![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
PLANT STRUCTURES |
Roots Stems Leaves Flowers Fruit and seeds |
|
|
Root - Types |
Tap roots Carrots, beets, turnips Fibrous roots Grains |
|
|
Roots – Functions and uses |
Absorb water and minerals Anchor plant to soil Reduce soil erosion (fibrous roots) Food source (carrots, beets, radishes) Medicines (ginseng) Dyes (madder) |
|
|
Stems |
Herbaceous stems -example: Tomato Plant (only lasts on season) Woody stems |
|
|
Stem Tissues |
Xylem Phloem Vascular cambium - Produces xylem inward - Produces phloem outward Bark -Woody plants -Cork cambium |
|
|
Stems - Structure |
•Dicotyledon •Rings •Monocotyledon •Scattered |
|
|
Stems – functions and uses |
Xylem Plant support Transports water and minerals from rootupward Uses -Wood -Paper -Rope |
|
|
Stems – functions and uses |
Phloem Transports sugars and organic molecules Uses -Sap -Latex -Maple syrup |
|
|
Bark - Cork |
Uses - Cork - Spices - Medicines |
|
|
Stems as Food Storage |
Tubers (spherical undergroundstorage stems) potatoes Rhizomes (swollen horizontalstorage) ginger Corms (vertical stems)Crocus, taro |
|
|
Leaves - Functions |
Photosynthetic organ Transpiration -Driving force for water movement from rootsthrough stems and leaves Food (spinach, lettuce) Food storage -Bulbs Herbs, tea, medicines, and psychoactives |
|
|
Plant Reproduction |
Asexual reproduction (clones) Vegetative propagation -Leaves, stems, rhizomes, tubers -Crop uniformity -More efficient than seeds |
|
|
Plant Reproduction |
Asexual reproduction (clones) Vegetative propagation - cuttings |
|
|
Plant Reproduction |
Vegetative propagation - runners |
|
|
Plant Reproduction |
Vegetative propagation - grafts |
|
|
Sexual reproduction |
Meiosis -Reduction division(diploid to haploid) -Increases geneticvariations(new varieties) Quality of new variety isunknown Sperm and eggproduction |
|
|
Meiosis |
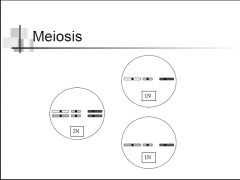
Non-disjunction - The chromosomes do not separate atanaphase I or anaphase II - Polyploidy (many copies of chromosomes) - Colchicine (from corm of crocus) |
|
|
Flowers - Reproductive Organs |
Flower Functions Gametophyte production (meiosis) -Gamete (sperm and egg) formation Pollination Fertilization Fruit and seed production |
|
|
Flowers - Anatomy (MALE) |
- Stamens (anthers and filaments) - Produce pollen that contains sperm nucleus |
|
|
Flowers - Anatomy (FEMALE) |
- Pistil (stigma, style and ovary) - Ovary contains the ovule - Ovule contains the egg and the polar nuclei(future embryo and endosperm) |
|
|
Flowers - Anatomy |
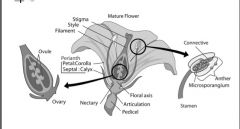
|
|
|
Gamete Formation |
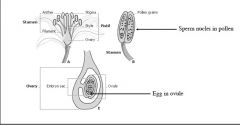
|
|
|
Pollination |
Movement of the pollen grain (male) onto stigma (female) |
|
|
Self-pollination |
Flower pollinates itself |
|
|
Cross-pollination |
Wind pollination Animal pollinators -Attracted by color, scent, and nectar -Bees, flies, moths and other insects,birds, and bats |
|
|
Flower Types - (Perfect flowers) |
- Both male and female components - Self or cross pollination - Mature at different times (cross) |
|
|
Flower Types - (Imperfect flowers) |
- Have either male or female parts(staminate and pistilate flowers) - Cross pollination |
|
|
Imperfect flowers - Monoecious plants |
Separate male and femaleflowers on the same plant(walnut and squash) |
|
|
Imperfect flowers - Dioecious plants |
Male flowers are on oneplant and female flowers ona different plant (carob trees,jojoba plant, and cannabis) |
|
|
Fertilization |
The joining of the sperm nucleus with the eggto produce the zygote. |
|
|
Seeds - Functions |
Development of a new plant -Embryo Food storage -Endosperm in monocots -Cotyledons in dicots |
|
|
Seeds – dicots and monocots |
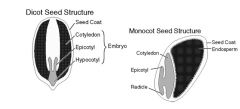
|
|
|
Seed Germination |
Growth of the embryo using foodstorage Activated by: -Water -Scarification -Smoke -Sunlight -etc. |
|
|
Fruit |
The structure that surrounds the seed or seeds -Dry Fruit -Fleshy Fruit |
|
|
Fruit - Functions |
Surrounds the seed Seed protection Seed dispersion -Water -Wind -Animals |
|
|
Fleshy fruits |
Invite consumption. Seeds travel in or onthe animal. |
|
|
Dry fruits |
Appendages that catch wind, animals, orwater for dispersal |
|
|
Auxins Fruit Ripening (hormones) |
- Produce fruit without seeds (tomato andcucumber)
- Low doses prevent fruit drop - High concentration activate fruit drop (apples,oranges) |
|
|
Gibberellins Fruit Ripening (hormones) |
- Increase the size of seedless grapes and stimulatebarley seed germination |
|
|
Cytokinins Fruit Ripening (hormones) |
- Slows down death used to prolong length of cutflowers. |
|
|
Ethylene gas Fruit Ripening (hormones) |
- Promotes flowering in pineapple - Stimulates fruit ripening (starch to sugar)apples, oranges, tomatoes, bananas,avocados. Pick green, store, applyethylene to ripen. |
|
|
Flowers and Fruit Structure |
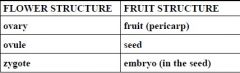
|

