![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
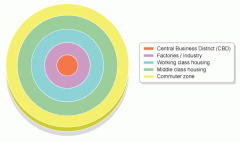
Which land use model is this? Describe the characteristics of the CBD. |
Burgess Model. CBD = High/multi-storey buildings. Expensive land values. Department stores or specialist shops, like jewellers. Shopping malls and pedestrian precincts. Cultural/historical buildings, museums and castles. Offices, finance, banks, administration, town hall (business sector). Bus and railway stations (transport centres). Multi-storey car parks. |
|
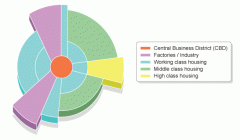
Which land use model is this? Describe the characteristics of the inner city. |
Hoyt Model. Inner City = It is typically found next to the CBD and has mainly terraced houses in a grid like pattern. These were originally built to house factory workers who worked in the inner city factories. Many of these factories have now closed down.Unemployment and other socioeconomic problems have led to periods of unrest in many inner city areas. Many inner city areas declined in the late 20th century and have undergone a period of regeneration in recent years. |
|

Which area of the city is this? |
The CBD |
|

Which area of the city is this? |
The Inner City |
|

Which area of the city is this? |
The rural-urban fringe |
|

Which area of the city is this? |
The suburbs |
|
|
Describe two strategies used to prevent urban sprawl. |
Greenbelts:areas of mainly open countryside and small settlements surrounding urban areas.They are protected from development. The number and type of buildings that canbe erected is restricted. Planning permission isnot normally given to developers. They stop the outward growth of city andprevent towns and cities merging together to form a continuous urban area. Theyprotect the open nature of the countryside and preserve the land for farmingand to provide access for recreation eg golf courses.•Brownfieldsites: have been redeveloped by building industrialsites with the built-up area rather than developing out-of-town greenfieldsites. •Inner-cityredevelopment: involving modernising of old properties meansthat people carry on living there, reducing the need for new estates around thecity. |
|
|
Describe one strategy that was used to improve the inner city |
The London Docklands Development Corporation (LDDC) The LDDC was at work for 17 years. In its final annual report in 1998 it headlined its achievements as follows: · £1.86 billion in public sector investment · £7.7 billion in private sector investment · 431ha of land sold for development · 144km of new and improved roads The construction of the Docklands Light Railway 2.3kmsq of commercial/industrial floorspace built 762ha of derelict land reclaimed 24,046 new homes built 2,700 businesses trading contributions to 5 new health centres and the redevelopment of 6 more funding towards 11 new primary schools, 2 secondary schools, 3 post-16 colleges and 9 vocational training centres 94 awards for architecture, conservation and landscaping 85,000 people now at work in London Dockland |

