation fails to maintain constant blood flow below what pressure?
|
70 mm Hg
|
|
|
the majority of NaCl and water is reabsorbed in which portion of the tubule?
|
proximal, driven by active processes
|
|
|
how does vasopressin work?
|
acts on receptors in the basolateral membrane of the principal cells. induces migration and insertion of water permeable protein channels to the luminal membrane. synthesized in the hypothalamus and secreted from post pituitary
|
|
|
the countercurrent multiplier system relies on active sodium transport in which portion of the loop of Henle?
|
ascending portion; it is impermeable to water
|
|
|
given that tubular reabsorption of calcium is inc in primary hyperparathyroidism, what is the net effect on urinary calcium excretion?
|
increased; d/t overwhelming effect of inc filtered calcium load
|
|
|
hydrogen ion secretion is accomplished by which cell type in the collecting ducts?
|
intercalated cells; also reabsorb K
|
|
|
high plasma aldosterone in combo with K depletion can lead to what acid-base disturbance?
|
metabolic alkalosis by excessive secretion of hydrogen ion. can also occur with K wasting diuretics
|
|
|
what is the mechanism of action of aldosterone on principal cells in the collecting duct?
|
stimulates sodium reabsorption by increasing Na conductance
|
|
|
what are the 4 major effects of angiotensin II?
|
arteriolar vaso-C, decreased renal blood flow with inc filtration fraction, Na retention, stimulation of aldosterone synthesis
|
|
|
name the 4 classes of diuretics that are K wasting:
|
loop, thiazide, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, and osmotic diuretics
|
|
|
hyponatremia occurs primarily with what type of diuretic?
|
thiazides, inhibit NaCl reabsorption in distal tubule
|
|
|
what effect does proximal (type II) RTA have on serum K levels?
|
hypoK present d/t high rates of K excretion from hyperaldosteronism and inc delivery of bicarb to collecting duct. Ca excretion is also elevated
|
|
|
which of the RTA is self-limited?
|
Type II (proximal); b/c equilibration of acid production and excretion at a lower plasma bicarb level; type I, distal RTA: excretion of titratable acid is impaired d/t impaired secretion of hydrogen ion in the collecting duct, so acidosis is progressive
|
|
|
how do loop diuretics work?
|
inhibit Na/K/Cl transport system on the luminal membrane of the thick ascending limb of loop of Henle, results in dec reabsorption of NaCl in this portion
|
|
|
how do thiazide diuretics work?
|
inhibit NaCl reabsorption from the luminal side of early segments of the distal convoluted tubule resulting in a diuresis; resulting dehydration causes compensatory inc in prox tubule absorption of Ca and NaCl
|
|
|
what are the normal maximums for AFP and B-HCG?
|
AFP: up to 9 ng/mL; 1/2 life = 6days; BHCG: up to 4mIU/mL; 1/2 life = 36hrs
|
|
|
What is the most common GCT in prepubertal boys?
|
yolk sac tumor
|
|
|
How many pts with clinical stage I NSGCT will have microscopic dz metastatic to the RPLN at time of orchiectomy?
|
30%; vascular or local invasion increases the risk, as does embryonal component
|

