![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
the general gravitational law
|
a body on the universe attracts another body by a force directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to square the distance between them.
|
|
|
Gravitational field
|
the space where the gravitational forces appear
|
|
|
the gravitational field intensity
|
the gravitational forces acting on a body of mass 1kg
|
|
|
Equation of gravitational force intensity:
|
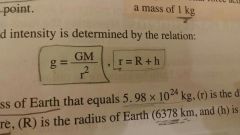
|
|
|
¤If a body is at HEIGHT above earth
¤If a body is at DEPTH below earth |
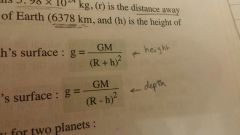
|
|
|
A satellite:
|
an object projected at a a certain velocity to rotate in a roughly circular path at a constant distance from the earth's surface
|
|
|
orbital velocity
|
the velocity that makes the satellite orbit the earth and rotate in a roughly circular path at a constant distance from earth's surface.
|
|
|
what happens when the satellite stops and the velocity becomes zero
|
it will move in a straight line and fall on earth surface
|
|
|
what happens when the gravitational force dissapears
|
the satellite will move in a straight line tangential of the circular path away from earth.
|
|
|
how to calculate the time take for one revolution around earth
|

circumfrance ÷ speed
|
|
|
Importance of a satellite:
|
¤communication: tv transmission, radio transmission, internet, phone calls
¤astronomical : huge telescopes ¤remote sensing: study emigrant birds , determine mineral sources. ¤explanatory: used by military and political leaders to make decisions ¤meteorological |

