![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
82 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
blunting of the calyces
|
pyelonephritis; get blunted under the scarred/contracted tissue
|
|
|
fever, rash, oliguria, pyuria (esosinophils) after a pt is put on a drug (methicillin)
|
acute drug induced interstitial nephritis
stop the drug (combo type I and IV hypersensitivity) |
|
|
nephrosclerosis
|
caused by chronic hypertension which causes hyaline arteriosclerosis in the kidney
|
|
|
pt w headache, blurry vision,
paiplladema, malignant htn |
"flea bitten kidney" red and black
This is called a flea-bitten kidney and is associated with glomerular damage, glomerulitis, arteriolitis and hemorrhage in a case of malignant hypertension. onion skinning arteriosclerosis, petechiae (ruptured blood vesels); petechial lesions on cortex |
|
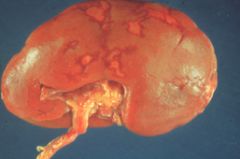
in a pt w irregular irregular pulse
|
Multiple pale renal infarcts
Note the irregular white areas on the cortical surface. Most infarcts occur from embolic disease from the left heart. |
|
|
pt w a renal mass. Pt is a smoker and obese.
labs show polycythemia and hypercalcemia |
renal cell carcinoma (VHL on chromosome 3, polyognal clear cells full of glycogen, paraneoplastic syndromes (ectopic EPO = polycythemia, PTHrP = hypercalcemia)
|
|
|
kid with unilateral flank mass and hypertension
|
wilms tumor
htn bc tumor is making renin chromosome 11 |
|
|
aniridia (absent iris) and one limb greater than the other
|
wilms tumor; chromosome 11
|
|
|
painless hematuria
|
bladder cancer (transitional cell)
|
|
|
baby w potters facies (flattened nose, low-set ears, and recessed chin)
|
ARPKD
|
|
|
hx of HTN, abnormality of ultrasound in the renal pelvis,
and had click murmur (therefore MVP) – dx? |
ADPKD
|
|
|
pt with HTN, abnormality on ultrasound in renal
area, lost 600 mls of blood all of a sudden, leading to hematochezia (MCC hematochezia = diverticulosis). |
Diverticulosis
associated w ADPKD |
|
|
how does an increase or decrease in capillary oncotic pressure affect GFR
|
increase = decreases GFR (reaches equilibrium faster)
decrease = increases GFR (takes longer to reach equilibrium) |
|
|
how does an increase or decresae in Kf affect GFR
|
increase Kf = increseased GFR (more can filter across bc o fincreased permeability)
decreased Kf = decreased GFR (less can filter across) |
|
|
how does afferent dilation or constriction affect hydrostatic pressure and renal plasma flow
|
afferent dilation = increased hydrostatic pressure, increased renal plasma flow
afferent constriction = decreased hydrostatic pressure, decreased renal plasma flow |
|
|
affects of efferent constriction and dilation on cap hydrostatic pressure
|
e. c. = increased hydrostatic pressure
e. d. = decresaed hydrostatic pressure |
|
|
tinnitus
|
salicylate poisoning
|
|
|
dense calcification of kidney
|
compication of chronic pyelonephritis
|
|
|
differentiate acute vs chronic pyelonephritis other than time frame
|
APN = fever, spares cortex
CPN: assymetrical scarring, blunted calyces, thyroidization of kidney (eosinophilic casts) |
|
|
primary pathogen capable of causing UTI + liver abscess and pneumonia in otherwise healthy people.
|
klebsiella pneumoniae
|
|
|
K capsular antigen
|
anti-phagocytic
|
|
|
electron dense deposits composed of Ig and complemtn within the basement membrane
|
MPGN II (dense deposit disease)
|
|
|
does MPGN type I or II involve complement activation
|
II
|
|
|
subepithelial deposits
|
acute GN (post streptococcal = subendothelial humps)
|
|
|
Epimembranous deposits
|
Membranous GN
|
|
|
Subendothelial deposits
|
lupus glomerulonephritis (diffiuse proliferative)
|
|
|
deposits in mesangium
|
IgA nephropathy/Henoch-Schonlein GN
|
|
|
fibromuscular dysplasia
|
stenotic renal artery; mc in YOUNG WOMEN
|
|
|
embryonic glomerular structures
|
Wilms tumor (deletions involving WT1 located on c11)
|
|
|
enlarging abdominal mass w normal VMA
|
Wilms tumor (deletions involving WT1 located on c11)
|
|
|
WAGR complex
|
Wilms tumor, aniridia, genitourinary malformation, mental motor retardation
|
|
|
19 y/o male w dysuria and yellow green urethral discharge; play odds
|
nongonococcal urethritis (more common than gonococcal)
i.e. chlaymdiae (intracellular) |
|
|
High fractional excretion of sodium indicates what
|
Post renal (can't reabsorb sodium)
>4% >40 urine Na |
|
|
Low fractional excretion of sodium indicates what
|
Pre-renal
<1% <10 urine Na |
|
|
leukocytes and neutrophils
|
tubulointerstitial nephritis
|
|
|
pulmonary congestion
|
due to fluid overload in acute glomerulonephritis
|
|
|
uniformly progresses to chronic renal failure if untreated
|
diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis (SLE)
mcc of death in SLE |
|
|
why would a pt be hypocalcemic in chronic renal failure
|
decreased calcitriol synthesis -> hypocalcemia
secondary hyperparathyroidism -> hypercalcemia, phosphauria |
|
|
management of hyponatremia
|
water restriction
|
|
|
management of hyperphosphatemia
|
phosphate binders (niital)
|
|
|
management of hypervolemia
|
decreased salt and water intake + loop diuretics
|
|
|
this dz is due to hyperparathyroidism and is associated w myopathy
|
Osteitis fibrosa
|
|
|
Adynamic bone disease
|
oversuppression of PTH
|
|
|
Suppressor of PTH production
|
1,24 dihydroxyvitamin D? not sure
|
|
|
hematuria time frame in APSGN vs IgA nephropathy
|
IgA = fast, very close
APSGN = 10 days or more after infection (often a cutaneous infection) |
|
|
pathologic features of predominant small artery involvement w intimal proliferation and sometimes thrombosis also termed "thrombotic microangiopathy" is found in which renal dzs
|
HUS, TTP, scleroderma, sickle cel nephropathy, malignnat htn
the primary process is endothelial damage |
|
|
why dont give loop diuretic sin nephrotic syndrome
|
high dose loop diureics can precipitate renal failure in nephrotics bc the intravascular volume cannot be defende dby hypoalbuminemia (thus you accelerate hypoalbuminemia worsening fluid status)
|
|
|
causes of euvolemic hyponatremia
|
SIADH
|
|
|
causes of hyponatremia w low urine sodium
|
CHF (decreased renal perfusion = decreased perfusion)
|
|
|
pt w hypertension, alkalosis, hypokalemia
|
Hyperaldosteronism (Conns syndrome)
|
|
|
diagnosis of medullar sponge kidney
|
IVP
|
|
|
function of the urine anion gap
|
differentiates renal from nonrenal causes of nongap acidosis
|
|
|
Pseudohyponatremia
|
associated w elevated lipids, glucose or plasma proteins
|
|
|
causes of hypervolemic hyponatremia
|
CHF, cirrhosis and nephrotic syndrome, massive edema of any cause
|
|
|
causes of isovolemic hyponatremia
|
SIADH, cerebral trauma
|
|
|
selective proteinuria
|
minimal change dz
|
|
|
prognosis of minimal change
|
good; responds to steroids
|
|
|
prognosis of ASGN
|
often resolves spontaneously
|
|
|
prognosis of RPGN
|
bad
|
|
|
prognosis of DPGN
|
bad (lupus)
|
|
|
what should you not use to tx malignant htn
|
ACe inhibitor (can bottom out GFR = renal failure)
|
|
|
stones in alkaline urine
|
ammonium magnesium phosphate (struvite)
|
|
|
lithium association
|
nephrogenic diabetes insipudus
|
|
|
how to differentiate nephrogenic diabetes insipudus from central diabetes isnipudus?
|
desmopressin injection
if central, will increase urine conc if nephrogenic, no effect |
|
|
ADH MAO
|
sitmulates production of cAMP -> insertion of aquaporins on apical surface of collecting ducts
|
|
|
waxy casts w very low urine flow
|
CESRD
|
|
|
WBC casts in urine
|
acute pyelonephritis or cystitis
|
|
|
vasculitis from exposure to endotoxin causing glomerular thrombosis
|
Schwartzman reaction (following second exposure to endotoxin)
|
|
|
Urethritis, conjunctivitis, arthritis in a male
|
Reiter's syndrome (reactive arthritis associated w HLA-B27)
|
|
|
Streak ovaries, congenital heart disease, horseshoe kidney
|
Turner syndrome (XO, short stature, webbed neck, lymphedema)
|
|
|
renal cell carcinoma, hemangioblastomas, angiomatosis, pheochromocytoma
|
VHL disease (dominant tumor suppressor gene mutation)
|
|
|
Red urine in the morning
|
paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
|
|
|
Polyuria, acidosis, growth failure, electrolye imbalances
|
Faconi's syndrome (proximal tubular reabsorption defect)
|
|
|
Palpable purpura, joint pain, abdominal pain (child)
|
Henoch-Shonlein purpura (IgA vasclitis affecting skin and kidneys)
|
|
|
Hypertension, hypokalemia, metabolic acidosis
|
Conn's syndroem (primary hyperaldosteronism)
|
|
|
deep, labored breathing/hyperventilation
|
Jussmaul breathing (diabetic ketoacidosis)
|
|
|
free water clearance
|
Defined as the volume of distilled water that would have to be added to or subtracted from the volume of urine produced in one minute so as to make that urine isomotic with plasma.
(-) free water clearance = concentrated urine (+) free water clearance = dilute urine (0) free water clearance = isomotic urine |
|
|
Cockcroft-Gault Prediction of Creatinine Clearance
|
CCr = 140 - AgxWt/Plasma creatinine x 72
for women multiply by .85 |
|
|
clinical examples of neurogenic flaccid bladder
|
CONUS MEDULLARIS OR CAUDA EQUINA SYNDROMES; NEOPLASM;
HERNIATED (EXTRUDED) DISC; DIABETES MELLITUS; MOTOR RADICULOPATHY |
|
|
The bladder frequently becomes distended,
the wall thins, and bladder tone decreases. However, some residual contractions remain because of the intrinsic contractile response of smooth muscle to stretch. As a rule, residual volume is present after urination. Incontinence is present, and urinary retention occurs. Perianal sensation, and the anal and bulbocavernous reflexes are abolished. Bladder volume is increased, but bladder pressure is decreased |
flaccid neurogenic bladder
|
|
|
Bladder volume is often
reduced and reflex hyperactivity may lead to a state of spastic neurogenic bladder, in which the bladder fills to a set point, and then spontaneously empties whether it is convenient for the patient or not. Perianal sensation is preserved, and the anal and bulbo- cavernous reflexes are normal. Bladder intravesical pressure is increased but bladder volume is decreased. |
spastic neurogenic bladder; frequent UTis bc of residual volume
In addition, during the period of overflow incontinence before the voiding reflex is re-established, these patients must be catheterized frequently, further predisposing them to urinary tract infections. The level of the lesion is between the lower brainstem or spinal cord above the level of the conus medullaris. |
|
|
what do the anal or bulbocavernous reflex measure
|
These reflexes measure the integrity of S2, 3, and 4.
|

