![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Mitral Stenosis
|
secondary to rheumatic fever/RHF (GAS);
|
|
|
Mitral valve Prolapse
|
Affects young women, associated with Marfan syndrome
Midsystolic click on auscultation Enlarged, floppy mitral valve leaflets prolapse into atrium Micro: myxomatous degeneration |
|
|
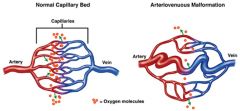
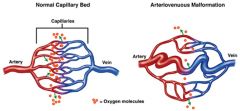
Deprives certain tissues of oxygen or release of C02
Connection between artery (high pressure system) and vein (low pressure) is fragile and prone to bleed. |
|
|
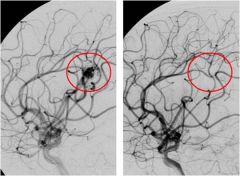
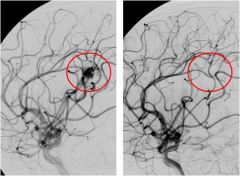
Atriovenous Malformation pre and post tx
|
|
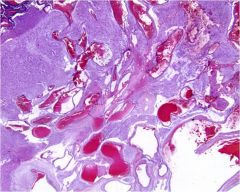
|
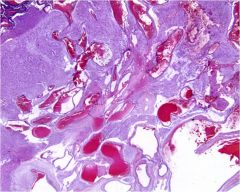
Atriovenous Malformation; shows numerous (noncapillary) blood vessels; increased # of larger vessels in AVM but vessels are normal
|
|
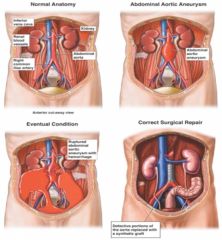
|
Aortic Aneurysm; results in hemorrhage; can detect an abdominal pulsatile mass by palpation
|
|
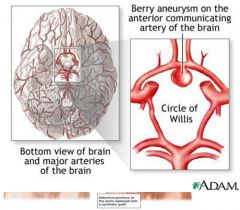
|
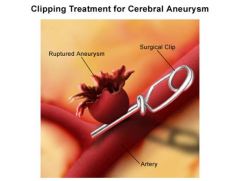
berry aneurysm
|
|
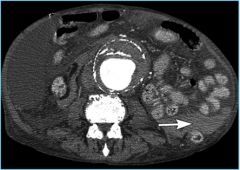
|
ruptured abdominal aortic aneusym
|
|
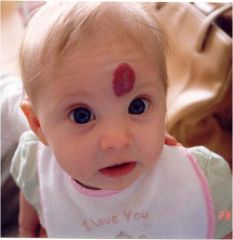
|
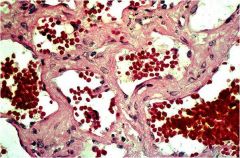
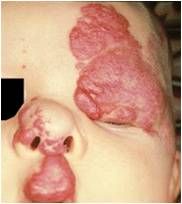
Hemiangiomas; if cavernous can suggest Sturge Weber syndrome
|
|
|
Hemangioma; cavernous; strawberry hemangiomas often not tx but cavernous emangiomas involving eyelids or other facial parts often tx with steroid injections
|
|
|
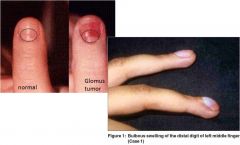
Glomus Tumor; macroscopically you will see a red blue nodule on the fingers of patients, which microscopically consists of uniform, rounded cells with a centrally placed nucleus.
|
|
|
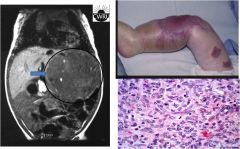
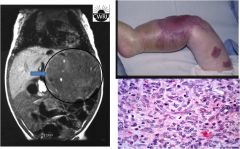
This is the case with hemangioendotheliomas, which are vascular neoplasms composed of different components including endothelial cells. These tumor have a wide spectrum of behaviors. Different variants exists depending on microscopic composition of the tumor. These are rare tumor and have an unknown etiology.
|
|
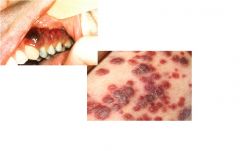
|
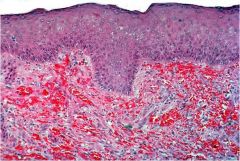
Kaposi Sarcoma; microscopically you see proliferation of vessels (though not well formed resulting in RBC extravasation)
low grade clonal endothelial proliferation with a variably vasoformative or spindle cell growth as a result to infection with human herpesvirus 8 (HHV8). Classically seen in ashkenazi jews |
|
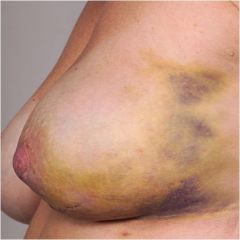
|
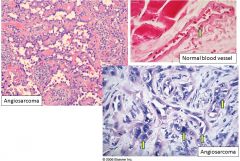
Angiosarcoma; malignant neoplasm derived either from blood or lyphatic vessels
Top right = normal endothelial cells; bottom right = malignant endothelial lining |
|
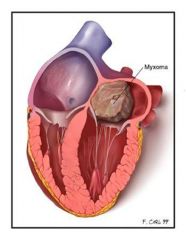
|
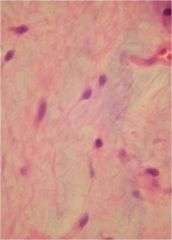
Cardiac Myxoma; benign cardiac tumor; tends to arise in left atrium where it is attached to the fossa ovalis
Note bland appearing spindle cells in a bluish background (spindle cells in myxoid background) |
|
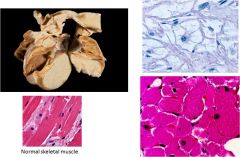
Associated with tuberous sclerosis
|
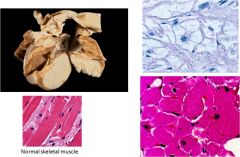
Cardiac Rhabdomyoma; benign proliferation of cardiac myocytes that occurs almost exclusively in the heart
Top right = spider cells (myocyte with clear cytoplasm with pink strands) |

