![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
123 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Process of forming human cells. Man produce sperm and women produce oocytes |
Gametogenesis |
|
|
How many chromosomes Human somatic have |
23 |
|
|
Which cells contain 23 pairs of chromosomes? Diploid or haploid |
DIPLOID |
|
|
Contain genes that code for cellular function and human characteristics like skin, eye color,height |
Autosome |
|
|
Contain genes that code for male or female sex |
Sex chromosome |
|
|
How many daugther cells the process of mitosis yield |
2 |
|
|
How many daughter cells the process of meiosis yields |
4 |
|
|
Fusion of male and female gametes |
Fertilization |
|
|
How many pairs of autosomes are found in human somatic cells |
22 |
|
|
Somatic cell division |
Mitosis |
|
|
Sex cell division |
Meiosis |
|
|
Produces daugther cells that are diploid |
Mitosis |
|
|
Produces daugther cells that are haploid |
Meiosis |
|
|
Cell division that Includes a process called passing over |
Meiosis |
|
|
A chromosome that initially has 2 identical sisters chromatids joined at the centromere |
Replicated chromosome |
|
|
A homologous material chromosome and paternal chromosome |
Pair of chromosomes |
|
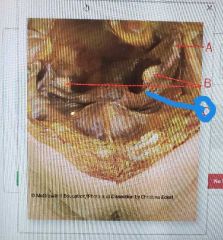
|
Uterine tube |
|
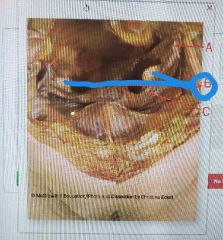
|
Ovaries |
|
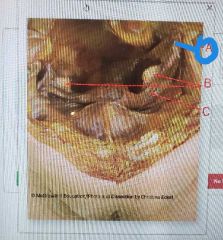
|
Fibriae |
|
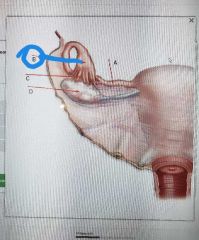
|
Infundibulum |
|
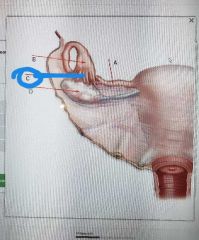
|
Fiambriae |
|
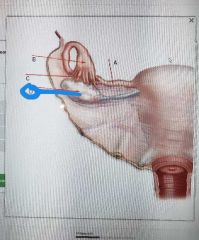
|
Ovary |
|
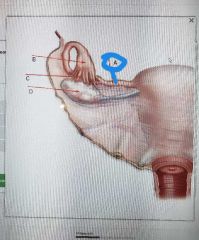
|
Uterine tube |
|
|
Inner portion of the ovaries known |
Medulla |
|
|
Most primitive follicle. Consist of a primary oocyte surrounded by a layer of follicle cell. |
Primordial follicle |
|
|
Forms from primary follicle. Consist of a primary oocyte, layers of granuloma cells and antrum |
Secondary follicle |
|
|
Forms from secondary follicle. Completed meiosis 1 |
Mature or tertiary follicle |
|
|
Forms from remanants of mature follicle. It secretes progesteron and estrogen |
Corpus lutem |
|
|
Formed from corpus luteum. White connective tissue. Most structure absorbed |
Corpus albicans |
|
|
Maturation of primary oocyte to secondary oocyte |
Oogenesis |
|
|
3 phases of ovarian cycle |
Follicular Ovulation Luteal |
|
|
4 segments of the uterine tube |
Infundibulum Ampulla Isthmus Uterine part |
|
|
Function of uterine tube |
Transport ovulated oocyte to uterus |
|
|
Segment where fertilization occurs |
Ampulla segment of uterine tube |
|
|
4 anatomic regions of uterus |
Fundus Body Isthmus Cervix |
|
|
The follicles are found in the ovarian ____ |
Cortex |
|
|
What gland produces seminal plasmin and PSA |
Prostate gland |
|
|
Alternative names for uterine tubes |
Fallopian tubes Oviducts |
|
|
When oogenesis begins |
Before birth |
|
|
When ovulation begins |
At puberty |
|
|
3 major accesory glands of the male reproductive system |
Seminal vesicles Prostate gland Bulborethral gland
|
|
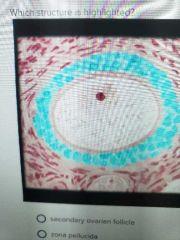
|
Granylosa cells |
|
|
List where Sperm passes through to the external environment |
Seminiferous tubule Epididymis Vas deferens Ejaculatory duct Urethra |
|
|
What component of the Male duct system stores sperm until fully mature |
Epididymis |
|
|
What component of the male duct system has thick walls and enlarges to form ampulla, and is neccessary for moving sperm |
Ductus deferens |
|
|
What substance the seminal vesicles produce |
Alkaline fluid with fructose and prostaglandins |
|
|
What substance the prostate gland produce |
Seminal plasmin and PSA (prostate specific antigen) |
|
|
Hormones involved in spermatogenesis |
Gnrh Fsh and LH ABP Testosterone Inhibin |
|
|
Main steps of spermatogenesis |
1. Spermatid becomes mature 2. Excess cytoplasm shed and nucleus elongates 3. Acrosone cap forms over nucleus 4. Tail forms from orginised tubules |
|
|
Order of how immature sperm passes through and out of the testes |
Seminiferous tubule Rete testis Efferent ductile Epididymis |
|

|
Endometrium |
|
|
involves a single cell division and results in two diploid cells |
Mitosis |
|
|
What is the normal chromosome number in a human cell? |
46 |
|
|
Involves two cell divisions and result in 4 haploid daughter cells |
Meiosis |
|
|
What occurs before mitosis or meiosis? |
DNA replication |
|
|
During meiosis, homologous pairs of chromosomes can exchange pieces of DNA after they _____ |
SYNAPSE |
|
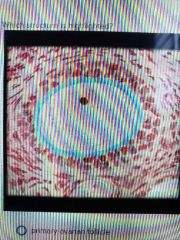
|
Zona pellucida |
|

|
Sperminiferous tubule |
|

|
Spermatic cord |
|
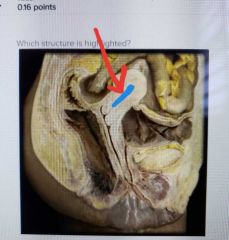
|
Uterine cavity |
|
|
The process of homologous pairing al ok ng the length of chromosomes during meiosis is known as____ |
Synapsis |
|
|
What is exchanged during crossing over? |
Genetic material |
|
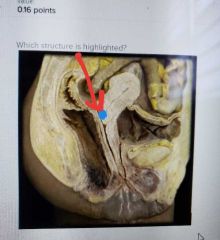
|
External OS |
|
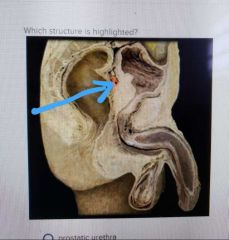
|
Seminal vesicle |
|
|
Which cells produce testosterone |
Interstitial cells |
|
|
How many sperm are produced in the testes each day? |
60 million |
|
|
Which duct of the male reproductory system passes through the prostate gland? |
Ejaculatory ducts |
|

|
Secondary follicle |
|

|
Corona radiata |
|
|
Different orientation of chromosomes along the cell equator during metaphase 1, resulting in gametes with different combinations of parental chromosomes is known as ____ |
Independent assortment |
|
|
Gonadrotropic releasing hormone is released by the ___ |
Hypothalamus |
|
|
What hormone e prevents degeneration of the corpus luteum? |
Human chorionic gonadotropin |
|
|
Decreasing levels of ____ lead to sloughing, or shedding of the endometrial linning |
Progesterone |
|
|
By What ligament is the ovary attached to the uterus and is held in place by what other ligament |
Ovarian , suspensory |
|
|
Where the ovarian follicles found |
Cortex of the ovary |
|
|
Clitoris |
|

|
Suspensory ligament |
|
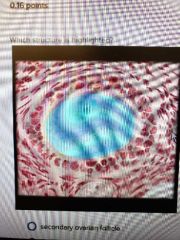
|
Primary oocyte |
|
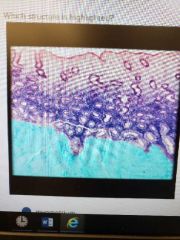
|
Myometrium |
|
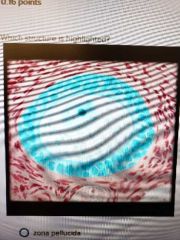
|
Primary ovarian follicle |
|
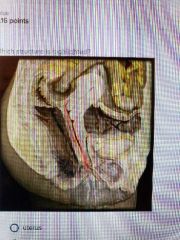
|
Vagina |
|
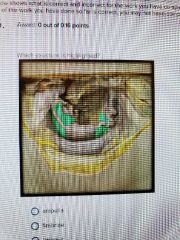
|
Broad ligament |
|
|
What is the name of the germ cell from wich sperm arise |
Spermatogonia |
|
|
Secondary spermatocytes divide to form |
Spermatids |
|
|
The nongerm cells of the seminiferous tubule epithelium are known as____ |
Sustentacular cells |
|
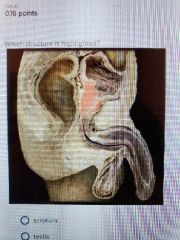
|
Prostate |
|
|
Correct sequence of embryonic stages |
Zygote Morula Blastocyst Embryoblast |
|
|
What stimulates the secondary oocyte to complete meiosis 2 |
When a sperm. Cell penetrates the oocyte membrane |
|
|
Which 2 hormones influence the endometrium to thicken and prepare for implantation |
Progesterone and estrogen |
|
|
What is the production of immature oocytes in the ovary called? |
Oogenesis |
|
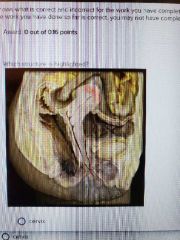
|
Fundus |
|
|
3 stages of labor |
Early and late dialation Expulsion Placental |
|
|
Product of fertilization |
Zygote |
|
|
Diploid cell produced when ovum and sperm pronuclei fuse |
Zygote |
|
|
What phase of preembrionic period sperm penetrates secondary oocyte. It completes meiosis 2 resulting on ovum and sperm plasma fuse |
Fertilization |
|
|
Where implantation occurs |
Functional layer of endometrium of uterus |
|
|
Chromosomes pairs arranged by size and similar features |
Karyotype |
|
|
Variants of 1 gene found at same locus on homologous chromosomes |
Allales |
|
|
Allele that expresses or physically shows the trait |
Dominant allele |
|
|
Allele that has the trait masked |
Recessive |
|
|
Hormone that plays a role in lenght of pregnancy and timminng of birthing |
CRH |
|
|
What hormone stimulates the thyroid to increase the women metabolic rate during pregnancy? |
HCT |
|
|
Hormone that influence breast milk production |
OXYTOCIN |
|
|
What hormone promotes blood vessels growth in the uterus during pregnancy? |
RELAXIN |
|
|
What hormone induce lactation during pregnancy? |
HPL |
|
|
Cells of the epiblasst migrate and form 3 primary germ layers |
Gastrulation |
|
|
3 types of germ layers formed through the process of gastrulation |
Ectoderm Mesoderm Endoderm |
|
|
Physiological conditioning that sperm must underg ok before they can accomplish fertilization |
Capacitation of sperm |
|
|
When is Fetal period ? |
The Third month to birth |
|
|
Which hormone Induce lactation, inhibit the effects of insulin, and affect how pregnant women metabolizes certain nutrients |
Human placenta lactogen (HPL) |
|
|
Component of the blastocyst that will form the chorion |
Trophoblast |
|
|
What thin membrane, continuous with the epiblast layer, secretes fluid to bathe the embryo? |
Amnion |
|
|
At 16 cell stage , the conceptus is known as a____ |
Morula |
|
|
Men or women produce more gametes that are similar en size? |
Men |
|
|
What Process takes place in the seminiferous tubules. It includes two meiotic divisions, where mature spermatozoa are haploid |
Spermatogenesis |
|
|
Which male reproductive structure is umparired(only 1 in the body)? |
Prostate gland |
|
|
What months consist the second trimester |
4-6 |
|
|
The trimester duri g which an e.bryo becomes a fetus |
First trimester |
|
|
Secretory structures that produce milk in a lactating female |
Alveoli |
|
|
A Female first menstrual cycle |
Menarche |
|
|
What enclose the ovary at the time of ovulation |
Fimbriae |
|
|
What phase is constant in lenght, although the lenght of menstrual cycle varies, menstruation always occurs 14 days after ovulation |
Secretory phase |
|
|
A secondary oocyte is arrested in what phase of meiosis |
Metaphase 2 |

