![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Pre-renal
|
Kidneys not getting enough perfusion (hemorrhage, shock, medications -> use hx and pe to estbalish diagnosis)
|
|
|
Post-renal
|
obstruction of outflow of urine; if obstruction unilateral healthy kidney can mask the problem; obstructions in kidney urteter or bladder caused by stone, clot, tumor, extrinsic ocmpression of from tumor, hematoma, fibrosis
hydronephrosis = swelling of one kidney due to backup of urine |
|
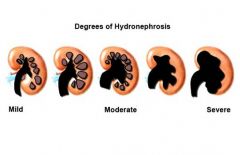
hydronephrosis
|
back up of urine into kidney bc of obstruction (post renal)
|
|
|
tubule
|
permits reabsorbsion of filtered fluid which is needed to maintain osmolarity
|
|
|
Primary hyperaldosternoism (high bp, low renin)
|
High aldosterone -> Na reabsorption -> increased ECF/blood volume/blood pressure -> increased renal perfusion -> decreased renin levels
|
|
|
Hormone levels in Cushings
|
Entire adrenal cortex oversecreting hormones; elevated aldosterone and cortisol
|
|
|
Conn syndrome
|
Adrenal gland releasing too much aldosterone
increased Na+ reabsorption in principal cells -> increased ECF volume -> increased venous return -> increased cardiac output (frank starling) -> increased arterial pressure |
|
|
Why might urinary excretion be normal in hyperaldosteronism?
|
Increased aldosterone -> increased ECF volume via Na+ reabsorption -> ECF volume expansion inhibits Na+ rebasorption in proximal tubule = normal urinary Na excretion
this is called mineralcorticoid escape |
|
|
Mineralcorticoid Escape Mechanisms
|
1. ECF volume expansion inhibits renal sympathetics = inhibition of Na reabsorption in the prox tubule
2. Diluted protein concentration in peritubular capillaries = decreased oncotic = decreased sodium/water reabsorption 3. Venous return to heart = ANP release = dilates renal afferent arterioles and constricts renal efferents -> increased GFR, more Na filtered and thus excreted |
|
|
skeletal muscle weakness
|
hypokalemia; low ECF K hyperpolarizes cells making it harder to fire/contract muscles
|
|
|
primary treatment for SIADH
|
water restriction; if pt restricts water intake then heyperosomoti urine is approriate.
if he drinks large quantiites however his kidneys will not be able to make appropriatey dilute urine (bc of his permanently high ADH state) and he will become hyponatremic and hyposmolar again |

