![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
Hemolytic anemia can cause what type of hyperbilirubinemia?
|
Unconjugated (indirect) hyperbilirubinemia
|
|
Why phototherapy in unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia?
|
UV light produces more hydrophilic (soluble) conformational species -> excretoin in urine and bile
|
|
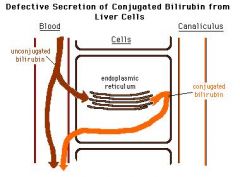
Dubin Johnson Syndrome
|
MRP2 transporter mutation leads to accumulation of conjugated bilirubin in the serum
|
|
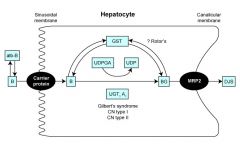
rotor Syndrome
|
Can't excrete bilirubin, benign, idiopathic origin
|
|
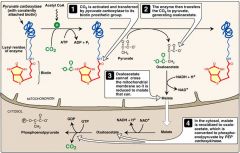
What energy source does ethanol generate in the liver? What are the impications of this?
|
NADH; increases NADH/NAD+ ratio; NAD+ needed to drive gluconeogenesis (via lactate/malate); results in alcohol induces hypoglycemia
|
|
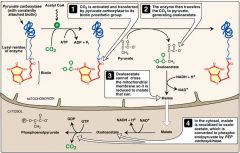
What effect can alcohol have on blood sugar levels?
|
Lowers them by disturbing NADH/NAD+ ratio; creates NADH; need NAD+ to drive gluconeogenesis
|
|
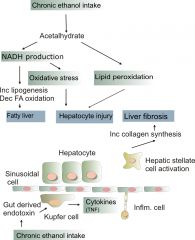
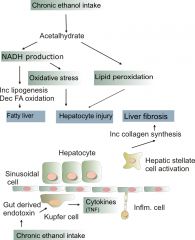
Describe acetaldehyde toxicity
|
Since acetaldehyde levels can be increased by ethanol, excess acetaldehyde can impair protein and lipid secretion, causing accumulation in the liver
|
|
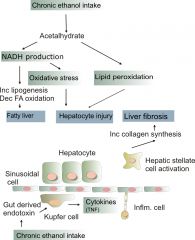
Disulfiram (antabuse)
|
Blocks aldehyde dehydrogenase activity and causes accumulatoin of acetaldehyde, which causes unpleasant affects by decreasing the synthesis of glucose
|
|
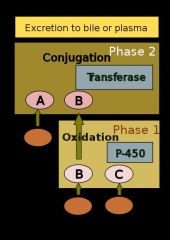
What are the two phases of drug metabolism in the liver?
|
Phase 1: Addition of polar group by oxidation
Phase 2: Conjugation with bigger molecules These all serve to increase their solubility/polarity to prevent their absorption |
|
How can excess iron (hemochromatosis) or copper (wilson's disease) affect the liver?
|
Excess free radicals damage tissue
|
|
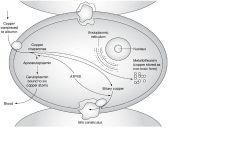
Where is the genetic defect in WIlson's disease?
|
Mutation in ATP-dependent copper transporter (ATP7B)
|
|

Classic clinical triad for hereditary hemochromatosis?
|

Skin pigmentation, cirrhosis, diabetes
|
|
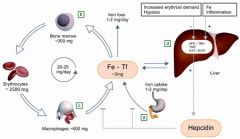
HFE related hemochromatosis
|
HFE regulates the release of hepcidin from the liver, which binds to ferroportin transporters on the base of enterocytes and macrophages preventing the secretion of iron into the portal system; if HFE is mutated, there is uncontrolled absorption/release of iron into the system
|
|
|
What are the lab findings for pre-hepatic hyperbilirubinemia?
|
Normal direct (conjugated), INCREASED INDIRECT (unconjugated), normal urine/stool
|
|
|
What are the lab findings for hepatic hyperbilirubinemia?
|
Normal to elevated direct/indirect bilirubin, dark urine color
|
|
|
What are the lab findings for post hepatic hyperbilirubinemia?
|
INCREASED direct (conjugated), normal indirect, dark urine, light stools
|
|
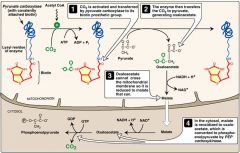
Pyruvate Carboxylase (irreversible enzymes)
|
In mitochondria
Pyruvate -> Oaxaloacetate Requires biotin, ATP, activated by acetyl-CoA |
|
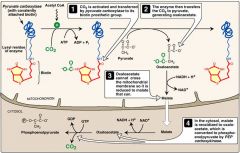
PEP carboxykinase
(irreversible enzymes) |
In cytosol
Oxaloacetate -> Phosphoenolpyruvate Requires GTP |
|
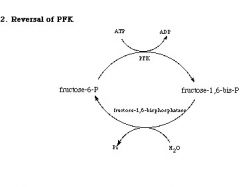
Fructose 1,6 biphosphatase
(irreversible enzymes) |
In cytosol
Fructose 1,6 biphosphate -> fructose 6 phosphate |
|
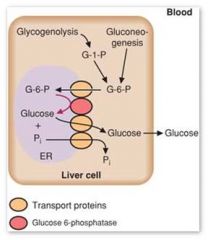
Glucose 6 phosphatase (irreversible enzymes)
|
In ER
Glucose 6-P -> glucose |
|
|
What does a deficiency of a key gluconeogenic enzyme cause?
|
Hypolycemia
|
|
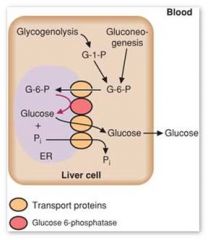
Why can't muscle participate in gluconeogenesis?
|
Because it lacks glucose-6-phosphatase
|
|
|
Significance of Pathway Produces Fresh Glucose?
|
P = pyruvate carboxylase
P = PEP carboxykinase F = fructose 1,6 biphosphtase G = glucose |
|
|
What are the four glucogenic amino acids?
|
Met, Val, Arg, His
|
|
|
What liver metabolic molecule is depleted in hyperammonemia?
|
Alpha ketglutarate; depletion of AKG leads to inhibition of TCA cycle
|
|
|
Symptoms of ammonia intoxication
|
Tremor, slurring of speech, somnolence (drowsiness), vomiting, cerebral edema, blurring of vision
|
|
|
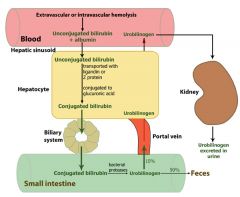
Describe the metabolism of bilirubin
|
|

