![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
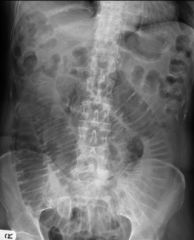
What is the best tool to do an initial screen for bowel dilatation??
|
Abdominal plain films (3 views)
|
|
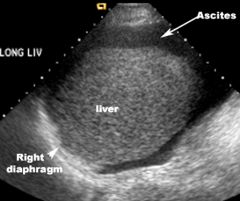
What should be used to confirm the presence or absence of ascites?
|
Ultrasound examination of the abdomen
|
|
|
What are the five F's?
|
Fluid, flatus, feces, fat, fetus,
|
|
|
A patient presents with generalized abdominal distension with pain. Is it more likely to be bowel dilation or ascites?
|
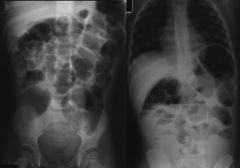
Bowel dilation
|
|
A patient presents with paucity of symptoms (early satiety, change in belt size, peripheral edema) - is this more likely to be ascites or bowel dilation?
|
Ascites
|
|
Why might a patient experiences dyspnea, orthopnea or tachypnea in tense ascites? (breathing problems)
|
Elevation of the diaphragm
|
|

Why might a patient experience indigestion or hurtburn due to tense ascites?
|
Increased intrabdominal pressure causes gastroesophageal reflux
|
|
|
A patient has lots of risk factors for liver diseaese. Is this more likely to cause ascites or bowel dilatation?
|
Ascites increased portal system pressure forces fluid into peritoneal cavity
|
|
|
A patient presents with bulging flanks and flank dullness as well as shifting dullness upon percussion with a fluid wave. What is this indicative of?
|
Ascites
|
|
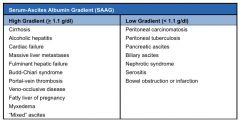
After performing paracentesis on a patient with ascites, how can you tell the difference between high and low gradient serum albumin?
|
High gradient = serum albumin - fluid albumin > 1.1 g/dl (transudate)
Low gradient = serum albumin - fluid albumin < 1.1g/dl (exudate) |
|

What does the albumin gradient tell you about the type of fluid in the peritoneum during ascites?
|
High gradient = transudate
Low gradient = exudate |
|

A patient presents with a low albumin gradient; Is this indicative of portal hypertension?
|
No; high albumin gradient indicates portal hypertension
|
|
|
What other physical signs should you look for in a patient with a high albumin gradient?
|

Hands: palmar erythema, Dupuytren’s (*), asterixis, clubbing, white nail bed
Upper extremities/trunk: gynecomastia, spider nevi, hair loss, muscle wasting, bruising Head/neck: encephalopathy, fetor hepaticus, parotid enlargement (*), scleral icterus, wasting Other: peripheral edema, ascites, testicular atrophy, splenomegaly, caput medusa |
|
|
What is a pertinent infectious concern with patients with ascites caused by cirrhosis?
|
Spontaeous bacterial peritonitis (SBP); up to 50% of pt who develop SBP do NOT develop fever or abdominal pain; confusion ma ybe the only presenting complaint
|
|
|
You perform paracentesis on a patient with ascites caused by cirrhosis. You note elevated wbc count (>500/mm and PMN > 250/mm). What does this indicate?
|
Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis
|
|
|
What are the two most common causes of peritoneal carcinomatosis?
|
Metastatic gastric and ovarian carcinoma
|
|

A patient presents with ascites, low albumin gradient and triglyceride levels > 975 mg/dl. What is this indicative of?
|
Chylous ascites; extraversion of milky chyle into the peritoneal cavity; due to cavity or lymphatic obstruction
|
|

Doming of the abdomen with visible ridges from underlying intestinal loops is usually due to what?
|
Intestinal distension
|
|
|
High pitched or decreased bowel sounds are usually due to what?
|
Bowel dilatation
|
|
|
A patient presents with bloating and antibodies to anti-endomysial and transglutaminase. What is the likely diagnosis?
|
Celiac disease
|
|

A patient who is unable to pass flatus after 24 hrs indicates what?
|
Complete bowel obstruction
|
|

Where would a bowel obstruction be located if the patient presents with profuse nausea and vomiting?
|
Proximal
|
|

What is the most common cause of small bowel obstruction?
|
Adhesions
|
|

What are the most common causes of large bowel obstructions?
|
Tumors, volvulus (twisted bowel loop)
|

