![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Line of Symmetry |
A line that divides a shape so that both sides of the shape are mirror images of each other. |
|
|
Polygon |
A figure made out of closed, straight lines |
|
|
Parallelogram |
A quadrilateral with 2 pairs of parallel sides |
|
|
Trapezoid |
A quadrilateral with 1 pair of parallel sides |
|
|
Square (Equilateral) |
A rhombus with all right angles |
|
|
Rhombus |
A parallelogram with all equal sides |
|
|
Rectangle |
A parallelogram with all right angles |
|
|
Diagonal |
A line that connects two non-adjacent angles in a polygon |
|
|
Point of Symmetry |
A point on a Line of Symmetry |
|
|
Trapezium |
A quadrilateral with no parallel sides |
|
|
Area of a Parallelogram |
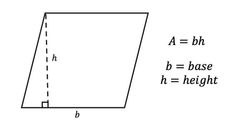
Area = base × height Base = long end Height = distance to opposite side at a right angle |
|
|
Angles in a parallelogram |
1. All angles add up to 360 2. Opposite angles are equal 3. Adjacent angles are supplementary (add to 180) |
|
|
Symbols of Inclusion (the "P" in PEMDAS) |
Parentheses (), brackets [], braces {}, absolute value ||, and the numerator and denominator of a fraction |
|
|
Acute Triangle Right Triangle Obtuse Triangle |
Acute - Each angle is less than 90° Right - One angle is exactly 90° Obtuse - One angle is more than 90° |
|
|
Equilateral Triangle Isosceles Triangle Scalene Triangle |
Equilateral - all sides are equal Isosceles - two sides are equal Scalene - no sides are equal |
|
|
Rational Number |
Any number that can be written as a fraction (7.284, 5.3838..., √121) |
|
|
Irrational Number |
A number that can't be written as a fraction (π, e, √24) |
|
|
Proportions |
Two ratios that are equal Used to represent proportional relationships |
|
|
Circle |
A closed curve where every point is the same distance from the center. |
|
|
Radius |
The distance from the center to the edge of a circle |
|
|
Diameter |
The distance across a circle, passing through the center. d=2r (r = radius) |
|
|
Circumfrence |
The distance around a circle C = πd or 2πr (d = diameter, r = radius) |
|
|
Pi π |
The ratio of the circumfrence and diameter of a circle, equal to ~3.14 or 22/7 (circumfrence ÷ diameter = π) |
|
|
Algebraic Addition |
Using opposites to write problems with only addition Ex: -3 - (-2) = -3 + 2 |
|
|
Quadrilateral |
Any 4-sided polygon |
|
|
Scientific Form |
A number "a" multiplied by 10 to the power of b 1 ≤ a < 10 · If b is positive, a gets bigger by b decimal places · If b is negative, a gets smaller by b decimal places Ex: 25000 = 2.5 × 10⁴ |
|
|
Volume of a Rectangular Prism |
V = l × w × h or b x h length × width × height base Volume for units are cubed (u³) |
|
|
Volume |
The amount of unit cubes it would take to fill a 3-dimensional object Volume for units are cubed (u³) |

