![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
135 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
4 concentric layers of Gi tract tube |
Mucosa Sunmucosa Muscularis Adventitia or serosa |
|
|
What the Portion of the serous membrane that lines the in inside surface of the body wall called? |
Parietal peritoneum |
|
|
Process of moving ingested materials from the oral cavity to the stomach. Aka swallowing |
Deglutition |
|
|
3 pairs of multicellular salivary glands located external to the oral cavity |
Paratoid Sublingual Submandibular |
|
|
6 general functions of digestive system |
1. Ingestion 2. Motility 3. Secretion 4. Digestion 5. Absorbtion 6. Elimination |
|
|
6 organs that make up GI tract |
Oral cavity Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine |
|
|
Accessory organs Involved in the digestive process |
Teeth Tongue Gall bladder |
|
|
Nerve plexus in the submucosa layer |
Meissner plexus |
|
|
Nerve plexus in the muscularis layer |
Myenteric plexus |
|
|
Thickened circular muscles it closes of the lumen at some point to control movement of material into next section |
Sphincter |
|
|
2 types of motility |
Peristalsis Mixing |
|
|
Motility |
To propel material through the lumen |
|
|
Portion that covers surface of internal organs |
Visceral peritoneum |
|
|
5 mesenteries |
Greater omentum Falciform ligament Lesser omentumFalciform ligamentMenestery Menestery proper Mescolon
|
|
|
Organs within abdomen completely surrounded by visceral peritoneum |
Intraperitoneal organs |
|
|
Organs that lie outside the parietal peritoneum against posterior abdominal wall |
Retroperiotenal organs |
|
|
2 types of receptors of the digestive tract |
Baroreceptor Chemoreceptors |
|
|
What kind of receptor detect either stretch or pressure of particular region |
Baroreceptor |
|
|
Receptor that detect precense of specific substance of passing contents within lumen |
Chemoreceptors |
|
|
3 hormones that participate in regulating digestion |
Gastrin Secretin Chlocystokinin |
|
|
3 major salivary glands |
Paratoid Submandibular Sublingual |
|
|
Part of the oral cavity that is involved In Sense of taste |
Papilla of tonge |
|
|
What moves the tonge |
Intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tonge |
|
|
What nervous system react during exercise or individual is excited or anxious .increase of viscous saliva due to constricted salivary glands decrease of water |
Sympathetic nervous system |
|
|
What nervous system makes sure that oral cavity remains moist by input from mechanoreceptors and chemoreceptors |
Parasympathetic nervous system |
|
|
Structure of the pharynx that prevents food going up the nose? |
Nasophanrynx |
|
|
What part of the stomach Allow it to expand greatly when it is filled |
Gastric folds Rugae |
|
|
What enzyme saliva glands release to brake down carbohydrates |
Amylase |
|
|
After the bolus has been completely processed In the stomach, what is the product called? |
Chyme |
|
|
Small narrow superior entryway into the stomach lumen from the esophagus |
Cardia |
|
|
Inferior covex curvature border of the stomach |
Greater curvature |
|
|
Superior concave border of the stomach |
Lesser curvature |
|
|
Regulation phase that is initiated by the thought, small, sight or taste of food |
Cephalic phase |
|
|
Regulation phase that is initiated as food enters the stomach |
Gastric phase |
|
|
Regulation phase that is initiated by presence of acidic chyme induodenum |
Intestinal phase |
|
|
3 smooth layers of the muscularis of the stomach |
Inner oblique Middle circular Outer longitudinal |
|
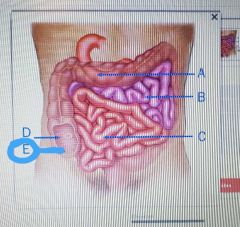
|
Cecum |
|
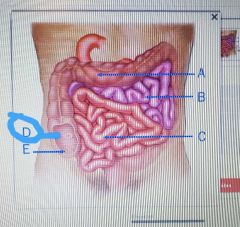
|
Ileocecal valve |
|
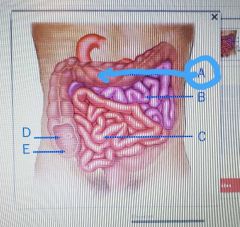
|
Deudenum |
|
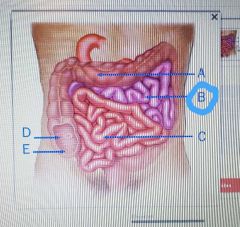
|
Jejunum |
|
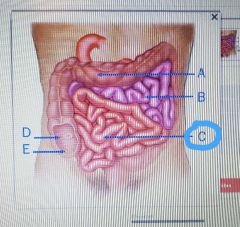
|
Ileum |
|
|
3 Important accessory digestive organs |
Liver Pancreas Gallbladder |
|
|
Hormone that causes release of alkaline solution containing HCO3 to neutralize acidic chyme |
Secretin |
|
|
Hormone that stimulates the smooth muscle in the gallbladder wall to contract to release bile |
CCK Cholecystokinin |
|
|
Composed of microvili. edge like that holds enzymes that complete chemical digestion of nutrients |
Brush border |
|
|
Lymphatic capillary within the villus. Absorbs lipids and lipid soluble vitamins |
Lacteal |
|
|
Mixes chyme with accessory gland secretions through back and forward motion |
Segmental movement |
|
|
Small channel that transports bile produced by hepatocytes |
Bile canaliculi |
|
|
Transports oxygenated blood to liver |
Hepatic arteries |
|
|
Where the hepatic vein empty to |
Inferior venacaba |
|
|
What vessel transport deoxygenated nutrient rich blood from capillary bed of GI tract , spleen and pancreas to liver |
Hepatic portal veins |
|
|
3 regions of large intestines |
Cecum Colon Rectum |
|
|
Wich carbohydrate is a disaccharide found in table sugar? |
Sucrose |
|
|
Most organic biomolecules needed by organisms to grow and maintain homeostasis |
Nutrients |
|
|
3 major biomolecules |
Lipids carbohydrates Proteins |
|
|
Substances absorbed across wall of large intestine |
Vitamin B and K |
|
|
3 classes of carbohydrates related to digestion |
Monossacharides Disaccharides Polysaccharides |
|
|
Enzyme that digest starches |
Amylase |
|
|
Enzyme that digest nucleic acids |
Nucleases |
|
|
Components of bile |
Water Bicarbonate ions Bile salts Bile pigments Cholesterol Lecitin Mucin |
|
|
4 type of nutrients |
Macronutrients Micronutrient Non essential Essential |
|
|
3 Organic biomolecules or macronutrients |
Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins
|
|
|
2 micronutrients |
Vitamins Minerals |
|
|
Whose function is to provide glucose to be broken down to release energy |
Carbohydrates |
|
|
What macronutrient has the function of energy storage? |
Lipids |
|
|
3 types of carbohydrates |
Sugars Starch Fiber |
|
|
3 types of lipids |
Triglycerides Phospholipids Steroids |
|
|
3 categories of triglyceride |
Saturated fatty acids Unsaturated fatty acids Polyunsaturated fatty acids |
|
|
2 fatty acids that the body needs but can not synthesize |
Alpha-linoleic Linoleic acid |
|
|
When equilibrium exist between diatary intake and its lost in urine and feces |
Nitrogen balance |
|
|
2 categories of vitamis |
Water or fat soluble Essential or no essential |
|
|
Water soluble vitamins |
B C |
|
|
Fat soluble vitamins |
A D E K |
|
|
What type of vitamin is absorbed into the blood from the digestive tract |
Water soluble |
|
|
What type of vitamin is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and enter lymphatic capillaries |
Fat soluble |
|
|
Inorganic ions that are diverse functions in the body |
Mineral |
|
|
Required amount of major minerals |
Greater than 100ml a day |
|
|
Required amount of trace minerals |
Less than 100mg a day |
|
|
Function of insulin on liver |
Increase glycogenesis |
|
|
Function of insulin on muscle |
Increase glycogenesis |
|
|
Function of insulin on adipose connective tissue |
Stimulates lipogenesis |
|
|
Function of insulin on most cells |
Increase amino acids uptake |
|
|
When nutrients are released into the blood from their storage in various body tissues |
During postabsorbative state |
|
|
Function of glucagon on liver |
Increases glycogenolysis and increase gluconeogenesis |
|
|
Function of glucagon on adipose connective tissue |
Increase lipolysis |
|
|
How VLDL(very low density lipoprotein) and LDL (low density lipoprotein) are transported |
From liver to peripheral tissues |
|
|
How HDL (high density lipoprotein) is transported |
From peripheral tissues to liver |
|
|
How chylomicrons are transported |
Within lymph enters venous blood to deliver lipids to liver and other tissues |
|
|
Oxidise glucose to produce 2 pyruvate, 2 ATP and 2 NADH. |
Glycolysis |
|
|
Convert pyruvate to acetyl COA, CO2, NADH |
Intermediate stage |
|
|
Acetyl COA forms 2 CO2,ATP, 3 NADH, FADH |
Citric acid cycle |
|
|
Form 34 ATP , NADH,FADH |
Electron transport system |
|
|
Which hormones inhibit gastric gland secretion |
Secretin Gastric inhibitory peptide Cholecystokinin |
|
|
Duodenum ph of less than 2 inhibits or promotes secretion of the gastric glands? |
Inhibits |
|

|
Major duodenal papilla |
|
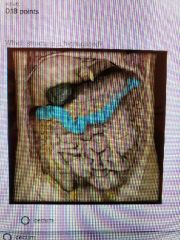
|
Transverse colon |
|
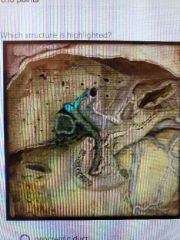
|
Hepatic duct |
|
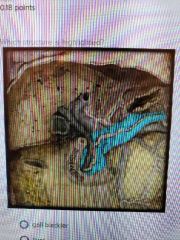
|
Pancreas |
|

|
Muscularis mucosae |
|
|
What cell of the gastric glands produces pepsinogen |
Chief cells |
|
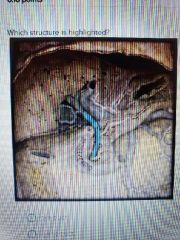
|
Bile duct |
|
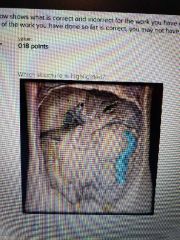
|
Descending colon |
|
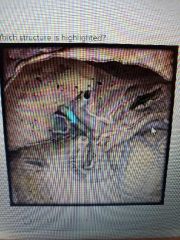
|
Common hepatic duct |
|

|
Body of pancreas |
|
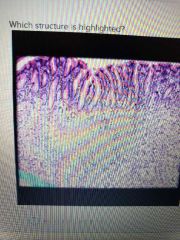
|
Muscularis mucosae |
|
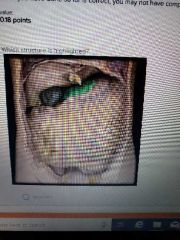
|
Lesser omentum |
|
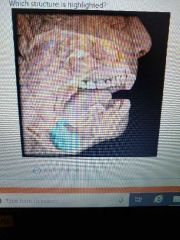
|
Submandibular salivary glands |
|
|
Which cells type is responsible for HCL production in the stomach? |
Parietal cells |
|
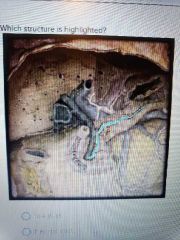
|
Pancreatic duct |
|
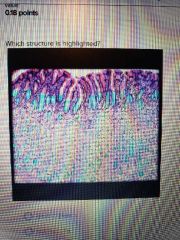
|
Gastric glands |
|

|
Muscularis externa |
|
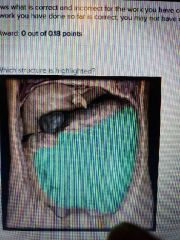
|
Greater omentum |
|
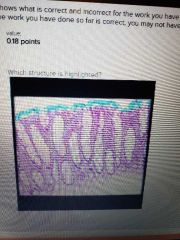
|
Simple columnar epithelium |
|
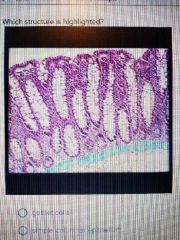
|
Muscalaris mucosae |
|
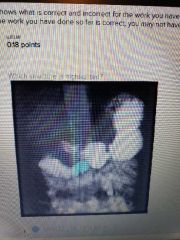
|
Ascending part of deudenum |
|
|
Lower esophageal sphincter |
|
|
Hepatopancreatic ampulla |
|
|
A portal triad consist of |
Branches of a hepatic artery,hepatic portal vein,and bile duct |
|
|
Mesentery of small intestine |
|
|
Rectum |
|
|
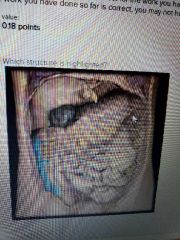
Ascending colon |
|
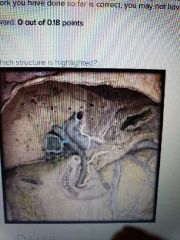
|
Cystic duct |
|
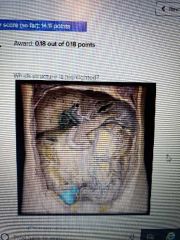
|
Cecum |
|
|
5 types of secretory cells from gastric ephitelium |
Parietal Mucus neck Chief Enteroendocrine Surface mucus |
|
|
2 components of saliva |
Mucus cells Serous cells |
|
|
Inferior esophageal sphincter is also known as__ |
Cardiac sphincter |
|
|
Which bones form the hard palate? |
Palatine bones and maxillae |
|
|
What would stenosis of the pyloric sphincter interfere with? |
Passage of chyme into the deudenun |
|
|
What enzyme initiate the Digestion of proteins? |
Pepsin |
|
|
Neucleosidase is a enzyme that brakes ____ |
Bind between the sugar and the nitrogen base of the neucleoside |
|
|
In response to the increased availability of nutrients during the absorptive state,liver and muscle increase or decrease glycogenesis or glycolysis |
Increase glycogenesis |
|
|
Outer tunic of jejunum? |
Serosa |
|
|
To decrease body temp, the big brain signals, |
Anterior pituitary to release thyroid -stimulating hormone |
|
|
Modified capillaries of liver lobules |
Sinusoids |
|
|
Iron zinc calcium iodine sodium and potasium are |
Minerals |

