![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are 4 legged animals called |
Quadrupeds |
|
|
|
What helped in evolution of prehensile activity of upperlims in humans |
1. Opposible thumb 2. Clavicle that prevents us from turning into dogs 3. Supination and protonation activity of uppperlimbs 4. Free movement of fingers and thumb of hand |
|
|
|
What are the type of grips |
Hook grip Power grip Precision grip |
|
|
|
What is pectoral limb girdle |
The set of clavicle and scapula which connect appendicular skeleton to axial skeleton |
|
|
|
Why is the pectoral girdle not regarded as a complete girdle |
Because it is connected to axial skeleton only anteriorly |
|
|
|
What is the primary function of pectoral girdle |
To provide site of attachment for various muscles. |
|
|
|
For ease of study how is the upper limb divided |
Shoulder Arm (brachium) Forearm (antebrachium) Hand (Manus) |
|
|
|
What does the shoulder region include |
Axilla (Armpit) Scapular region (shoulder blade) Pectoral region (Brest region) |
|
|
|
What are the bones of the shoulder region |
Scapula Clavicle |
|
|
|
The joint between acromian and clavicle is called |
Acromioclavicular joint |
|
|
|
The joint between sternum and clavicle is |
Sternoclavicular joint |
|
|
|
What type of joint is sternoclavicular joint |
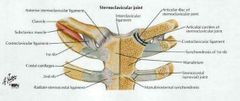
synovial joint The Sternoclavicular Joint (SC joint) is formed from the articulation of the medial aspect of the clavicle and the manubrium of the sternum. It is one of four joints that compose the Shoulder Complex. The SC joint is generally classified as a plane style synovial joint, and has a fibrocartilage joint disk. |
|
|
|
What type of joint is acromioclavicular joint |
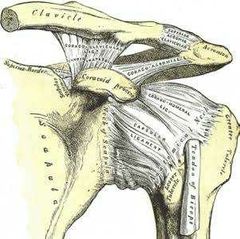
synovial joint The Acromioclavicular Joint, or AC Joint, is one of four joints that compride the Shoulder complex. The AC Joint is formed by the junction of the lateral clavicle and the acromion process of the scapula and is a gliding, or plane style synovial joint |
|
|
|
What is the scientific term for elbow |
Cubitus |
|
|
|
What is the scientific term for arm |
Brachium |
|
|
|
What is the scientific term for forearm |
Antebrachium |
|
|
|
What are the bones of hand proper |
Metacarples |
|
|
|
The naming of metacarpals as 1-5 is medial to lateral or lateral to medial |
Lateral to medial Thumb first and pinky last |
Remember it as that pissiform is located near to pinky and the mnemonic is She is too pretty try to catch her |
|
|
What is the number of phalangeal bones |
14 (2+3+3+3+3) |
|
|
|
What type of joint is interphalangeal joint |
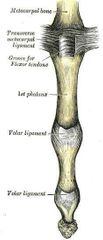
hinge joints (synovial joint) Interphalangeal Joints. Interphalangeal joints are formed between the phalanges. These are uniaxial type of hinge joints where only possible movement is flexion and extension. |
|
|
|
What type of joint is the elbow joint |
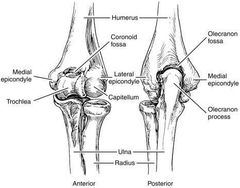
The elbow joint is a complex hinge joint formed between the distal end of the humerus in the upper arm and the proximal ends of the ulna and radius in the forearm. The elbow allows for the flexion and extension of the forearm relative to the upper arm, as well as rotation of the forearm and wrist |
|
|
|
What type of joint is the inter carpal joint |
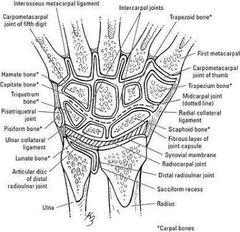
Ellipsoid joints (synovial)The intercarpal joints are synovial joints formed between the individual bones of the proximal row of the carpal bones, between the individual bones of the distal row of carpal bones, and between the proximal and distal rows (the midcarpal joint). |
|
|
|
When does the development of limbs start in the intrauterine life |
In the 4th week |
|
|
|
What is direction of rotation of preaxial border of upper and lower limb
|
Upper limb (laterally through 90 degree) Lower limb (medially through 90 degree) They rotate such that the flexor compartment of muscles is located anteriorly for upper arm where as it is located posteriorly for lower limb. |
|
|
|
The strongest ligament of upper arm |
Corrococlavicular ligament |
|
|
|
The muscles of anterior compartment act as flexor or extensor? |
Upper limb flexor Lower limb extensor |
|
|
|
The nerve supply to the upper limb is derived from the |
Brachial plexus |
|
|
|
How is the brachial plexus formed |
It is formed by the ventral Rami of C5-C8 and T1 C5,C6- superior trunk of brachial plexus C7- middle trunk of brachial plexus C8-T1- inferior trunk of brachial plexus |
|
|
|
Name the first bone to ossify in the body |
Clavicle |
|
|
|
Artery commonly used to take arterial pulse |
Radial artery in front of wrist on lateral side just below the thumb |
|
|
|
Artery commonly used for ausculation |
Brachial artery in front of the elbow |
|
|
|
Most preferred muscle for tendon graft |
Palmaris longus |
|
|
|
Muscle most commonly used for intramuscular injection |
Deltoid |
|
|
|
Strongest ligament in the upper limb |
Corrococlavicular ligament |
|
|
|
Joint with maximum type of movement |
Shoulder joint |
|
|
|
Most mobile joint of the body |
Shoulder joint |
|
|
|
Most important digit of the hand |
Thumb |
|
|
|
Part of the upper limb having largest representation in the brain |
Hand |
|
|
|
Most important feature of the hand |
Opposition of thumb to execute precision grip |
|
|
|
Only point of body contact between upper limb and chest |
Sternoclavicular joint |
|
|
|
What is the most common dislocation surgery |
Dislocation of shoulder |
|
|
|
Give certain unique features of clavicle |
It keeps the shoulder strut Transmits force from appendicular skeleton to axial skeleton It provides site for attachment of various muscles Namely: subclavius Pectoralis major Deltoid Trapeziums Sternocleidomastoid And various ligaments like corrococlavicular Costoclavicular etc. |
|
|
|
Name the peculiarities of the clavicle |
1)It has 2 primary center of development 2)It has no medullary cavity 3)It is the only long one that is horizontal in anatomical position 4)It is the only ariculation of arm to thorax 5)It is the first bone to start ossification and last to complete ossification at 25 6)It is the only bone with membranocartilagenous ossification 7) It may be pierced by cutaneous nerve (intermediate subscapular nerve) |
|
|
|
Explain the destinguishing features for defining anatomical position of clavicle |
Conoid tubercle Trapezoid line Subclavius groove Nutrient foramen |
|
|
|
Describe the position of connoid tubercle and it's function |
It is located on lateral and inferior aspect of clavicle, medial to the trapezoid line and lateral to the nutrient foramen and subclavian groove |
|

