![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
122 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Two functional zones of the respiratory tract |
Conducting zone Respiratory zone |
|
|
Structures involved in upper respiratory tract |
Nose Nasal cavity Pharynx |
|
|
4 pairs of paranasal sinuses |
Frontal Ethmoidal Sphenoidal Maxillary |
|
|
3 paired cartilaginous structures of the larynx |
Arytenoid Corniculate Cuneiform |
|
|
Structures that produces mucin |
Globet cells in the epithelium lining Mucus and serous glands in lamina propia |
|
|
Airborne molecules that dissolve in the mucus covering the _____. stimulate olfactory receptors to detect different oddors |
Olfactory epithelium |
|
|
Functions of the respiratory system |
Air passageway Site for exchange of oxygen to co2 Detection of odors Sound production |
|
|
What portion of the respiratory system is where gas exchange with the blood occurs |
Respiratory |
|
|
What portion of the respiratory system transport air |
Conducting |
|
|
The mucus membrane is composed of ____ |
Epithelium |
|
|
What is found in the mucus lining of the respiratory tract |
Immunoglobins Defensin Lysozyme Mucin |
|
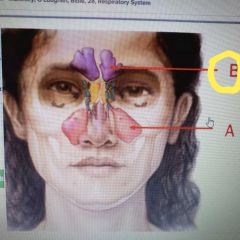
|
Frontal |
|
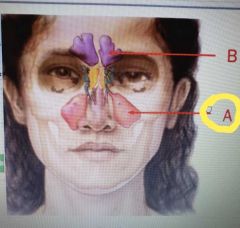
|
Maxillary sinus |
|
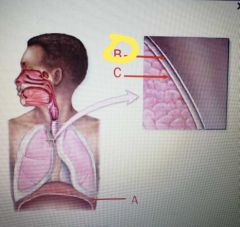
|
Parietal pleural |
|
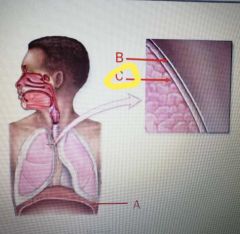
|
Visceral pleura |
|
|
Which are mechanisms for carrying carbon dioxide in the blood |
Bound to hemoglobin Dissolved in plasma As bicarbonate |
|
|
Which tonsils are also called adenoids |
Pharyngeal |
|
|
Equalize pressure between the middle ear and the atmosphere by allowing excess pressure to be released into the nasophanrynx |
Auditory tubes |
|
|
Equalizes air pressure on either side of eardrums by allowing air to move between nasophanrynx and middle ear |
Auditory tube(eustachian tube) |
|
|
3 unpaired cartilaginous structures of the larynx |
Thyroid Cricoid Epiglodis |
|
|
Elastic ligaments covered with mucosa that extend between the thyroid and arytenoid |
Vocal folds |
|
|
True vocal cords |
Vocal folds |
|
|
2 tonsils of the oropharynx |
Palatine Lingual |
|
|
Determined by the amount of tension on the vocal folds. The more tension the more vibrations of the vocal folds |
Pitch |
|
|
extends from the soft palate superiorly to the hyoid bone inferiorly |
Oropharynx |
|
|
Pharyngeal tonsils, auditory tube opening and tubal tonsil are part of what region of pharynx |
Nasophanrynx |
|
|
Extends from the level of the hyoid bone and is continuos on its inferior end with the larynx anterior and esophagus posteriorly |
Laryngopharynx |
|
|
Supriormost region of the pharynx |
Nasophanrynx |
|
|
Divides the nasal cavity into left and right portions |
Nasal septum |
|
|
Why the air remains in the nasal cavity for a longer time? |
So it can be warmed and humidified |
|
|
Coarse hair near the vestibule of the nose |
Vibrissae |
|
|
Olfactory receptors are stimulated when airborne molecules are inhaled and dissolved in the mucus covering the _____ |
Olfactory epithelium |
|
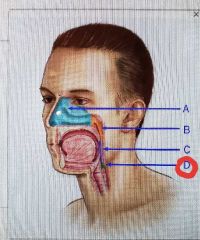
|
Laryngopharynx |
|
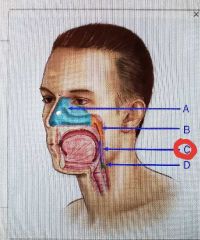
|
Oropharynx |
|
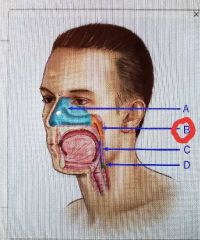
|
Nasophanrynx |
|
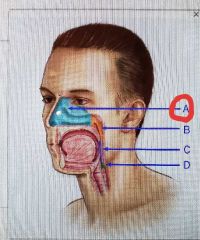
|
Nasal cavity |
|
|
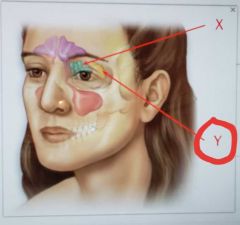
Sphenoidal sinus |
|
|
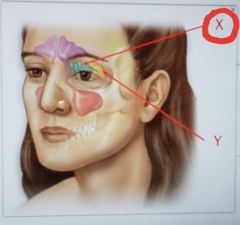
Ethmoidal sinus |
|
|
Four bones of the skull contain paired air spaces called_______ that help to lighten the heavy load of the head |
Paranasal sinuses |
|
|
What is inferior of larynx |
Thachea |
|
|
What is posterior of the larynx |
Esophagus |
|
|
The overall growth of the ____ cartilage is stimulated by testosterone; this, the Adam's apple is usually prominent and larger in males after puberty |
Thyroid |
|
|
Ring shaped cattialge of the interior portion of larynx connects to the trachea inferiorly |
Cricoid |
|
|
The ____ the vocal fold, the deeper the voice |
Longer |
|
|
Trachea is known as |
Windpipe |
|
|
What the respiratory membrane consist of? |
1. Alveolar ephitelium (type I cell ) 2. Fused basement membranes membranes of alveolar and capillary endothelium 3. Capillary endothelium |
|
|
Secrets pulmonary surfactant fluid to the inner alveolar surface to prevent collapse of alveoli |
Alveolar type II |
|
|
Barrier that separates alveoli's air from pulmonary capillaries blood |
Alveolar type I |
|
|
Also called Dust cells, fixed or free leukocytes. Engulf any organisms in the alveoli |
Alveolar macrophages |
|
|
Number of lobes in the right lung |
3 |
|
|
Number of lobes in the left lung |
2 |
|
|
Secondary bronchi that brach off the primary bronchi is called |
Lobar bronchi |
|
|
Where are objects more likely to be lodged |
Right primary bronchus |
|
|
All laryngeal cartilage are made of ____ cartilage, except for the epiglottis, which is made of______ cartilage |
Laryngeal= Hyaline, epiglottis= elastic |
|
|
Rima glottidis + vocal cords = |
GLOTTIS |
|
|
Larynx's opening between vocal ligaments |
Rima gottidis |
|
|
4 Structures found in the hilum. Called the root of the lung |
Bronchi pulmonary vessels Lymph vessels Autonomic nerves |
|
|
Structures in each lobule of bronchopulmonary segment |
Terminal bronchioles Arteriole Venule Lymph vessel |
|
|
What symphatetic innervation input from T1-T5 generally causes ____ |
Bronchodilation |
|
|
Parasympathetic innervation from vague causes______ |
Bronchoconstriction |
|
|
Outer lining of lungs. Includes visceral and parietal pleura. Composed of simple squamous epithelium |
Pleura membrane. |
|
|
Locates between visceral and parietal serous membranes. Considered a potential space when lungs are inflated |
Pleural cavity |
|
|
Function of serous fluid in pleural cavity |
Lubricates to allow pleural surfaces to slide by easily |
|
|
Pressure between membranes. |
Intrapleural Pressure |
|
|
Pressure in alveoli |
Intrapulmonary pressure |
|
|
Why lungs remain inflated |
Because pressure in intrapulmonary is greater than intrapleural pressure |
|
|
Type of alveolar cell that promotes ra po I'd gas diffusion across the alveolar wall |
Alveolar type 1 cell |
|
|
What connects nasophanrynx to middle ear |
Auditory tubes |
|
|
4 processes of respiration |
Pulmonary ventilation Alveolar gas exchange Gas transport Systematic gas exchange |
|
|
Movement of gases between atmosphere and alveoli |
Pulmonary ventilation |
|
|
Exchange of gases between alveoli and blood |
Alveolar gas exchange |
|
|
Transport of gases in blood between lungs and systematic cells |
Gas transport |
|
|
Exchange of respiratory gases between the blood and systematic cells |
Systematic gas exchange |
|
|
Muscles of forced inspiration |
Sternocleidomastoid Scalenes Serratus posterior superior Pectoralis minor Erector spinse |
|
|
Muscles of quiet breathing |
Diapharm External interscostals |
|
|
Difference in pressure between atmospheric and intrapulmonary pressure. It can be changed by altering volume of thoracic cavity |
Pressure gradient |
|
|
Amount of air moving in and out of lungs |
Airflow |
|
|
Flow is directly related to _____ and inversely related to____ |
Related to pressure gradient Inversely related to resistance |
|
|
3 factors that increase resistance to airflow |
1. Decrease elasticity of chest walls and lungs 2. Decrease in bronchiole diameter 3. Collapse of alveola |
|
|
Ease with which lungs and chest wall expand |
Compliance |
|
|
What law States that the total pressure in a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the individual partial pressures |
Dalton's law |
|
|
Measured in mm Hg, pressure exerted by each gas within a mixture of gases |
Partial pressure |
|
|
Lined with pseudostrattified cilliated columnar. Bronchis or bronchioles? |
Bronchis |
|
|
Lined simple columnar membrane. Bronchis or bronchioles |
Bronchioles |
|
|
What the parietal pleura lines? |
Internal thoracic walls Lateral surfaces of the mediastum Superior surface of the diaphragm |
|
|
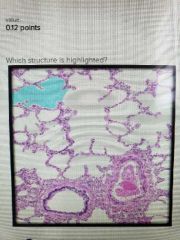
Alveolar sac |
|

|
Arytenoid |
|
|
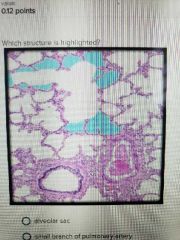
Alveolus |
|
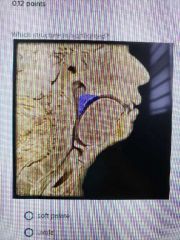
|
Soft palate |
|
|
As the diaphragm relaxes, it moves superiorly or inferiorly |
Superiorly |
|
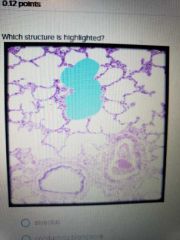
|
Alveolar duct |
|
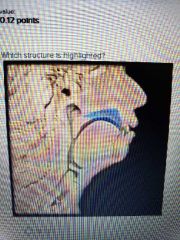
|
Hard palate |
|
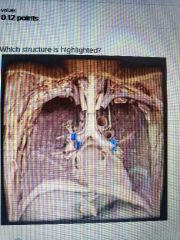
|
Lobar bronchus |
|
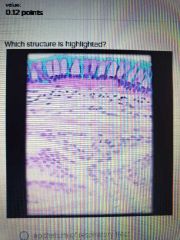
|
Ciliated cell of respiratory epithelium |
|
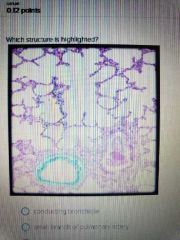
|
Conducting bronchiole |
|
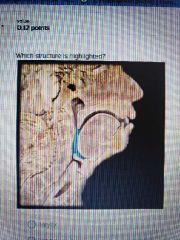
|
Oropharynx |
|
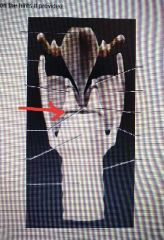
|
Muscular process |
|
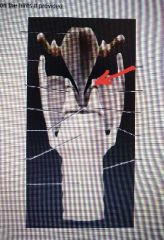
|
Corniculate |
|
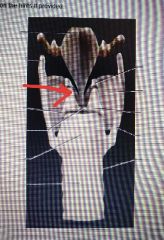
|
Arytenoid |
|
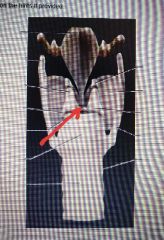
|
Vocal ligament |
|
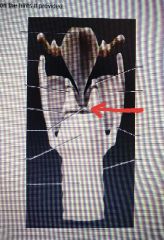
|
Vocal process |
|
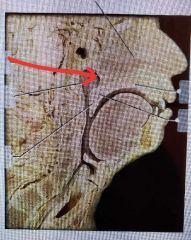
|
Choana |
|
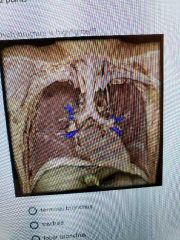
|
Segmental bronchus and branches |
|
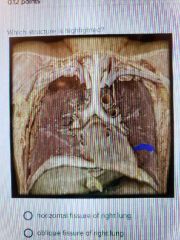
|
Oblique fissure of left lung |
|
|
In alveolar gas exchange oxygen diffuses into the blood or out of the blood? |
Into the blood |
|
|
In systematic gas exchange oxygen diffuses into the blood or out of the blood? |
Out of the blood |
|
|
Food is normally prevented from enter the nasophanrynx by |
Elevation of the soft palate |
|
|
The less breaths a minute the greater or lesser the alveolar ventilation rate is? |
Greater |
|
|
Thoraxic cavity volume decreases during inspiration or expiration? |
Expiration |
|
|
Airway obstruction can lead to hypoventilation, which can cause ___ |
Hypoxia and respiratory acidosis |
|
|
About 70% of the co2 that diffuses into systematic capillaries combines with water to form carbonic acid, which then dissociated into______ |
bicarbonate and hydrogen ions |
|
|
All obstructive lung disorders interfere with or reduce the flow of air |
Interfere |
|
|
All restrictive lung disorders interferes with or reduce the amount of air that flows |
Reduce |
|
|
Pulmonary fibrosis, asbestosis, myasthenia, als, tuberculosolis are obstructive or restrictive disorders? |
Restrictive |
|
|
Cystic fibrosis, asthma, chronic bronchitis, emphysema are obstructive or restrictive disorders? |
Obstructive |
|
|
What law states " at a given temp, the solulability of gas into liquid dependent upon partial pressure of gas in the air and solubility coefficient of the gas in the liquid |
Henry's law |
|
|
What gas is 24 times as soluble as oxygen |
Carbon |
|
|
What gas is half as soluble than oxygen? |
Nitrogen |
|
|
Partial pressure of O2 in alveoli is higher or lower than in atmosphere |
Lower |
|
|
The amount of air that reaches the alveoli and is available for gas exchange per minute |
alveolar ventilation |
|
|
2 respiratory centers in the brain stem |
Medullary respiratory center Pontine respiratory center |
|
|
4 types of sensory receptors that relay sensations to the respiratory center |
Chemoreceptors Irritant Baroreceptor Propioreceptors |

