![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
point |
names or indicates a location; capital Latin Letters |
|
|
|
line |
a straight path (extends forever); lowercase letter (cursive l) |
|
|
|
plane |
a flat surface (extends forever); italicized capital letter; or three noncollinear points |
|
|
|
collinear |
two or more points that are part of the same line (share a line) |
|
|
|
coplanar |
points, lines, and rays that are in the same plane |
|
|
|
segment |
a portion of a line that is all the points between two points called endpoints |
|
|
|
endpoint |
a point on an end of a segment or ray |
|
|
|
ray |
part of a line that starts at a point and extends in a direction forever |
|
|
|
opposite rays |
2 rays that have a common endpoint and form a line |
|
|
|
postulate/axium |
statement that is accepted as true without proof |
|
|
|
Unnamed Postulates (5) |
1. Through any 2 points, there is exactly one line 2. Through any 3 non-collinear points, there is exactly one plane 3. If two points lie in the same plane, then the line containing those points lies in the plane 4. If 2 lines intersect, then they intersect at exactly one point 5. If 2 planes intersect, then they intersect at exactly one line |
regarding lines, points, intersection, and planes |
|
|
Ruler Postulate |
points on a line can be put into a one to one correspondence with the real numbers |
|
|
|
Segment Addition Postulate |
If point B is between points A and C, then AB + BC = AC |
|
|
|
Different Types of Angles (4) |
1. Acute Angle: an angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 degrees 2. Right Angle: an angle with a measure of 90 degrees 3. Obtuse Angle: an angle whose measure is between 90 and 180 degrees 4. Straight Angle: measure to 180 degrees |
|
|
|
angle |
formed by 2 rays joined at their endpoint |
|
|
|
adjacent angles |
two angles that share a ray, but no common interior point |
|
|
|
LInear Pair Theorem |
the sum of the measure of a linear pair of angles is 180 degrees |
|
|
|
Complementary Angles |
a pair of angles whose measures add to be 90 degrees |
|
|
|
Supplementary Angles |
a pair of angles whose measure add to 180 degrees |
|
|
|
Vertical Angles |
If 2 lines intersect, then pairs of non-adjacent angles are vertical angles |
|
|
|
Inductive Reasoning |
the process of reasoning that a rule or statement is true because specific cases are true |
|
|
|
Conjecture |
a statement you believe to be true based on inductive reasoning |
|
|
|
Counterexample |
one example that shows the conjecture is not true |
|
|
|
Conditional Statement |
a statement of the form if p, then q; where p is the hypothesis and q is the conclusion |
|
|
|
Other Conditional Statement Forms |
1. Converse: if q, then p 2. Inverse: if not p, then not q 3. Contrapositive: if not q, then not p |
|
|
|
logically equivolent statements |
related conditional statements that have the same truth value: conditional and its contrapositive; converse and inverse |
|
|
|
deductive reasoning |
using definitions, postulates, previously proven theorems, and logic to draw conclusions |
|
|
|
Law of Detachment |
If p then q is a true statement, then when p is true, q is also true |
|
|
|
Law of Syllogism |
If p then q and q then r are true statents and p is true, then p then r is true |
|
|
|
biconditional statement |
p if and only q, bothp then p then q and its converse are true |
|
|
|
reflexive property of equality |
a = a |
|
|
|
symmetric prop of = |
if a = b, then b = a |
|
|
|
transitive prop of equality |
if a = b and b = c, then a = c |
|
|
|
substitution prop of equality |
if a = b, then b may be substituted in place of a |
|
|
|
linear pairs theorem |
if 2 angles form a linear pair, then they are supplementary |
|
|
|
congruent supplements theorem |
if 2 angles are supplementary to the same angle (or supplementary to 2 angles), then the 2 angles are congruent |
|
|
|
vertical angles theorem |
if 2 angles are vertical angles, then they are congruent |
|
|
|
right angle congruence theorem |
all right angles are congruent |
|
|
|
congruent complements theorem |
if 2 angles are complementary to the same angle (or 2 congruent angles), then the 2 angles are congruent |
|
|
|
common segments theorem |
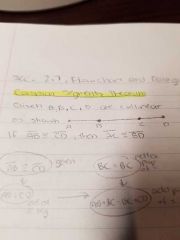
can pertain to common angles theorem |
|
|
|
unnamed theorem |
if 2 congruent angles are supplementary, then they are right angles |
relates to right angles |
|
|
parallel lines |
2 coplanar lines that don't intersect |
|
|
|
skew lines |
2 noncoplanar lines that don't intersect |
|
|
|
perpendicular lines |
2 lines that intersect on a 90 degree angle |
|
|
|
transversal |
a line that intersects 2 coplanar lines at 2 different points; 8 angles are formed |
|
|
|
corresponding angles |
angles that are in the same position of the intersection |
|
|
|
alternate interior angles |
angle pairs that are in the interior and on alternate sides of the transversal |
|
|
|
same side interior angles |
angle pairs that are in the interior and on the same side of the transversal |
|
|
|
alternate exterior angles |
angle pairs that are in the exterior and on alternate sides of the transversal |
|
|
|
corresponding angles postulate |
if 2 parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then corresponding angle pairs are congruent; converse is true |
|
|
|
alternate interior angles theorem |
if 2 parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the alt. int angles are congruent; it's converse is true |
|
|
|
alternate exterior angles theorem |
if 2 parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the alternate exterior angles are congruent; converse is true |
|
|
|
same side interior angles theorem |
if 2 parallel lines are cut by a transversal, then the same side interior angles are supplementary; converse is true |
|
|
|
parallel postulate |
through a point P, not on the line l, there is exactly one line parallel to l |
|
|
|
Unnanmed Theorem |
if 2 intersecting lines on the same plane form a linear pair of congruent angles, then the lines are parallel |
relates to intersecting lines |
|
|
Unnamed Theorem |
if 2 congruent supplementary, then they are right angles |
pertains to right angles |

