![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
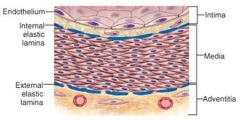
Heart develops from a simple blood vessel and thus retains the 3 concentric tunics of vessel walls
|
|
|
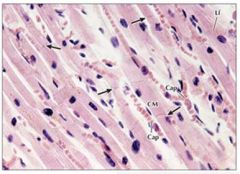
cardiac muscle
Lf = lipfuscin pigment |
|
|
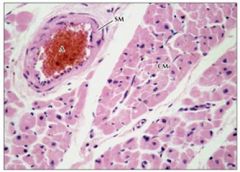
Cardiac muscle
SM = smooth muscle surrounding artery |
|
|
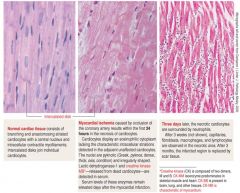
Ischemia;
|
|
|
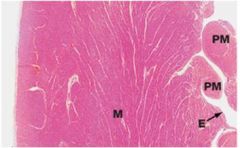
Left ventricular wall
Tunica intima = Endocardium (E) Tunia media = Myocardium (thickest in L ventricle) Tunica adventicia (epicardium or visceral pericardium) Papillary muscles = myocardium extensions that form anchors for chordae tendinae that tether the cusps to the AV valve (for left ventricle = mitral valve) |
|
|
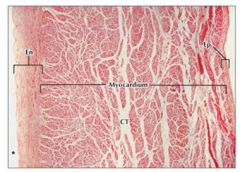
Atrial Wall
Ct = connective tissue; separates cardiac muscle fibers |
|
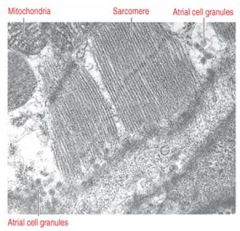
|
Atrial Natriueretic Fiber; stimulates diuresis, relaxes cardiac muscle by inhibiting vasopressin and angiotensin II, prevents hypervolemia and hypertension, pressure across atrial wall induces ANF release
|
|
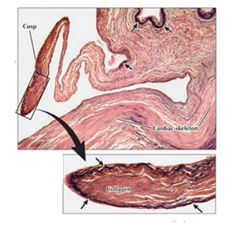
|
Aortic Valve; contains dense collagen matrix, continous with cardiac skeleton w/ anchors at the valve base; arrows indicate elastic fiber network under intima
|
|
|
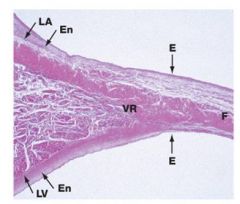
LEft AV valve (bicuspid = mitral)
F = lamina fibrosa in core of valve |
|
|
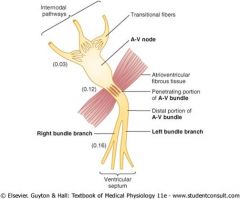
Av node
|
|
|
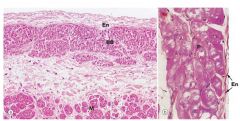
interventricular septum; left branch bundle
P = purkinje fibers; just deep to endocardium lining the IV septum |
|
|
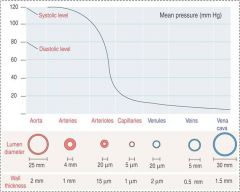
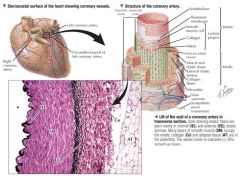
Arteries have thicker walls than aorta
|
|

|
Aorta; larger lumen relative to wall thickness
|
|
|
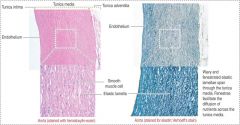
Aorta
note fenestrated elastic sheet |
|
|
|
Aorta; elastif fibers in tunica media
|
|
|
Aorta; elastif fibers in tunica media
|
|

|
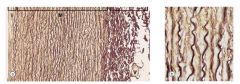
Marfans Aorta
|
|
|
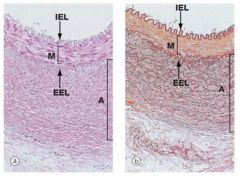
Muscular artery; two elastic sheets (internal elastic lamina, external elastic lamina); tunica media contains concentrically arranged smooth muscle
|
|
|
Muscular artery; 2 elastic layers (dark staining)
|
|
|
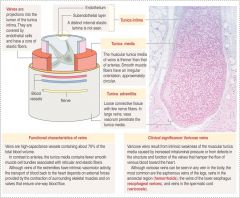
Vein Histology
Varicose veins = weak tunica media |
|
|
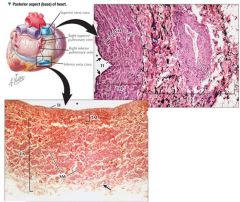
Superior Vena Cava; tunica media not well developed; circular smooth muscle; adventicia is thickest tunic, longitudinal smooth muscles, helical collagen/elastic fibers
Compared to arterial walls, veins have more extensive vasa vasorum |
|
|
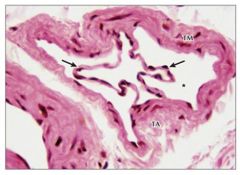
Arrows = valve leaflets in vein
|
|
|
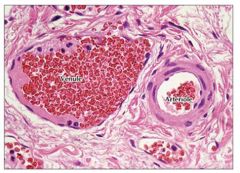
Muscular venule has thin wall and relatively larger lumen than arteriole
|
|
|
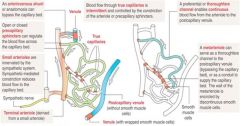
Arterioles -> Capillaries
Arterioles -> metaarterioles -> capillaries Arterioles shunt blood via sphincter constrictions |
|
|
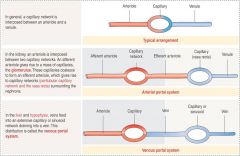
Capillary Portal Systems
|
|
|
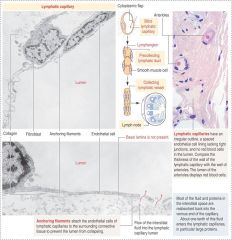
Lymphatics
|
|
|
Lymphatic velve
One layer of flat endothelial cells; incomplete basement membrane with gaps; small/medium lymph vessels contain valves (thinner than venous valves, V/arrows on pic) |
|
|
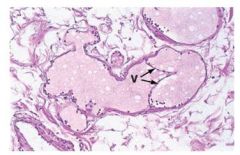
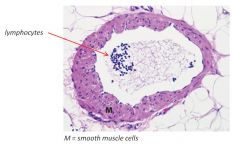
Medium Lymphatic Vessel
|

