![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
MacKonkey Agar
purpose interpretation |
Selective for GNB, differential for lactose fermenters
pink colonies = LF colorless colonies = NLF |
|
|
EMB agar
purpose interpretation |
selective for GNB, differential for lactose fermenters and E. coli sp
dark blue/black/purple colonies = LF dark colonies w/ metallic sheen = E. coli colorless colonies = NLF |
|
|
Xylose-Lysine-Desoxycholate Agar (XLD)
purpose interpretation |
selective and differential for stool pathogens (Salmonella, Shigella)
red colonies = Salmonella or Shigella red colonies w/ black centers = Salmonella yellow colonies = not Salmonella or Shigella
|
|
|
Hektoen Enteric agar (HE)
purpose interpretation |
selective for stool pathogens (Salmonella, Shigella), inhibits normal bowel flora
green colonies = Shigella or Salmonella green colonies w/ black center = Salmonella yellow/orange colonies = normal flora
|
|
|
Salmon-Shigella agar (S-S)
purpose interpretation |
selective/differential for stool pathogens
colorless colonies = Shigella colorless colonies w/ black center = Salmonella pink/red colonies = normal flora |
|
|
MacKonkey Sorbitol (SMAC)
purpose interpretation |
selective/differential for sorbitol fermentation, isolates pathogenic E. coli (E. coli 0157:H7) in stool specimens.
clear colonies = sorbitol nonfermenter = possibly E. coli O157:H7 pink colonies = sorbitol fermenter = rules out E. coli O157:H7 |
|
|
CIN agar
purpose interpretation |
selective/differential for mannitol fermentation, recovery of Yersinia enterocolitica
pink colonies = mannitol fermenters pink center and colorless border (bull’s eye) = mannitol fermenter, likely Y. enterocolitica clear colonies = mannitol nonfermenter |
|
|
Kligler’s Iron Agar (KIA)
purpose interpretation |
Contains glucose and lactose. Detects for fermentation of sugars (acid production lowers pH, results in color change) Also demonstrates hydrogen sulfide (H2S) production.
red slant/Yellow butt = Alkaline/Acid = glucose fermentation only yellow Slant/yellow butt = Acid/Acid = glucose and lactose fermentation red slant/red butt = Alkaline/Alkaline = nonfermentative Black precipitate = H2S production cracking of media = gas production
|
|
|
Triple Sugar Agar (TSI)
purpose interpretation |
Contains glucose, lactose, and sucrose. Detects for fermentation of sugars (acid production lowers pH, results in color change). Also demonstrates hydrogen sulfide (H2S) production.
red slant/Yellow butt = Alkaline/Acid = glucose fermentation only yellow Slant/yellow butt = Acid/Acid = glucose & lactose and/or sucrose, or all three ferment red slant/red butt = Alkaline/Alkaline = nonfermentative Black precipitate = H2S production cracking of media = gas production
|
|
|
Indole
purpose interpretation |
Spot or liquid test Shows ability to oxidize tryptophan to indole
no color development = negative red ring (liquid test) or red saturation (spot) = positive for indole production
|
|
|
Methyl Red/Voges Proskauer tests (MR/VP)
purpose interpretation |
differentiates two pathways for pyruvic acid production, either the production of mixed acid products from the fermentation of glucose (MR) or the production of neutral acetoin (VP).
MR tube red at surface = positive MR tube yellow at surface = negative VP tube pink/red at surface = positive VP tube yellow at surface = negative
|
|
|
Citrate
purpose interpretation |
detects ability of using citrate as sole source of carbon
growth and blue color, or just growth = positive no growth, green = negative
false positives may occur with inoculum that is too heavy |
|
|
Decarboxylase Reactions (Lysine Decarboxylase - LDC Ornithine Decarboxylase - ODC)
purpose interpretation
|
detects bacteria’s ability to remove carboxyl group off of amino acids. Different tests use different amino acids. MUST have control tube, which should turn yellow, to demonstrate that specimen is viable.
red/purple = positive for decarboxylation yellow = glucose fermentation only, negative for decarboxylation
|
|
|
Deaminase Reaction (PDA, TDA, or LDA)
purpose interpretation |
detects bacteria’s ability to remove amine group (possess deaminase enzyme). Only Proteus, Providencia, Morganella sp. possess deaminase. Different amino acids are used in different media (phenylalanine, tryptophan, lysine).
PDA green or brown = deaminase positive no color = deaminase negative
LDA burgundy slant/yellow butt = deaminase positive colorless = negative
TDA brown/red = deaminase positive colorless = negative
|
|
|
Lysine Iron Slants (LIA)
purpose interpretation |
differentiates enteric bacteria based on ability to decarboxylate or deaminate lysine, and to produce H2S.
Interpretation: Purple butt = Alkaline = decarboxylase positive Yellow butt = Acidic = decarboxylase negative Red slant = deaminase positive black precipitate = H2S production |
|
|
ONPG
purpose interpretation |
detects late or slow lactose fermenters. Note: fast lactose fermenters will also show positive (often w/in 20 minutes).
yellow color within 20 minutes to 24 hours = positive for lactose fermentation colorless after 24 hours = negative for lactose fermentation |
|
|
Urease
purpose interpretation |
detects organisms who produce urease
Red throughout media = positive (strong/fast) Red in slant = positive (weak/slow) yellow = negative |
|
|
DNase
purpose interpretation |
detects production of DNase
clearing of tube or plate media = positive no clearing = negative |
|
|
Gelatinase
purpose interpretation |
detects production of Gelatinase, which results in the liquefaction of gelatin.
solid tube = negative liquid tube = possibly positive, place in refrigerator for 30 mins and check again solid tube after refrigeration = negative liquid tube after refrigeration = positive |
|
|
O/F (Carbohydrate Utilization) Hugh Leifson’s or King's
purpose interpretation |
Detects carbohydrate utilization acid end products in aerobic and anaerobic environments. Media is semi-solid with a particular carbohydrate (glucose, maltose, lactose or xylose). Two tubes are used for each specimen--one is aerobic, and one is anaerobic (covered w/ mineral oil). Media used for testing of non fermentative organisms.
Media used for Enterobacteriaceae (King’s O/F) is same principle but has different composition of carbohydrates and peptone
Both tubes yellow = fermentative organism aerobic tube yellow/anaerobic tube green/blue = oxidative organism both tubes green/blue = asaccharolytic organism
|
|
|
Arginine dihydrolase (ADH) (decarboxylation)
purpose interpretation |
FOR NONFERMENTATIVE GNB
detects bacteria’s ability to remove carboxyl group off of amino acids. Different tests use different amino acids. MUST have control tube, which should turn grey, to demonstrate that specimen is viable.
purple = positive for decarboxylation yellow = negative for decarboxylation |
|
|
Acetamide
purpose interpretation |
FOR NONFERMENTATIVE GNB
Determines if an organism can use acetamide as its sole source of carbon.
blue = deamination of acetamide = positive yellow = no deamination of acetamide = negative |
|
|
Burkholderia Cepacia Selective Agar (BCSA) and OFPBL agar
purpose interpreation |
selective for Burkholderia cepacia (from cystic fibrosis patients)
BCSA pink and yellow halos around colonies = B. cepacia
OFPBL yellow colonies = B. cepacia |
|
|
Nitrate Reduction
purpose interpretation |
to determine whether organism can reduce nitrate to nitrite
red = positive
clear, then red after addition of zinc dust = negative (i.e. nitrates still remain in broth)
clear, then clear after addition of zinc dust = positive (i.e. nitrates were reduced to nitrites were reduced to NO2) |
|
|
Catalase
purpose interpretation |
detects catalase enzyme which breaks hydrogen peroxide into O2 and H2O
rapid bubbling = positive no bubbling or very minor bubbles = negative |
|
|
Bile Esculin Hydrolysis
purpose interpretation |
tests ability to grow in 40% bile and hydrolyze esculin
growth and blackening of media = positive no growth or growth w/out blackening = negative |
|
|
Hippurate Hydrolysis
purpose interpretation |
used in the presumptive identification of Gardnerella vaginalis, Campylobacter jejuni, Listeria monocytogenes and group B streptococci, by detecting the ability of the organism to hydrolyze hippurate.
positive = deep blue/violet color in 30 minutes. negative = faint blue color change, or no color change.
|
|
|
Reverse CAMP
purpose interpretation |
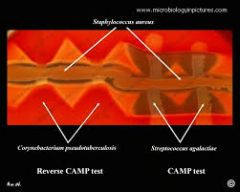
production of enzyme that inhibits the beta-lysin produced by S. aureus.
Perpendicular streaks of S. aureus and organism to be tested are made
dark triangle at intersection of organisms where beta hemolysis is inhibited = Reverse CAMP positive
compare to positive CAMP in which beta hemolysis is increased |
|
|
Partial Acid Fast
purpose interpretation |
Modification of Acid Fast stain/View under microscope
partially acid fast = pink or red non acid fast = color of counter stain (usually blue) |
|
|
Lysozyme resistance
purpose interpretation |
Tests ability to grow in lysozyme
growth = positive for resistance no growth = not resistant |
|
|
Oxidase
purpose interpretation |
tests for production of oxidase
can be done with filter paper test, swab, direct plate method, and test tube method. Take organism from BA or CHOC, not MAC agar.C
oxidase positive = when the color changes to dark purple within 5 to 10 seconds oxidase negative = color does not change or it takes longer than 2 minutes. |
|
|
Cetrimide Agar
purpose interpretation |
Selective for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Used to detect pyocyanin and pyoverdin production.
growth with blue, blue-green, or yellow-green pigment = pyocyanin and fluorescein = P. aeruginosa |
|
|
Burkholderia Cepacia Selective Agar (BCSA) and OFPBL Agar
purpose interpretation |
selective/differential for B. cepacia. Used for isolating B. cepacia from patients with Cystic Fibrosis
BSCA pink or yellow halos around colonies = B. cepacia
OFPBL yellow colonies = B. cepacia
|
|
|
TCBS Agar (Thiosulfate Citrate Bile Salts Sucrose Agar)
purpose interpretation |
Selective isolation and cultivation of Vibrio species, differentiates Vibrio based on sucrose fermentation
yellow colonies = sucrose fermenter = V. cholerae or V. anginolyticus
green colonies = non sucrose fermenter = V. parahemolyticus or V. vulnificus |
|
|
CAMPY-BAP or Skirrow's
purpose interpretation |
Selective media for Campylobacter jejuni. Inhibits overgrowth of faster-growing enterics.
Growth of small, mucoid colonies, usually grayish in coloration = C. jejuni |

