![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Coronal suture joined by the cranial bones |
Frontal bone and parietal bones |
|
|
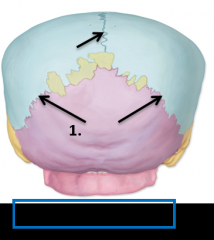
Lambdoid suture joined by cranial bones |
Parietal bones and occipital bone |
|
|
Sagittal suture joined by cranial bones |
Right and left parietal bones |
|
|
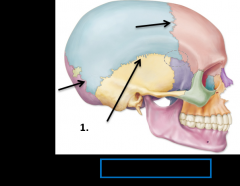
squamous suture joined which by cranial bones ? |
Temporal bone and parietal bone |
|
|
Fontanelle |
membranous interval at the margins of cranial bones in fetal skull |
|
|
Functions of neurocranium? |
1. Protects the brain, 2. houses of the organs of hearing and balance, 3. site of attachment for head and neck muscles |
|
|
calvarium |
Domelike roof of neurocranium |
|
|
what is the inferior of the perpendicular plate? |
The vomer bone |
|
|
Functions of Neurocranium (Cranial Vault) |
1. –Protects the brain 2. –Houses the organs of hearing and balance 3. –Site of attachment for head andneck muscles Consists of:•4 singular bones (Frontal, Ethmoid,Sphenoid, & Occipital) 2 sets of paired bones (Temporal& Parietal) |
|
|
What is a calvarium? |
Domelike roof of the neurocranium |
|
|
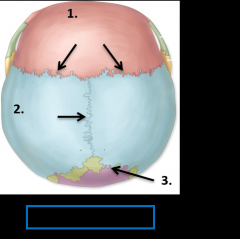
1. Frontal bone 2. Temporal bone 3. Parietal bone (left) 4. Parietal bone (right) 5. Occipital bone |
|
|
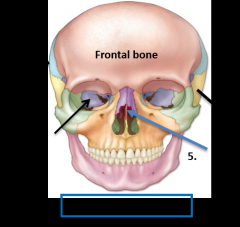
2.Parietal bone 3. Sphenoid bone 4. Temporal bone 5. Ethmoid bone (perpendicular plate) |
|
|
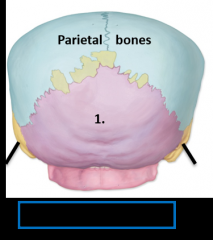
1. Occipital bone |
|
|
Suture |
immovable joints forming boundaries between cranial bones. |
|
|
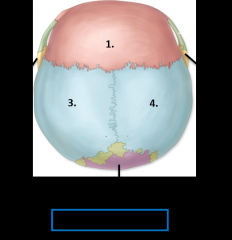
1. Coronal suture 2. Sagittal suture 3. Lambdoid suture |
|
|
1. Squamous suture |
|
|
1. Lambdoid suture |
|
|
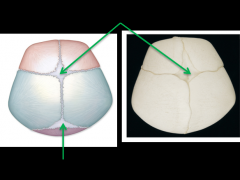
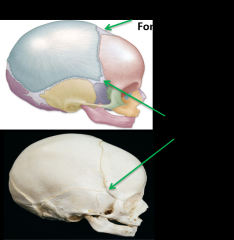
Fontanelle |
Membranous interval at the margins of cranial bones in fetal skull |
|
|
1. Anterior fontanelle 2. Posterior fontanelle |
|
|
1. Sphenoid fontanelle |
|
|
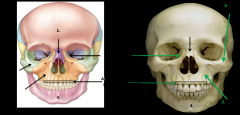
1. Nasal bone 2. Zygomatic bone 3.Maxilla bone 4.Mandible 5.Lacrimal bone |
|
|
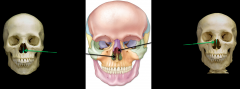
1. Vomer 2. Perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone |
|
|
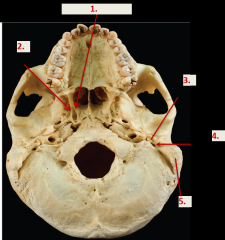
1. Medial pterygoid plate 2. Lateral pterygoid plate 3. Styloid process 4. Stylomastoid foramen 5. Mastoid process |
|
|
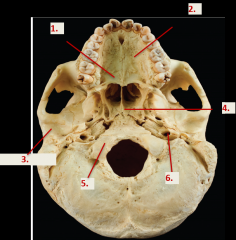
1. Palatine bone
2. Palatine process (of maxilla) 3.Mandibular fossa 4.Vomer 5.Occipital Condyle 6.Carotid canal |
|
|
Supraorbital notch/foramen |
Branch of Cranial Nerve V1 (Supraorbital Nerve) |
|
|
Infraorbital foramen |
Branch of Cranial V2 (infraorbital nerve) |
|
|
sUPERIOR ORBITAL FISSURE |
Cranial nerve III, IV, V1 (infraorbital nerve) |
|
|
Nasolacrimal canal |
Nasolacrimal duct |
|
|
Carotid canal |
passage for internal carotid artery |
|
|
Stylomastoid foramen |
passage for cranial nerve VII (facial nerve) |
|
|
Cribiform plate |
CN I (olfactory nerve) |
|
|
Optic canal |
CN II (optic nerve) |
|
|
Foramen rotundum |
CN V2 (maxillary branch of trigeminal N) |
|
|
Foramen ovale |
CN V3 (Mandibular branch of trigeminal N) |
|
|
Foramen spinosum |
Middle menigeal vessels |
|
|
foramen lacerum |
Not a true opening filled with cartilage when a live |
|
|
internal acoustic meatus |
CN VIII (vestibulocochlear) |
|
|
Jugular foramen |
Internal jugular V, Cranial nerves IX,X,XI |
|
|
hypoglossal canal |
CN XII (Hypoglossal N) |
|
|
foramen magnum |
Vertebral arteries, spinal cord, CN XI (Accessory N) |
|
|
Mandibular foramen |
Passage for inferior alveolar nerve (Where you are injected with anesthetic during dental procedures. |

