![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
85 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
cerebrum |
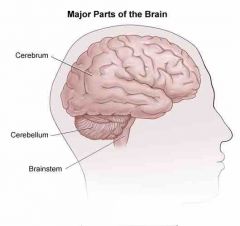
largest part of the brain that interprets all the senses including taste, touch, sight, smell, and hearing. other areas of the cerebrum are in charge of decision making, movement and speech |
|
|
cerebellum |
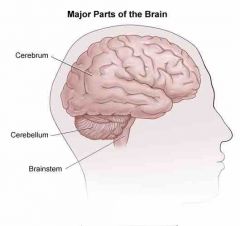
2nd largest part of the brain. controls basic movement, balance and posture |
|
|
brain stem |
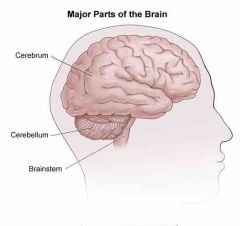
it's made up of the Pons and Medulla Oblongota. it connects the cerebrum to the cerebellum and the spinal cord. the brain stem is VITAL to survive because it control involuntary responses, like breathing |
|
|
frontal lobe |
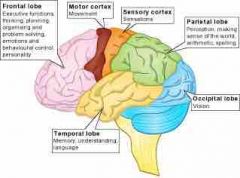
think and create. at the back of the frontal lobe lies the motor area which is responsible for controlling the body's movement |
|
|
parietal lobe |
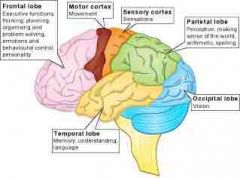
help us find our way and recognize objects and their uses. located in the front part of the parietal lobes lies most of the sensory area |
|
|
occipital lobe |
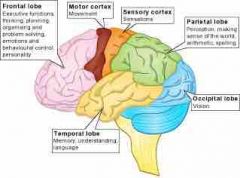
where messages from the eyes are received and interpreted |
|
|
temporal lobe |
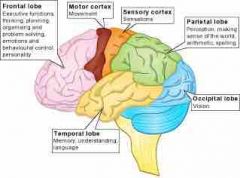
regulates our hearing, speech, and memory |
|
|
public health |
the science that deals with protecting and improving the health of the people in a community ex: obesity |
|
|
infection diseases |
those which can be spread from one organism to another ex: common cold
|
|
|
pathogens |
organisms and agents that cause infectious diseases ex: mosquitos |
|
|
noninfectious diseases |
diseases not spread from one organism to another ex: cancer |
|
|
parasitic |
an organism that lives on or in another organism and obtains nutrients from the hosts body tissue ex: lice |
|
|
toxin |
a poison that ate on a particular body system ex: ethanol |
|
|
viruses |
tiny particles of genetic material surrounded by a protein coat ex: ebola |
|
|
vaccines |
weakened or deactivated forms of a disease-causing agent that are introduced into the body to cause the immune system to produce antibodies that fight off the pathogen ex: chicken pox vaccine |
|
|
viruses |
tiny particles of genetic material surrounded by a protein coat ex: ebola |
|
|
vaccines |
weakened or deactivated forms of a disease-causing agent that are introduced into the body to cause the immune system to produce antibodies that fight off the pathogen ex: chicken pox vaccine |
|
|
immune system |
the organ system that protects the body from diseases |
|
|
vaccines |
weakened or deactivated forms of a disease-causing agent that are introduced into the body to cause the immune system to produce antibodies that fight off the pathogen ex: chicken pox vaccine |
|
|
immune system |
the organ system that protects the body from diseases |
|
|
white blood cells |
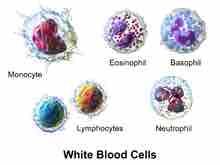
the blood cells that are specialized for fighting diseases |
|
|
vaccines |
weakened or deactivated forms of a disease-causing agent that are introduced into the body to cause the immune system to produce antibodies that fight off the pathogen ex: chicken pox vaccine |
|
|
immune system |
the organ system that protects the body from diseases |
|
|
white blood cells |
the blood cells that are specialized for fighting diseases |
|
|
macrophages |
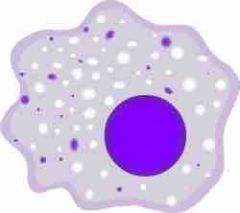
large whole blood cells that engulf and destroy pathogens |
|
|
infection |
the multiplication of a pathogen in body tissue ex: flu |
|
|
infection |
the multiplication of a pathogen in body tissue |
|
|
antibody |
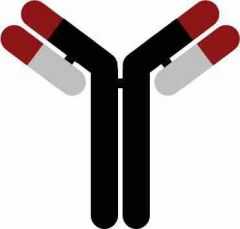
a y-shaped protein that attaches to a specific foreign substance |
|
|
vaccines |
weakened or deactivated forms of a disease-causing agent that are introduced into the body to cause the immune system to produce antibodies that fight off the pathogen ex: chicken pox vaccine |
|
|
immune system |
the organ system that protects the body from diseases |
|
|
white blood cells |
the blood cells that are specialized for fighting diseases |
|
|
macrophages |
large whole blood cells that engulf and destroy pathogens |
|
|
infection |
the multiplication of a pathogen in body tissue |
|
|
antibody |
a y-shaped protein that attaches to a specific foreign substance |
|
|
active immunity |
a disease that results from exposure to a specific pathogen ex: vaccine |
|
|
parasitic |
an organism that lives on or in another organism and obtains nutrients from the hosts body tissue |
|
|
passive immunity |
created by transferring antibodies made by one organism into another organism. ex: mother's breast milk to baby |
|
|
toxin |
a poison that ate on a particular body system |
|
|
viruses |
tiny particles of genetic material surrounded by a protein coat ex: ebola |
|
|
vaccines |
weakened or deactivated forms of a disease-causing agent that are introduced into the body to cause the immune system to produce antibodies that fight off the pathogen ex: chicken pox vaccine |
|
|
immune system |
the organ system that protects the body from diseases |
|
|
white blood cells |
the blood cells that are specialized for fighting diseases |
|
|
macrophages |
large whole blood cells that engulf and destroy pathogens |
|
|
infection |
the multiplication of a pathogen in body tissue |
|
|
antibody |
a y-shaped protein that attaches to a specific foreign substance |
|
|
active immunity |
a disease that results from exposure to a specific pathogen ex: vaccine |
|
|
parasitic |
an organism that lives on or in another organism and obtains nutrients from the hosts body tissue |
|
|
passive immunity |
created by transferring antibodies made by one organism into another organism. ex: mother's breast milk to baby |
|
|
antibiotics |
drugs that either kill bacteria or prevent their production |
|
|
toxin |
a poison that ate on a particular body system |
|
|
viruses |
tiny particles of genetic material surrounded by a protein coat ex: ebola |
|
|
vaccines |
weakened or deactivated forms of a disease-causing agent that are introduced into the body to cause the immune system to produce antibodies that fight off the pathogen ex: chicken pox vaccine |
|
|
immune system |
the organ system that protects the body from diseases |
|
|
white blood cells |
the blood cells that are specialized for fighting diseases |
|
|
macrophages |
large whole blood cells that engulf and destroy pathogens |
|
|
infection |
the multiplication of a pathogen in body tissue |
|
|
antibody |
a y-shaped protein that attaches to a specific foreign substance |
|
|
active immunity |
a disease that results from exposure to a specific pathogen ex: vaccine |
|
|
parasitic |
an organism that lives on or in another organism and obtains nutrients from the hosts body tissue |
|
|
passive immunity |
created by transferring antibodies made by one organism into another organism. ex: mother's breast milk to baby |
|
|
antibiotics |
drugs that either kill bacteria or prevent their production |
|
|
nonspecific immune response |
includes the 1st two lines of defense which which are the barriers to infection and the inflammatory response ex: skin and swelling/redness |
|
|
toxin |
a poison that ate on a particular body system |
|
|
viruses |
tiny particles of genetic material surrounded by a protein coat ex: ebola |
|
|
vaccines |
weakened or deactivated forms of a disease-causing agent that are introduced into the body to cause the immune system to produce antibodies that fight off the pathogen ex: chicken pox vaccine |
|
|
immune system |
the organ system that protects the body from diseases |
|
|
white blood cells |
the blood cells that are specialized for fighting diseases |
|
|
macrophages |
large whole blood cells that engulf and destroy pathogens |
|
|
infection |
the multiplication of a pathogen in body tissue |
|
|
antibody |
a y-shaped protein that attaches to a specific foreign substance |
|
|
active immunity |
a disease that results from exposure to a specific pathogen ex: vaccine |
|
|
parasitic |
an organism that lives on or in another organism and obtains nutrients from the hosts body tissue |
|
|
passive immunity |
created by transferring antibodies made by one organism into another organism. ex: mother's breast milk to baby |
|
|
antibiotics |
drugs that either kill bacteria or prevent their production |
|
|
nonspecific immune response |
includes the 1st two lines of defense which which are the barriers to infection and the inflammatory response ex: skin and swelling/redness |
|
|
specific immune response |
this is the 3rd line of defense, which is the immune response-where the t-cells and b-cells help fight pathogens ex: t-cells and b-cells |
|
|
toxin |
a poison that ate on a particular body system |
|
|
viruses |
tiny particles of genetic material surrounded by a protein coat ex: ebola |
|
|
vaccines |
weakened or deactivated forms of a disease-causing agent that are introduced into the body to cause the immune system to produce antibodies that fight off the pathogen ex: chicken pox vaccine |
|
|
immune system |
the organ system that protects the body from diseases |
|
|
white blood cells |
the blood cells that are specialized for fighting diseases |
|
|
macrophages |
large whole blood cells that engulf and destroy pathogens |
|
|
infection |
the multiplication of a pathogen in body tissue |
|
|
antibody |
a y-shaped protein that attaches to a specific foreign substance |
|
|
active immunity |
a disease that results from exposure to a specific pathogen ex: vaccine |

