![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the most common cause of flexor tendon injuries?
|
Lacerations
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of extensor tendon injuries?
|
laceration and blunt trauma such as a mallet finger
|
|
|
How can you tell if a flexor tendon injury is deep or superficial?
|
PIP joint is superficial, DIP joint is deep
|
|
|
Explain why extensor tendons are the ones most commonly injured
|
extensor tendons have a superficial nature on the dorsum of the hand.
|
|
|
What gets injured more often; flexor or extensor tendons?
|
extensor
|
|
|
Discuss what should be examined with a flexor or extensor injury
|
PE: devascularization, skin status, posture of fingers, deformities, bleeding, grip strength, compare bilaterally, nerve testing, tendon testing, x-rays and consult.
|
|
|
Discuss the management of flexor and extensor injuries
|
treat anything with neurovascular compromise ASAP. Control px and swelling. NPO if surgery. Consult prn. immobilize
|
|
|
Define the term Mallet finger, MOI, tx and consequences of not treating
|
Zone 1 extensor tendon injury of distal phalanx and DIP. MOI: sharp or blunt trauma. Most common injury in athletes. tx: splint DIP in extension or hyper extension. If 25% refer. Consequences: necrosis
|
|
|
DISORDERS OF THE UPPER EXTREMITIES
|
DISORDERS OF THE UPPER EXTREMITIES
|
|
|
What are the 2 most common types of injuries with PIP dislocations
|
lateral involving the radial collateral ligament and dorsal involving the volar plate.
|
|
|
What is the treatment for PIP injuries
|
splint at 30* flexion for 3 weeks. However, if not reduceable, may need surgery.
|
|
|
What should you do prior to reducing any fracture?
|
Get an x-ray! 2 views; AP and always get a lateral
|
|
|
List 2 terms referring to a ruptured thumb metacarpal-phalangeal ligament and discuss how they are evaluated and treated
|
Gamekeepers or skier's thumb. Check for weakness of pincer function and point tenderness at volar-ulnar aspect of thumb MCP joint. Surgery recommended.
|
|
|
What kind of injuries are a gamekeeper's or skier's thumb?
|
ulnar collateral ligament injuries
|
|
|
How are distal phalynx fractures classified? MOI? Tx?
|
tuft (nailbed) shaft or intraarticular MOI: crush or shearing Tx: tx as a soft tissue injury
|
|
|
Mallet finger
|
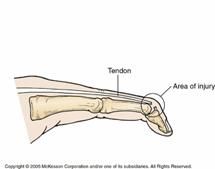
What kind of injury is this?
|
|
|
Discuss MOI of distal phalanx injuries, and Tx
|
MOI: crush or shearing which may involve nailbed lacerations. Tx: protective splinting
|
|
|
Discuss Tx of proximal and middle phalange injurues
|
Stable: buddy tape. Unstable: closed reduction, splint from elbow to DIP with wrist at 20* extension and MP joint in 90* flexion or surgery
|
|
|
What is a boxer's fracture? MOI? Tx?
|
fracture of the 5th metacarpal NECK. MOI: direct impact force. Tx: closed reduction and splint/cast with wrist dorsiflexion of 20* and MCP @90*'s
|
|
|
Describe a paronychia, MOI, Tx
|
infection of lateral nail fold or perionychium. MOI: biting, manicures or hangnails. Tx: warm soaks, abx, I&D
|
|
|
Describe a felon, pathogen, and Tx
|
infection of the pulp of tip of finger. presents red, swollen, painful. staph, I&D on lateral aspect of finger.
|
|
|
List the 4 cardinal signs of flexor tenosynovitis
|
slight flexion, swelling, tenderness over flexor tendon sheath, pain on passive extension
|
|
|
What is the most common ligamentous injury to the wrist
|
scapholunate ligament injuries
|
|
|
What is the MOI for scapholunate ligament injuries? Tx?
|
fall on outstretched extremity. Tx: Don says orthopedic referral / surgery. Book says gutter splint or short arm volar posterior mold
|
|
|
What 3 radiographic signs help to diagnose scapholunate ligament injuries
|
1. Terry Thomas sign: widening of joint space mor than 3mm 2. Grip-compression or motion study 3. Dorsal intercalated segment instability (DISI)
|
|
|
Describe the PE, MOI, Tx and complications for scaphoid fractures
|
PE: px in snuffbox. Most occur in middle 1/3 of scaphoid. MOI: fall on outstretched. Tx: splint dorsiflexion, radial deviation. Unstable long arm spica and refer. Consequences: avascular necrosis
|
|
|
What is a colles fracture? MOI? PE? Tx?
|
fx of distal radius with displacement / angulation. MOI: fall outstretched. PE: dinner-fork deformity, palmar paresthesias, tension on median nerve. Tx: reduce splint, unstable surgery
|
|
|
What is a Smith's fracture
|
reverse colles fx. produces a garden-spade deformity but angulation is volar rather than dorsal!
|
|
|
What is a type I supracondylar fracture?
|
undisplaced
|
|
|
What is a type II supracondylar fracture?
|
displaced nad have cortical contact.
|
|
|
What is a type III supracondylar fracture?
|
subdivided into posterolateral and posteromedial fx's based on displacement and have no cortical contact.
|
|
|
What age is more at risk for supracondylar fractures?
|
children from a fall off swings or jungle gyms
|
|
|
Name the 2 kinds of supracondylar fractures and Tx
|
Extension (most common) and Flexion. Tx: Don says refer! Book says non-displaced splint long arm cast 4-6 wks, displaced surgery
|
|
|
What important signs should you look for on plain films with a supracondylar fracture
|
fat pad sign in undisplaced fx
|
|
|
Describe MOI, PE and Tx for radial head fractures
|
MOI: fall on outstretched. PE: radiocapitellar line; radial head should always face capitellum. XR show abnormal fat pad. Tx: nondisplaced splint. displaced surgery
|
|
|
What is the most common kind of elbow fracture
|
radial head fracture
|
|
|
Describe MOI, PE, and Tx of proximal biceps rupture
|
MOI: repetitive microtrauma and overuse. PE: snap heard, swelling, tender, crpitus over bicipital groove, arm "ball" Tx: sling, ice, analgesics, referral
|
|
|
Describe MOI, Tx for radius and ulna fractures
|
MOI: high impact MVC. Tx: nondisplaced rare! tx with plaster immobilization. Refer quickly
|
|
|
Identify the 2 major nerves that can be injured in a forearm fracture
|
Radial and ulnar
|
|
|
How would you evaluate the radial nerve for potential injury from ulnar/radial fracture
|
have pt extend both the wrist and fingers against resistance. Sensation is tested over the dorsum of the thumb index web space
|
|
|
How would you evaluate the ulnar nerve for potential injury from ulnar/radial fracture
|
ability to abduct index finger against resistance and 2-point discrimination over the tip of the little finger
|
|
|
Describe MOI, PE, Tx and typcial patient for a proximal humerus fracture
|
PT: elderly female with osteoporosis MOI: fall on outstretched PE: px, swelling, ecchymosis Tx: sling, analgesics
|
|
|
Discuss the MOI and treatment of humeral shaft fractures
|
bimodal age distribution in 30's & 70's. MOI: direct blow resulting in transverse fx. Torsion forces results in oblique fx sometimes with comminution. Tx: coaption splint, sling
|
|
|
What is the most common MOI of clavicular injury for any patient?
|
Blow to shoulder
|
|
|
What is the most common part of clavical to sustain a fracture? Tx?
|
80% middle 1/3 of clavicle. Immobilize with sling, dispaced with figure 8. Severely displaced shoulder spica or open reduction.
|
|
|
Describe MOI, PE and associated injuries with scapular fractures
|
MOI: high energy, MVC's. PE: tenderness over scapula, flattened appearance. Associated: lung, shoulder, humeral head, girdle, rib, abd, spine
|
|
|
Identify the MOI, PE, and Tx for an AC joint injury
|
MOI: trauma with arm adducted. PE: tenderness, deformity. Tx: rest, ice, analgesics, immobilization
|
|
|
What is a more common injury - anterior or posterior shoulder dislocation?
|
Anterior.
|
|
|
What is MOI, PE and complications of anterior shoulder dislocations
|
MOI: abduction and external rotation. PE: px, squared off. Complications: recurrent dislocations
|
|
|
What is the MOI for posterior shoulder dislocations
|
Adduction and internally rotated, flat and posterior aspect appears full, coracoid process prominent
|
|
|
What nerve is at risk for injury with anterior shoulder dislocations
|
axillary nerve
|
|
|
What nerve is at risk with a lateral elbow injury
|
ulnar
|

