![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

What is the difference between ammonium and ammonia?
|
At physilogic pH, ammonium (NH4) is found predominantly in the undissociated state. The dissociated form (NH3) is called ammonia
|
|
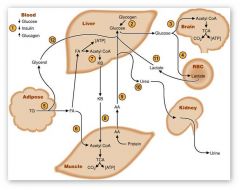
What is being used as the source of amino acids for guconeogenesis during the fasting state?
|
Protein
|
|

What is the role of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) in the synthesis of pyruvate from alanine?
|
Transfers NH3 to pyruvate to form alanine in muscle. When alanine is in the liver it is broken down to form nitrogen (excrted via urea cycle) and carbon (which is carbon skeleton is used for gluconeogenesis)
|
|

Describe how alanine and glutamine are used to transport amino acid nitrogen to the liver
|
NH3 transferred to alpha ketoglutarate to form glutamate and second to pyruvate to form alanine. The alanine moves to the liver where the nitrogen is transferred back to alpha-ketoglutarate to form glutamate. The pyruvate formed in the process is used to synthesize glucose via gluconeogenesis
|
|
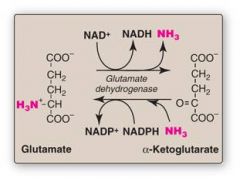
NH3 being used to directly synthesize glutamate via glutamate dehydrogenase is an example of what kind of reaction
|
Reductive Animation (Putting on the NH3)
|
|
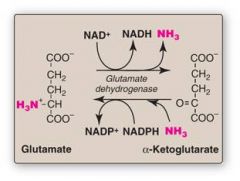
The release of NH3 from glutamate to form alpha-ketoglutarate via glutamate dehydrogenase is an example of what kind of reaction?
|
Oxiative Deamination
|
|
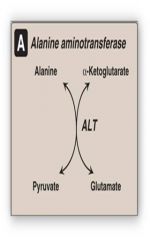
Transfer of the NH3 group to pyruvate to form alanine via ALT is an example of what kind of reactions
|
Transamination
|
|
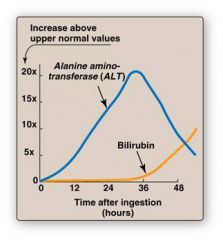
Discuss how ALT and AST values are used as an indicator of liver function
|
AST/ALT ratio is low in most types of liver disease bc ALT is usually higher than AST
|
|
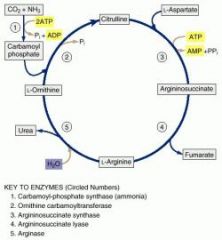
What is the most common urea cycle deficiency?
|
Ornithine Transcarbamoylase
|
|
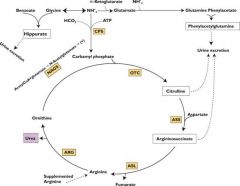
What is the function of N-Acetylglutamate in the regulation of the urea cycle?
|
Positive regulator of the rate limiting step (carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I)
Protein containing meal generates N-acetylglutamate, so it makes sense that you want to drive the urea cycle forward |
|
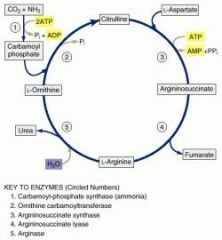
Why does orotic acid accumulate in the urine of patients with a deficiency in ornithine transcarbamoylase?
|
Excess carbamoyl phosphate is converted to orotic acid (part of the pyrimidine synthesis pathway)
|
|
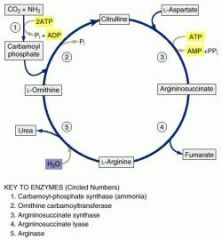
What are some treatment options for pts suffering from urea cycle defects?
|
Low protein diets
Arginine Supplementation (except in the case of arginase deficiency) Drugs - benzoic acid/phenylbutyrate conjugate w/ AA and are excreted |
|
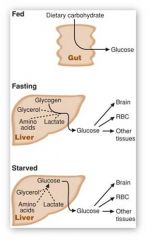
How are blood glucose levels maintained in the fed state?
|
Dietary intake
|
|

How are blood glucose levels maintained in the fasting state?
|
Glycogen breakdown in liver (first) and gluconeogenesis (second)
|
|

How are blood glucose levels maintained in the starved state?
|
Gluconeogenesis via AA, glycerol and lactate breakdown
|
|
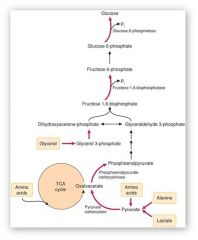
What are the three primary substrates for gluconeogenesis are they used to immediately form?
|
Amino Acids - alanine is the most commonly used (protein)
Glycerol (fatty chains) Lactate They all immediately form pyruvate |
|
Where is lactate derived from?
|

anaerobic glycolysis in RBCs and skeletal muscle
|
|

Where is alanine derived from?
|
Amino acids all derived from breakdown of skeletal muscle
|
|
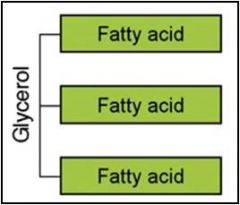
Where is glycerol derived from?
|
Backbone of triglycerides (fats) that originate from adipocytes
|
|
|
What does glucogenic mean?
|
refers to amino acids that can be used to make glucose by gluconeogenesis
|
|
|
How are ketone bodies formed?
|
B-oxidation within the mitochondria of hepatocytes releases acetyl-CoA units that are converted to ketone bodies (acetoacetate and B-hydroxybutyrate)
|
|
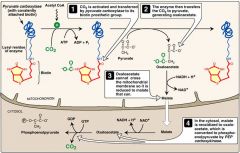
Does PEPCK (phosphoenolpyruvate) require the conversion of oxaloacetate to malate in the mitochondria or the cytosol?
|
Cytosol
|
|
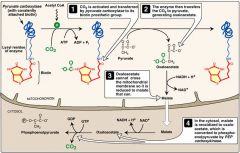
Pyruvate Carboxylase requires what for its activity
|
Both biotin and acetyl-coA
|
|

High levels of NADH can stimulate fat synthesis in the liver. Why is this clinically relevant?
|
High levels of NADH do not favor conversion of Malate back to Oxoloacetate in the cytosol; it gets converted to faty. Fatty liver of alcoholics
|
|
A newborn becomes progressively lethargic after feeding and increases his respiratory rate. He becomes virtually comatose, responding only to painful stimuli, and exhibits mild respiratory alkalosis. Suspicion of a urea cycle disorder is aroused and evaluation of serum amino acid levels is initiated. In the presence of hyperammonemia, production of which amino acid is always increased?
|
Glutamine
|
|
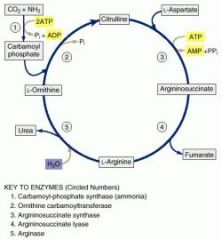
A 9-month-old boy is brought to the emergency department after his mother is unable to rouse him. His past medical history is significant for the onset of seizures at the age of 4 months and for a delay in reaching developmental milestones. Laboratory studies show a high blood urea nitrogen and ammonia level. A plasma amino acid analysis fails to detect citrulline, while his urinary orotic acid level is increased. The patient suffers from a deficiency of which enzyme?
|
Ornithine Transcarbamoylase
|
|
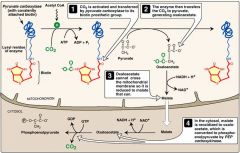
A 7-year-old female presents with anxiety, dizziness, sweating, and nausea following brief episodes of exercise. These symptoms are relieved by eating and do not occur if the patient is frequently fed small meals. Labs reveal hypoglycemia and lactic acidosis. Alanine fails to increase blood sugar, however glycerol or fructose can. Which enzyme is deficient in this individual?
|
Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxykinase
|
|
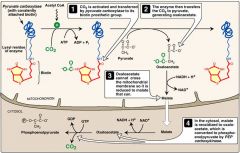
Fully activated pyruvate carboxylase depends on the presence of which two substances?
|
Acetyl-CoA and biotin
|
|
|
Which of the following is a primary substrate for gluconeogenesis?
A. Galactose B. Glycerol C. Glycogen D. Sucrose |
Glycerol
|
|
|
At what bilirubin levels does jaundice and icterus become apparent?
|
2-2.5 mg/dL
|
|
|
Physioogic Jaundice of the Newborn
|
Immature liver; poorly synthesized liver enzymes (UDPGT enzyme does not conjugate bilirubin so it becomes insoluble/toxic)
|
|
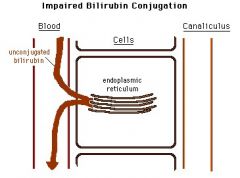
Crigler-Najjar Syndrome (I/II)
|
Total absence or decrease of bilirubin UDPGT (UGT1A1); severe jaundice/high serum levels of unconjugated bilirubin; histologically normal liver
w/o liver transplant, fatal kernicterus will ensue |
|
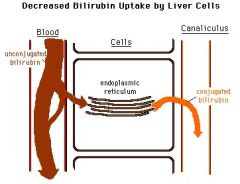
Gilbert's Syndrome
|
Decreased levels of UDPGT (UGT1A1); mild fluctuating unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia
Often not detected until TEENS or ADULTHOOD during conditions of stress (compare to Crigler Najjar which is in infants) |
|
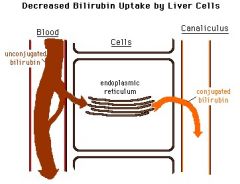
A teenage patient presents with jaundice which increases after fasting. There is mild hyperbilirubinemia.
|
Gilbert's Syndrome
|
|
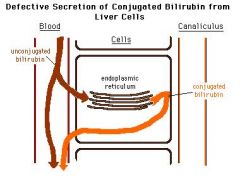
Dubin Johnson Syndrome
|
Asymptomatic conjugated hyperbilirubinemia with defects in conjugated bilirubin excretion from hepatocytes. Normal ALT, AST. EPINEPHRINE (not bilirubin) polymer pigment deposition in lyosomes causes the liver to turn black/brown. Patients may present as chronically jaundiced.
|
|
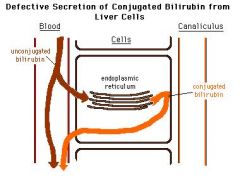
A patient presents with chronic jaundice, conjugated hyperbilirubinemia, and brown/black liver, normal AST/ALTs.
|
Dubin Johnson Syndrome
|
|

A pediatric patient presents with chronic jaundice and idiopathic conjugated hyperbilirubinemia. The liver does not show any pigmentation.
|
Rotor Syndrome
|
|
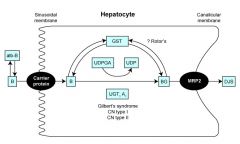
Rotor Syndrome
|
Asymptomatic conjugated hyperbilirubinemia with multiple defects in hepatocellular uptake and excretion of bilirubin pigments. Liver is NOT pigmented, most pts have chronic jaundice with normal lifespan.
|
|
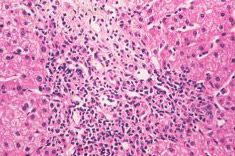
A middle aged woman presents with fatigue, hepatomegaly, skin hyperpigmentation and early signs of cirrhosis. History is notable for RA, SLE, scleroderma and a host of other autoimmune diseases. A biopsy reveals lymphoytic infiltration of the portal tracts.
|
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
|
|

Primary BIliary Cirrhosis
|
Chronic, progressive cholestatic liver disease characterized by intrahepatic bile duct destruction and portal inflammaiton and scarring, with progression to cirrhosis nad liver failure.
|
|
|
Secondary Biliary Cirrhosis
|
Obstruction of the biliary system and progression to cirrhosis secondary to a certain etiology (cholelithiasis, biliary atresia, tumors, strictures)
|
|

Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
|
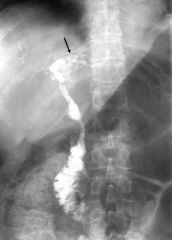
Cholestatic liver disease common in middle aged men; inflammation/obliterative fibrosis of intrahepatic/extrahepatic bile ducts.
STRONG association with IBD, mainly ulcerative colitis. "onion skin fibrosis"/"beading" of bilitary tree |
|

Morphology of Primary Sclerosing
|

Onion skin fibrosis and characteristic beading on radiographs of biliary tree caused by stricture and dilation of ducts
|
|
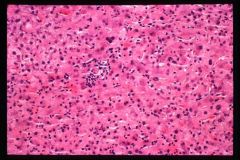
Autoimmune Hepatitis
|
Hepatitis without serologic markers of viral infection; elevated serum IgG, ANa, SMA and AAA
Tx/ with steroids Dx based on clinical exclusion of other hepatic disorders |
|

Alpha 1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (A1ATD)
|
A1At protects tissue (especially pulmonary) from inflammation; lack of A1AT results in damage to lung and liver from accumulation of protein in hepatocytes
Liver cirrhosis present |
|
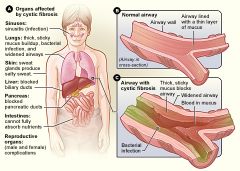
How can cystic fibrosis affect the liver
|
CF results in thick mucus, which can cause obstruction in the biliary system leading to jaundice, icterus and cirrhosis due to secondary biliary cirrhosis
|
|
|
Wilson's Disease
|
Hereditary disorder that results in excess coper deposition in LIVER and brain; transporter protein mutation which moves copper from hepatocyte into bile
Clinically neurologic dysfunctions with hepatic signs and Kayser-Fleisher Rings |
|
|
Hemochromatosis
|
Abnormal iron deposition in liver and other organs
|
|
|
Reye's Syndrome
|
Asprin + Viral Illness in Children leads to vomiting, lethargy, confusion, encephalopathy, brain edema, coma, seizures, etc in children
Leads to damage to cellular mitochondria in liver |
|
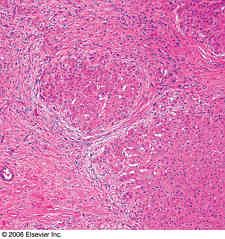
nodular hyperplasia
|
Solitary or multiple benign hepatocellular nodules in the absence of cirrhosis
|
|
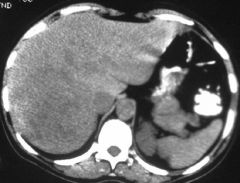
Hepatic Adenoma
|
Benign tumors of hepatocytes; occurs in women during reproductive years (ONLY HEPATOCYTES)
|
|

Hepatic Hemangioma
|
Benign, intrahepatic vascular tumor
|
|
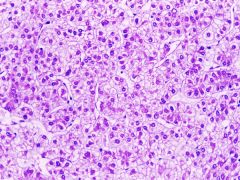
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
|
Primary malignancy neoplasm of liver arising from hepatocytes; cirrhosis is major risk factor as well as viral infection (HBV and HCV)
Serum alpha-fetoprotein levels often elevated |
|
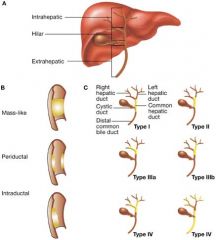
Cholangiocarcinoma
|
Primary malignant neoplasm of bile ducts (including intrahepatic and extrahepatic biliary system)
Often CEA and CA19-9 elevation |
|
|
Pyridoxal Phosphate (B6)
|
Needed for ALL transamination reactions
|

