![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
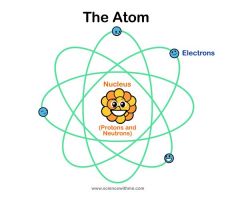
atom |
the basic unit of a chemical element. |
example: carbon
Everything is made up of atoms! |
|
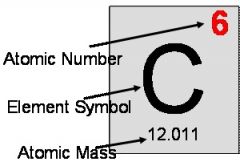
atomic mass |
the mass of an atom of a chemical element expressed in atomic mass units. It is approximately equivalent to the number of protons and neutrons in the atom (the mass number) or to the average number allowing for the relative abundances of different isotopes. |
example: 12.011= Carbon's atomic mass
Carbon's atomic mass is 12.011.
|
|
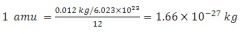
atomic mass unit |
a unit of mass used to express atomic and molecular weights, equal to one-twelfth of the mass of an atom of carbon-12. It is equal to approximately 1.66 x 10-27 kg. |
example: uranium (235)= 235 amu
The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average of the masses of all the stable isotopes of the element (if it has any), weighted by the natural occurrence levels of the isotopes in the elements.
|
|
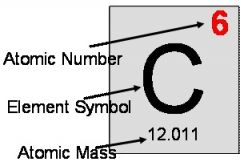
atomic number |
the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom, which determines the chemical properties of an element and its place in the periodic table. |
example: Carbon atomic number= 6
Carbon has an atomic number of 6. |
|
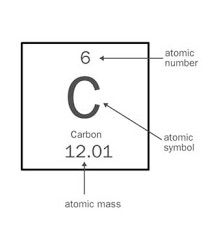
atomic symbol |
the letter(s) representing the element with number and mass |
example: C= Carbon
The atomic symbol of carbon is C. |
|
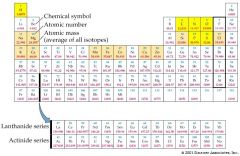
chemical symbol |
A chemical symbol is a code for a chemical element. It is usually derived from the name of the element, often in Latin. This is an example of an atomic symbol. The text boxes explain where the numbers are derived from. |
example: Iron: Fe
The chemical symbol for Iron is Fe. |
|
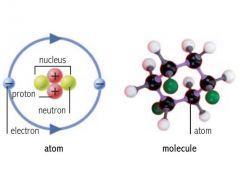
electron |
A stable subatomic particle with a charge of negative electricity, found in all atoms and acting as the primary carrier of electricity in solids. |
example: Lithium= 3 electrons
lithium has 3 electrons. |
|
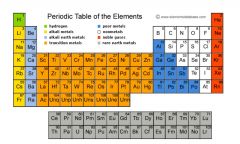
group |
In chemistry, a group (also known as a family) is a column of elements in the periodic table of the chemical elements. |
Example: alkali metals
one group is the alkali metals. |
|
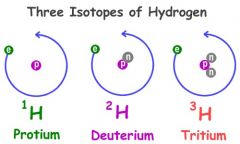
isotope |
Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element such that while all isotopes of a given element have the same number of protons in each atom, they differ in neutron number. |
example: there are 3 naturally occurring isotopes of hydrogen.
The most common isotope of carbon is carbon-12.
|
|
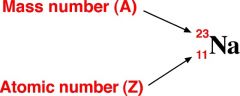
mass number |
All atoms of a chemical element have the same atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus) but may have different mass numbers (from having different numbers of neutrons in the nucleus). Atoms of an element with the same mass number make up an isotope of the element. |
Example: Sodium (Na)= 23
Sodium has a mass number of 23. |
|
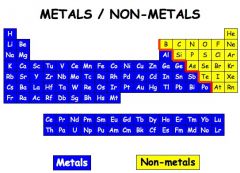
metal |
Definition of Metals. Elements that form cations when compounds of it are in solution and oxides of the elements form hydroxides rather than acids in water. Most metals are conductors of electricity, have crystalline solids with a metallic luster and have a high chemical reactivity. |
Example: Carbon= metal
Carbon is a metal. |
|
metalloid |
A metalloid is a chemical element that has properties in between, or is a mixture of, those of metals and nonmetals. There is no standard definition of a metalloid, nor is there complete agreement as to which elements are appropriately classified as such. |
Example: Boron= metalliod
Boron is a metalloid. |
|
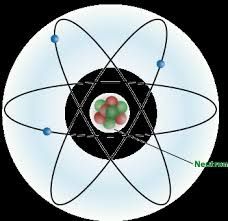
neutron |
The neutron is a subatomic particle, symbol n or n0, with no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton. Protons and neutrons, each with mass approximately one atomic mass unit, constitute the nucleus of an atom, and they are collectively referred to as "nucleons". |
Example: neutrons shown as n or n0
Neutrons are found in atom. |
|
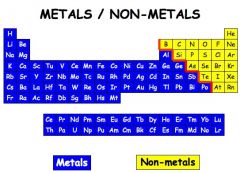
nonmetal |
In chemistry, a nonmetal (or non-metal) is a chemical element that mostly lacks metallic attributes. |
example: Oxygen= nonmetal
Oxygen lacks metallic attributes. |
|
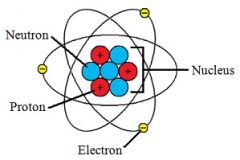
nucleus |
Nucleus means center. In chemistry, nucleus refers to the positively charged center of the atom containing protons and neutrons. |
Example: Nucleus is in center of atom.
Nucles contains protons and neutrons. |
|
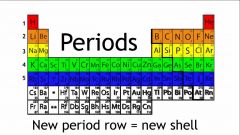
period |
In chemistry, the term period refers to a horizontal row of the periodic table. |
Example: period 2
period 2 is the second row on periodic table. |
|
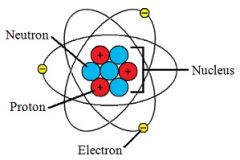
proton |
a stable subatomic particle occurring in all atomic nuclei, with a positive electric charge equal in magnitude to that of an electron, but of opposite sign. |
example: shown as a+
protons are are found in atom. |
|
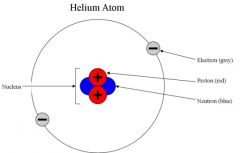
Subatomic particle |
In the physical sciences, subatomic particles are particles much smaller than atoms. There are two types of subatomic particles: elementary particles, which according to current theories are not made of other particles; and composite particles. |
Example: elementary particles and composite particles
subatomic particles are much smaller than atoms. |

