![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A patient complains of nausea when riding in a moving vehicle. What prototype drug should you prescribe?
|
Scopolamine; used to PREVENT (BUT NOT TREAT) motion sickness; block M1 receptors centrally and M1/3 in the periphery
|
|
|
A patient being treated for cancer becomes nauseous the second she pulls up to the hospital for treatment.
|
Lorazepam or diazepam (benzodiazepines); reduces NV originating from central cortical regions
|
|
|
A patient on a boat is currently experiencing constant motion sickness. What prototype drug should you consider?
|
Dimenhydrinate or diphenhydramine (antihistamine/antimuscarinic)
Addresses the vestibular component of motion sickness |
|
|
A patient presents with chemotherapy induced, estrogen induced, and likely blood borne cause of NV. Which drugs should you use to treat this combo?
|
Prochlorperazine; metoclopramide; domperidone
These drugs all act on dopamine receptors at the chemoreceptor trigger zone |
|
|
A patient presents with appendicitis, a GI visceral inflammatory condition that releases serotonin. What drug should you consider?
|
Odansetron; blocks serotonergic receptors involved in the initiation of the vomiting reflex
FLAT DOSE RESPONSE; so increasing the dose in patients that do not respond within 24 hrs is useless |
|
|
A patient presents with late phase chemo induced NV (day 2-5). What are the best medications to use?
|
Apretinant (substance P) or casopitant
|
|
|
A patient presents with refractory cancer (cancer that does not respond to treatment). The patient is also being treated for HIV drug induced NV. You warn the patient the medication you are going to prescribe may cause intoxication and hallucinations.
|
Nabilone and dronabinol
|
|
|
Which anticancer drug is the most emetogenic?
|
Cisplatin
|
|
|
A conscious patient comes in suspected of an overdose by CNS depressants. What is the best emetic to give?
|
Ipecac; acts at enteric receptors and stimulates the CTZ to trigger voimting reflex; must be administered with large amoun
|
|
|
A conscious patient comes in who accidently drank a toxic non-causatic non CNS depressant substance. What is the best emetic to give?
|
Apomorphine; directly activates D2R in CTZ; must be given paternally; can be administered to an uncooperative patient
|
|
|
What type of NV are 5HT3R antagonists best for?
|
Tx of post-operative and cytotoxic drug induced NV; Also useful for appendicitis
PT: Odansetron |
|
|
Which type of drugs are best for treating estrogen induced NV?
|
Dopamine antagonists; (they're good for treating blood born causes of NV which would include high estradiol)
prochlorperazine, metoclopramide, and domperidone |
|
|
Why would you administer dexamethasone along with odansetron?
|
Corticosteroids like dexamethasone enhance 5HT3 antagonist efficacy in delayed
|
|
|
What do the depressions on each end of the ectoderm form?
|
Future mouth (buccopharyngeal membrane) and anus (colacel membrane)
|
|
|
Which cross sectional structure below the belly button is the mesodermal lining and the ectodermal outer surface?
|
Somatopleure; really just the body wall
|
|
|
Which cross sectional structure below the belly button is composed of the endodermal lining and the mesodermal exterior
|
Splanchnopleure; gut wall
|
|
|
What is the name for the single cavity from which all cavities are derived?
|
Intraembryonic Coelom; forms from lateral plate mesoderm; begins as a horseshoe shaped tube
|
|
|
Folding of the intraembryonic coelum anteriorly causes it to surround what structure?
|
The heart
|
|
|
What does the endoderm turn into in the gut?
|
Mucous Epithelium including its glands
|
|
|
What does the mesoderm turn into in the gut?
|
Liver, biliary system, pancreas, everything EXCEPT mucous epithelium and glands
|
|

If an organ is covered on all of its surfaces by reflections of peritoneum it is called....
|
Intraperitoneal (Spleen)
|
|

If an organ is covered on only some of its surfaces it is called....
|
Extraperitoneal (Kidney)
|
|
|
What action causes fusion fascia to form?
|
Pressing of intraperitoneal organs against an abdominal wall; these organs become secondarily retropritoneal
|
|
|
The duodenum is an example of what kind of retroperitoneal structure?
|
Secondarily retroperitoneal
|
|
|
Which organ forms entirely from lateral plate mesoderm?
|
Spleen
The entire peritoneum forms from lateral plate mesoderm too |
|

What are the four contritbutions to the formation of the diaphragm?
|
Septum transversum, pleuroperitoneal membranes, dorsal mesentery, body wall myoblasts
|
|

A failure of the pleuroperitoneal membrane to develop or fuse with other components of the diaphragm results in what condition?
|
Diaphragmatic hernia; abdominal contents hernia into the pleural cavity, compressing the lung and creating a "hypoplastic" lung
|
|
|
A congenital diaphragmatic hernia may result from failure of the...
|

pleuroperitoneal membranes to fuse in a normal fashion
|
|
|
A congenital diaphragmatic hernia is usually life threatening because it is associated with...
|
pulmonary hypoplasia
|
|
|
An 8 day old boy presents with a history of complete loss of breath at times and of turning blue on a number of occasions. If the baby is placed in an upright or sitting position, his breathing improves. Physical examination reveals an unusually flat stomach when the newborn is lying down; auscultation demonstrates no breath sounds on the left side of the thorax. What is the diagnosis?
|
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia
|
|
|
During week 4, the developing diaphragm is located at what spinal levels
|
C3, C4, C5
|
|
|
A congenital diaphragmatic hernia most commonly occurs on which side
|
Left posterolateral side
|
|

The foregut is supplied by which blood supply?
|
Celiac
|
|

The midgut is supplied by which blood supplies?
|
Superior Mesenteric
|
|

The hindgut is supplied by which blood supply?
|
Inferior Mesenteric
|
|

Where is pain in the midgut localized to and what nerve path does it use?
|
Periumblical; uses sup mesenteric
|
|

Where is pain in the hindgut localized to and what nerve path does it use?
|
Hypogastric; uses inf mesenteric
|
|
|
Where is pain from the foregut localized to and what nerve path does it use?
|

Epigastric; celiac nerve path
|
|
|
Which part of the primary intestinal loop will form most of the small intestine?
|
Cranial limb
|
|
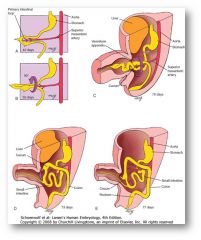
Which part of the primary intestinal loop will form the distal part of the ileum and the proximal part of the large intestine?
|
Caudal limb
|
|
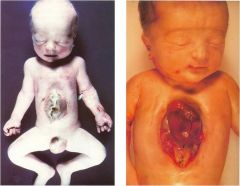
What condition occurs when the intestines fail to return to the abdominal cavity in the 10th through 11th week?
|
Omphalocele
|
|

An MRI reveals the large intestine is located towards the left side of the body and the small intestine on the right side; what has happened?
|
Nonrotation of the gut (left sided colon); occurs if the intestine does not rotate 180 degrees as it returns into the abdominal cavity
|
|
|
Which embryological foregut process is responsible for the lesser sac (or omental bursa)?
|
rotation of the stomach 90 degrees
|
|
|
What embryological foregut process is responsible for the renaming of the left and right vagal nerves?
|
rotation of the stomach 90 degrees; greater curvature points left, lesser curative points right; left vagal nerve rotates to the anterior and right vagal nerve rotates to the posterior
|
|
|
Where is the greater omentum located?
|
Hangs off of the greater curvative; results from the thinning of the dorsal mesentery
|
|

What is the function of the ventral mesentery in the stomach?
|
Attaches the developing liver to the stomach
|
|

Where does the coronary ligament attach?
|
The bare area where the liver contacts the diaphragm; there is no peritoneum here
|
|

A failure of stomach rotation during development would also displace what other organ?
|
spleen; which forms in the dorsal mesentery - it normally relocates to the right when the stomach rotates
|
|

The pancreas forms from where?
|
Ventral bud which is an outgrowth of the hepatic duct and the dorsal bud; ventral bud forms main pancreatic duct
|
|
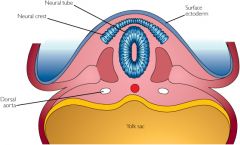
From what embryological structure is all gut and visceral neural innervation derived?
|
Neural crest
|
|
|
Which sympathetic nerve innervates the hindgut?
|
Lumbar splenic nerve synapses on inferior mesenteric ganglion which innevates hindgut
|
|

Describe the blood supply to the liver?
|
Blood is brought to the liver by the hepatic artery and portal vein; it leaves through the hepatic vein
|
|
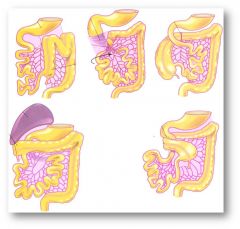
What happens in a volvulus?
|
A loop of bowel has abnormally twisted on itself
|
|

Which condition is characterized by a persistent yolk stalk whihc occurs about 3 feet from the ileocecal junction?
|
Mecekel's Diverticulum
|
|

Which condition is characterized by a pancreas that migrates the wrong way and encircles and strangles the duodenum?
|
Annular Pancreas
|
|

If recannalization or the blood supply is compromised to the developing GI tract, what condition can occur?
|
Stenosis (narrowing of lumen)
Atresia (complete occlusion) |
|

Which condition is characterized by a defect in the ventral abdominal wall in which there is a massive evisceration of intestines which are not covered by a peritoneal membrane
|
Gastroschisis
|

