![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
94 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Will indicate acid-base balance.
helps protect against bacterial growth. stands for several hours will become alkaline. |
PH 4.6-8.0
|
|
|
|
Normally not present in the urine.
Common in renal diease because damange to glomeruli or tubules allows it to enter the urine |
Protein none or upto 8mg/100 ml
|
|
|
|
Clients with Diabetes Mellitus often have this in their urine as a result to inability of tubules to reabsorb high concentrations.
(>180mg/100ml) |
Glucose NONE
|
Also note that when injesting high concentrations of gluose causes some glucose to appear in the blood.
|
|
|
End products of metabolism.
Clients who Diabetes Mellitus is poorly controlled experience breakdown of fatty acids |
Ketones NONE
|
|
|
|
Some clients with dehydration,starvation, or excessive aspirin usage have
|
Ketonuria
|
|
|
|
A positive test occurs when intact erthrocytes, hemoglobin , or myoglobin is present.
|
Blood
|
* For Women- contamination from menstrual fluid
|
|
|
Measures the concentration of particles in urine
High- Concentrated Low- Diluted |
Specific Gravity
|
* Dehydration, reduced renal blood flow, and increases ADH secretion elevates specific gravity.
*Overhydration,early renal diease and inadequate ADH secretion reduce specific gravity |
|
|
Collect during normal voiding, from an indwelling catheter or urinary diversion collection bag.
|
Random (Routine Urinalysis)
|
Use clean Specimen Cup
|
|
|
Use Sterile Specimen Cup
Cleanse/Dry(front to back) Initate stream Pass container into stream and collect 30 to 60 ml urine |
Clean -voided or midstream
|
Culture and Sensitivity
|
|
|
Swab port
Insert sterile syringe Withdrawl at least 3 to 5 ml of urine Collect urine using aseptic techniques through sample port found on side of catheter tube |
Sterile Specimen
|
Culture and Sensitivity
|
|
|
Begins after the client urinates and ends with a final voiding at the end of the period.
Voids into clean receptacle and the urine is then tranferred to the special collection container |
Timed urine specimens
|
Time required may be2-,12- or 24 hour collection.
*Missed specimens result in starting process over |
|
|
Examine specimen with in 2 hr
Quick test used with ___? |
Urinalysis
Regeant strips |
Make sure its the first voided specimen in the morning.
|
|
|
damage to glomeruli or tubules allows RBC's to enter the urine.
Truama, diease or surgery of lower urinary tract also causes blood to be present |
RBCs (up to 2)
|
|
|
|
Greater numbers indicated Urinary Tract Infections
|
WBCs (0-4 per low-power field)
|
|
|
|
Indicates urinary tract infections
|
Bacteria (none)
|
CLients do not always have symptoms
|
|
|
are cylindrical bodies whose shapes take on likeness of objects within the renal tubule.
Ex: hyaline, WBCs,RBCs,granular cells, & epithelial cells |
Casts(None)
|
The increases presence is always an abnormal finding
|
|
|
a result of food metabolism
Ex: Uric acid or calicum phosphate result in stone formation |
Crystals (NONE)
|
|
|
|
View the collecting ducts and renal pelvis and outline the ureters,bladder, and urethra.
Special IV injection (iodine based) that converts the dye in urine |
IVP Intravenous Pyelogram
*Assess for structure function and abnormalities. |
Nursing consideration:
Bowel cleansing-Only clear liquids permitted until test is complete. Asses for shellfish allergy b4 test. After test encourage fluid intake to flush out dye & observe for latesymptoms of allergy. |
|
|
Identify structural abnormalities of bladder or lower urinary tract
Also used to estimate the volume of urine in the bladder |
Bladder Scanner
*performed at the bedside by the nurse to determine need for voiding or straight catherization |
If needed ask client to drink fluids before the test to cause bladder distention for better results.
|
|
|
Direct visualization of the urethra & bladder
*Assesment for prostatic hypertrophy, Urethral Structures, bladder calculi, tumors,polyps,congenital abnormalities |
Cystoscopy
|
obtain signed consent
*if ordered bowel cleanse will be completed. *When client returns asses V/S Characteristics of Urine, I&O,encourage fluids,observe ever,dysuria,and pain in suprapubic region |
|
|
Urine is normally acidic and tends to inhibit growth of microorganisms.
What types of foods help increase acidity? |
Meats,eggs,whole-grain breads,cranberries, and prunes.
|
Cranberry juice decreases baterial adherence to the bladder wall.
|
|
|
Loss of urine caused by factors outside the urinary tract that interfere with the ability to respond in a socially appropriate way to the urge to void.
Most common type among older adults with arthritis, Parkinson's disease or Alzheimer's disease. These people are often unable to control their bladder before reaching the bathroom due to limitations in moving, thinking or communicating. |
Functional Urinary Incontinence
* Non Urinary Problem |
Interventions:
Modify clothing Enviromental alterations Schedule tolieting Absorbent products |
|
|
Involuntary leakage of urine during increased abdominal pressure in the absence of bladder muscle contraction.
ex: Involuntarily leak urine while exercising, coughing, sneezing, laughing or lifting. |
Stress Urinary Incontinence
* Urinary Problem |
Interventions:
Kegel exercises Absorbant Products Biofeedback |
|
|
Involuntary passage of urine after a strong sense of urgency to void.
More often then every 2 hours bladder spasms or contractions |
Urge Urinary Incontinence
* Urinary Problem |
Interventions:
Kegel exercises Absorbant Products Biofeedback Lifestyle modifications- smoking cessation,weight loss and fluid modifcation. |
|
|
Combination of urge & stress urinary incontinence signs and symptoms
|
Mixed Urinary Incontinence
*Urinary Problem |
Main treatments based on symptoms that are most bothersome to the client.
|
|
|
Involuntary loss of urine at intervals without sensation if urge to void
Relevant Factors: spinal cord dysfunction-loss of cerebral awareness or impairment of reflex arc. |
Reflex Urinary Incontinence
*Non Urinary Problem *lack of urge to void, Unawareness of bladder refilling, reflex emptying when certain volume is reached |
Intermittent Catherization
Condom Cath. Crede's Method |
|
|
Straight Cath.
Long enough to drain the bladder for 5 to 10 mins and then immediately removing the cath. |
Intermittent Catherization
|
Indications:
Relief of discomfort of bladder distention, provision of decompression(providing pressure) obtain sterile specimen assesment of residual urine |
|
|
Catheter that remains in place for short term period
|
Short Term Indwelling Cath.
|
Indications:
Obstruction to urine outflow (prostate enlargement) Surgical repair of bladder,Urethra,surrounding structers prevention of urethral obstruction from blood clots after surgery measurement of output in critical ill . |
|
|
Catheter that remains in place for long term.
|
Long term indwelling catheter
|
Indications:
Severe Urinary retention with recurrent episodes of UTI skin rashes,ulcers, or wounds irritated by contct with urine terminal illness when bed linen changes are painful for client. |
|
|
clients that have catheter should have a daily intake of
|
2000 to 2500ml of fluid intake
|
|
|
|
Catheter size used for child
|
8 to 10 Fr
|
|
|
|
Catheter size for most clients
|
14 to 16 Fr
|
|
|
|
Catheter size for Men
|
16 to 18 Fr
|
|
|
|
Catheter generally used to aid in urination for men who have enlarged prostates or suffer from benign prostatic hyperplasia
|
Coude Catheter
|
*Can also sometimes be used for women, although a coude tip issually designed to aid in permeating a small opening.
|
|
|
retraction and constriction of the foreskin behind the glans penis is known as
|
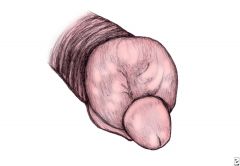
Paraphimosis
|
foreskin gets stuck and unable to revert back to normal.
|
|
|
Position for male client during catherization
|
Supine or fowlers position
|
|
|
|
Position for female client during catherization
|
dorsal recumbent or side lying sims position with upper leg flexed at hip if unable to be in DR
|
|
|
|
Involves surgical placement of a catheter through the abdominal wall above the symphysis pubis and into the urinary bladder
|
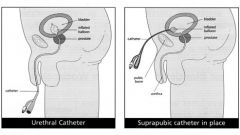
Suprapubic Catheterization
|
|
|
|
Nighttime voiding without awakening sometimes continues until age 5
|
Nocturnal Enuresis
|
|
|
|
Because an older adult can not contract effectively an older adult often retains urine in the bladder after voiding
|
Residual Urine
|
becomes more alkaline znc is an ideal site for microorganism growth
|
|
|
infection in the upper urinary tract (Kidneys) with flank pain tenderness, fever and chills are commonly known as
|
Pyelonephritis
|
|
|
|
is the involuntary leakage of urinetha is sufficent to be a problem.
|
Urinary incontinence
|
|
|
|
clients with UTI have pain or burning during urination as urine flows over inflammed tissues
|
Dysuria
|
|
|
|
bacteria in the urine
|
Bacteriuria
|
leads to the spread of organisms into the kidneys leads to bacteremia or urosepsis.
|
|
|
bacteria in the bloodstream
|
Bacteremia or Urosepsis
|
|
|
|
When client needs urinary drainage directly from one or both kidneys.
Tube is directly placed in to the renal pelvis procedure is called |
nephrostomy
|
|
|
|
Feeling the need to void immediately
|
Urgency
|
Full bladder,Bladder irriatation or inflam. from infection, overactive bladder,psychological stress.
|
|
|
Painful or difficult urination
|
Dysuria
|
Bladder inflammation, trauma or inflam. of urethral spincter
|
|
|
Voiding at frequent intervals (<2HR)
|
Frequency
|
Increased fluid intake, bladder inflam., increased pressure on bladder due to pregancy,diuretic therapy.
|
|
|
Difficulty initiating urination
|
Hesitancy
|
Prostate enlargement, anxiety,urethral edema
|
|
|
Voiding large amounts of urine
|
Polyuria
|
excessive fluid take,diabetes mellitus or insipidus, use of diuretics,postobstructive diuresis.
|
|
|
Diminished urinary output relative to intake
(usually 400ml/24hr) |
Oliguria
|
Dehydration,renal failure,UTI, increased ADH secretion,congestive heart failure
|
|
|
Voiding one or more times at night
|
Nocturia
|
Excessive fluid intake before bed(especially coffee or alchol), renal diease,aging process,prostate enlargement
|
|
|
Leakage of urine despite voluntary control of urination
|
Dribbling
|
Stress incontinence,overflow from urinary retention
Eg. BPH Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia |
|
|
Enlargement of the prostate gland
|
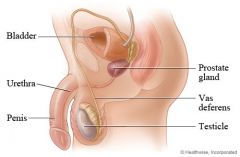
Benign Prostate Hyperplasia
|
The prostate is a doughnut-shaped gland with two lobes, and it is located below the bladder about halfway between the rectum and the base of the penis. It encircles the urethra (the tube that carries urine from the bladder out through the penis), and in young men it is normally about the size of a walnut. The prostate produces most of the fluid that makes up semen.
|
|
|
Accumulation of urine in the bladder with inability of bladder to empty fully
|
Retention
|
Urethral obstruction Stricture, decrease sensory activity neurogenic badder, prostate enlargement, postanesthesia effects,side effects of med's Ex: anticholinergics, opios narcotics.
|
|
|
Body Mass Index
|
LBS / Height (INCHES) x 703
|
Height/ Weight / Nutritional status
|
|
|
measurement of the distance round the navel
|
Abdominal Girth
|
|
|
|
During Exam blunt percussion at this area with fisted hand
|
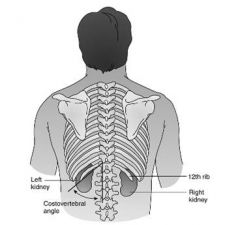
Costovertebral angle
|
|
|
|
Normal color ranges for urine are ..
|
Pale, straw color to amber depending on concentration
|
Urine is usually concentrated in the morning or with fluid volume deficits
More fluids less concentrated |
|
|
Bleeding from the kidneys or ureters causes urine to become..
|
Dark red
|
|
|
|
Bleeding from the bladder or urethra causes urine to become
|
Bright red
|
|
|
|
a urinary analgesic, colors the urine bright orange
|
Pyridium
|
Eating beets,rhubard or blackberries causes red urine
|
|
|
Dark amber urine is the result of ..
|
High concentrations of Bilirubin
|
caused by liver dysfunction
|
|
|
Normal urine appears transparent at voiding but as it sits in the container
|
it becauses cloudy
|
Renal diease clients urine will appear cloudy bc of high protein concentrations.
|
|
|
If urine appears thick and cloudy that will show
|
That bacteria is present with WBC's
|
|
|
|
agents inhibit the action of acetylcholine. They stop the transmission of parasympathetic nerve impulses therefore lessen the spasms of smooth muscle, such as in the gastrointestinal tract and in the bladder. They are used to treat spasms or conditions with disturbances in the bladder or gastrointestinal motility.
|
Anticholinergics
*antispamodics |
Ex :Oxybutynin
|
|
|
is an anticholinergic medication used to relieve urinary and bladder difficulties, including frequent urination and inability to control urination (urge incontinence), by decreasing muscle spasms of the bladder.
|
Oxybutynin
-*Ditropan |
Anticholinergics
*antispamodics |
|
|
is used to treat overactive bladder. This medicine reduces frequency and urgency. It may also help to control wetting accidents.
- Causes dry mouth& eyes , Urinary retention |
Tolteroldine
|
Anticholinergics
*antispamodics |
|
|
Pelvic Floor Exercises Kegel
|
30-100x's daily
Hold contractions x's 10 secs Relax 10 secs X4 weeks |
effective in treating stress incontinence
-learns while voiding, then practiced at nonvoiding times |
|
|
Bladder Log Training
|
3 day 24hr log
verifies patterns/leakage & baseline for management plans |
*Indicates more serious GU problems related to UTI or other renal dieases
|
|
|
frequent and urgent sensation of the need to void.
Suprapubic pain,hematuria,fever,confusion in older adults |
Cystitis
|
|
|
|
Preventative measures
|
Symptomatic Relief
|
|
|
|
Bladder Training Management Plan
|
pt asked to suppress urination for each voiding and ^ time by increments of 15mins.
Goal-Urinate every 3 to 4 hrs 240 -500 ml |
STRESS Incontinence--
Kegel exercises toliet schedule: (Q2h-day/evening & Q4h-night) Avoid overfilling of bladder ^ pressure minimize caffeine -tea alcohol diuretic meds should be taken in AM Weight control management |
|
|
a steriod used to reduce inflamation and irritation of the skin
*Spray or cream |
Kenalog
|
|
|
|
antifungal used for fungal growth development on the skin
*Cream or powder |
NyStatin
Mycostatin |
|
|
|
Waste Product from meat protein & normal wear and tear of muscles
|
Creatinine
|
fairly consistent levels regardless of fluid intake exercise or nutrition
|
|
|
waste product from food protein
|
BUN
|
|
|
|
Normal BUN
|
7-20mg/dl
|
Always use lab reference
|
|
|
Normal Creatinine
|
0.6- 1.2 m.g/dl
|
Always use lab reference
No increase until 50 percent of renal function is lost |
|
|
Normal adult output is
|
1500 to 1600 ml/day
|
|
|
|
indication of possible renal alerations
|
less than 30 ml/hr
|
|
|
|
Responisble for maintaininga normal RBC volume by producing erythropoietin
|
KIDNEYS
|
|
|
|
Pt with chronic kidney alterations can not produce sufficient quatities of _____.
- are prone to _____. |
-Erythropoietin
-Anemia |
|
|
|
the bladder normally holds how many ml's of urine
|
600ml
|
|
|
|
Adults/child are able to sense the desire to urinate when bladder contains.
|
adults-150 to 200ml
child- 50 to 100ml |
|
|
|
____, interferes with the productions and characteristics of urine and affect the act of urination
|
medications including anesthesia.
|
|
|
|
Decreased bloodflow to and throught the kidneys is known as
|
prerenal
|
|
|
|
Obstruction in the lower urinary tract that prevents urine flow from the kidneys
|
postrenal
|
|
|
|
diease conditions of the renal tissue is known as...
|
renal
|
|
|
|
dieases that cause irreversible damage to kidney tissue result in
|
ESRD
End stage renal diease |
|
|
|
an increase in nitrogenous wastes in the blood marked fluid and electrolyte, abnormalities, nausea, vomitting, headache, coma, and convulsions characterize this syndrome?
|
Uremic syndrome
|
|
|
|
renal replacement
|
dialysis
organ transplant |
|
|
|
-The presence of large proteins in the urine.
- The sign of glomerulus injury |
Proteinuria
|
|

