![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
34 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
plantar aponeurosis works as |
support for longitudinal arch of the foot |
|
|
plantar aponeurosis begins at _________, extends to __________ |
beginsat calcaneousbone, extendsto toesto turn into tendonousdigital bands to connect to skin, LL, and bone of digits |
|
|
between tendonous digital bands there are |
transverse metatarsal LL to hold foot together |
|
|
intrinsic dorsal aspect of the foot |
Extensor digitorum brevis M Toes I-IV |
|
|
intrinsic plantar foot has ____ layers |
4 |
|
|
all intrinsic plantar foot layers are innervated by |
Tibial N (but different branches) |
|
|
action of all intrinsic plantar foot MM |
flex, and/or abduct, and/or adduct toes 1-4 |
|
|
first layer is deep to |
plantar aponeurosis |
|
|
muscles of the first layer of intrinsic plantar foot |
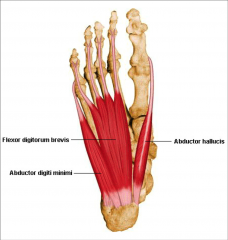
Abductorhallucis M –medial margin of foot Flexor digitorum brevis M –acts on toes II-V Abductor digiti minimiM -lateral margin of foot |
|
|
second layer of intrinsic plantar consists of |
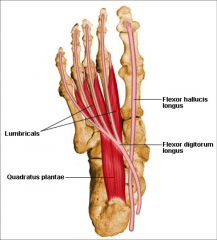
quadratus plantar and lumbricals |
|
|
2nd order for quadratus plantae |
O: calcareous bone I: tendon of flexor digitorum longus where it starts to divide N: lateral plantar A: assists in flexion of foot |
|
|
2nd order for plantar lumbricals
|
O & I: on flexor digitorum longus m. N: 1: medial plantar N from tibial; 2-4: lateral plantar N from tibial A: Flexmetatarsal phalagealjoint, extend Interphalangealjoint |
|
|
third layer of plantar consists of |
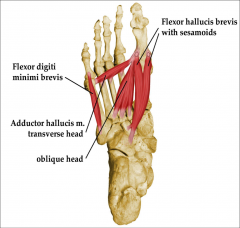
flexor hallucis brevis M adductor hallucis M Flexor digiti minimi brevis |
|
|
2nd order for flexor hallucis brevis M |
O: cuboid bone and posterior tibial tendon N:medial plantar N A: flex great toe |
|
|
the two tendons of flexor hallucis brevis are split by |
flexor hallucis longus tendon |
|
|
There are _____ in each tendon of flexor hallucis brevis M. These insert on ___________. |
sesamoid bones; lateral and medial sides of first digit |
|
|
2nd order for adductor hallucis M |
Two origins to produce"7" shape: transverse and oblique head N: lateral plantar N A: adduct great toe |
|
|
forth intrinsic layer consists of |
Dorsal interossei (4) Plantar interossei (3) |
|
|
attachments and action of dorsal and plantar interossei |
Both attachment: sides of metatarsals Dorsal interossei (4) A: abductII-IV toes, relative to long axis of 2nd toe Plantarinterossei (3) A: aduct III-V toes, relativeto long axis of 2nd toe |
|
|
what is innervated by medial plantar branch of tibial N |
Flexor digitorum brevis 1st plantar lumbrical Flexor hallucis brevis Adductor hallucis |
|
|
what is innervated by lateral plantar branch of tibial N |
abductor digiti minimi quadratus plantae lumbricals 2-4 Flexor digiti minimi brevis plantar interossei dorsal interossei |
|
|
arteries of the foot |
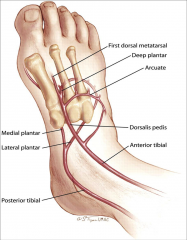
doralis pedis A lateral and medial plantar AA |
|
|
dorsalis pedis comes from _________ |
anterior tibial to name change as it crosses the ankle and divesdeep to plantar surface |
|
|
doralis pedis terminates as |
deep plantar A to connect with deep plantar arch |
|
|
Deep plantar arch gives rise to |
plantar metatarsal a. and finally digital a. |
|
|
Medial plantar a. courses from |
heel to medial great toe |
|
|
lateral plantar A is the larger branch of _______. |
posterior tibial A |
|
|
lateral plantar a courses from __________ to form _________ |
heel to metatarsal region; deep plantar arch |
|
|
veins of the foot |
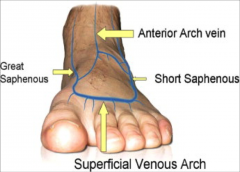
Deepand superficial VV of the foot drain into dorsal venous arch Greatsaphenous V: ascends medial leg Smallsaphenous V: ascends posterior leg |
|
|
medial and lateral plantar NN give rise to |
plantar digital branches |
|
|
major innervation (motor/sensory) of medial and lateral plantar NN |
medial: major sensory to sole of foot lateral: major motor, some sensory |
|
|
is medial or lateral plantar N larger |
medial |
|
|
innervation of deep fibular |
sensory to skin on toes one and two |
|
|
deep fibular N gives rise to |
dorsal digital branches |

