![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
circumventricular organs
|
median eminence
vascular organ of lamina terminalis (close to nuclei that regulates blood volume; senses osomotic pressure differences by letting electrolytes into blood to adjust vasopressin) median eminence; important for feeding and metabolism neurohypophysis; releases hormones from hypothalamus |
|
|
anterior vs posterior pituitary
|
posterior; neurons stimulate neurohypophysis
anterior; nerves release hormones into first part of hypophyseal portal system; |
|
|
only nerve IN the cavernous sinus
|
VI; all others are in the lateral bone (III, IV, V1, V3
|
|
|
where does blood in the cavernous sinus go?
|
jugular -> anything that goes into cavernous sinus (i.e. hormones) ends up in the venous circulation
|
|
|
lateral nucleus
|
hunger center; destruction -> anorexia, failure to thrive (infants)
inhibited by leptin |
|
|
which area does leptin inhibit
|
lateral area
|
|
|
no leptin present
|
no latereal nucleuar inhibition -> constant hunger/obesity
|
|
|
ventromedial nucleis
|
satiety area; Desturction (craniopharyngioma) -> hyperphagia; stimulated by leptin
|
|
|
which nucleus does leptin stimulate
|
ventromedial area
|
|
|
leptin deficiency
|
make you fat
|
|
|
MCR4 gene deficiency
|
receptor for melanocortin; more common than leptin deficiency
results in obesity |
|
|
melanocortin
|
leptin gains entrance through median eminance; 2 receptors for leptin on neurons in arcuate nucleus
POMC/CART receptor (stimulated by leptin) NPY/AgRP receptor (inhibited by leptin) leptin decreases feeding |
|
|
POMC/CART
|
Leptin stimulates these neurons which inhibits hunger
decreased hunger |
|
|
NPY/AgRP
|
Leptin inhibits these which stimulate hunger
decreased hunger |
|
|
POMC
|
pro-opio-melanocortin
|
|
|
suprachiastmatic nucleus
|
circadian rhythm
you need sleep to be charismatic (chiasmatic) |
|
|
SCN clock machinery
|
Clock/BMAL, cryptochrome/period = heterodimers that regulate eachother and make up the SCN clock machinery
|
|
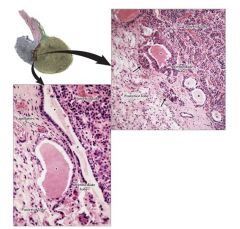
|
intermediate lobe
|
|
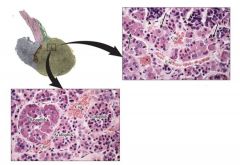
|
anterior pituitary
|
|
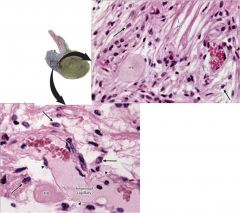
|
posterior pituitary
|

