![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
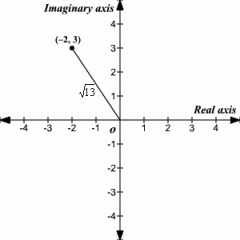
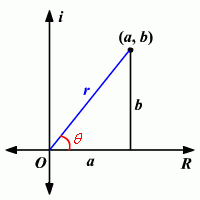
Absolute Value of a Complex Number |
The absolute value of a complex number , a+bi (also called the modulus ) is defined as the distance between the origin (0,0) and the point (a,b) in the complex plane |
|
|
|
Complex Number |
number that can be expressed in the form a + bi, where a and b are real numbers and i is the imaginary unit, satisfying the equation i2 = −1 |
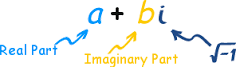
|
|
|
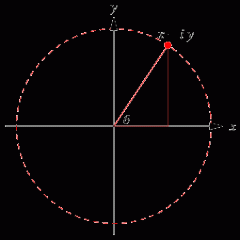
Argand Plane |
a plot of complex numbers as points |
|
|
|
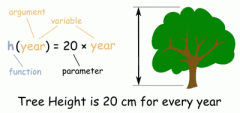
Argument |
a specific input in the function, also known as an independent variable |
|
|
|
Cartioid |
a plane curve traced by a point on the perimeter of a circle that is rolling around a fixed circle of the same radius |
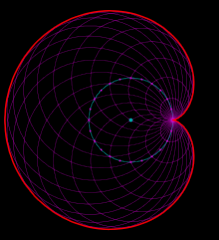
|
|
|
Complex Plane |
an infinite two-dimensional space representing the set of complex numbers, especially one in which Cartesian coordinates represent the real and imaginary parts of the complex numbers |
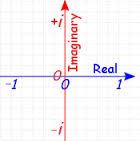
|
|
|
Imaginary Axis |
The vertical line in the complex plane, every point on which corresponds to a complex number having zero real component |
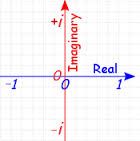
|
|
|
Limacon |
roulette formed by the path of a point fixed to a circle when that circle rolls around the outside of a circle of equal radius |
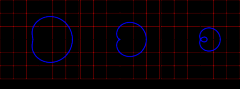
|
|
|
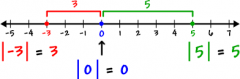
Modulus |
another term for absolute value |
|
|
|
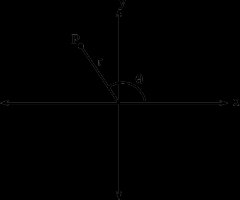
Polar Axis |
the fixed line, usually horizontal, from which the angle made by the radius vector is measured in a polar coordinate system |
|
|
|
Polar Coordinate System |
a two-dimensional coordinate system in which each point on a plane is determined by a distance from a reference point and an angle from a reference direction |
|
|
|
Polar Coordinates |
point on a plane determined by a distance from a reference point and an angle from a reference direction |
|
|
|
Polar Equation |
equation defining an algebraic curve expressed in polar coordinates |
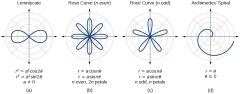
|
|
|
Polar Form |
another way to represent a complex number |
|
|
|
Polar Graph |
A system of coordinates in which the location of a point is determined by its distance from a fixed point at the center of the coordinate space (called the pole), and by the measurement of the angle formed by a fixed line (the polar axis, corresponding to the x-axis in Cartesian coordinates) and a line from the pole through the given point |
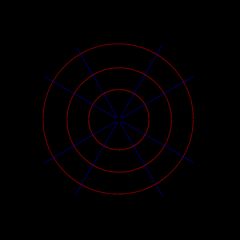
|
|
|
Pole |
denote a singularity of a complex function |
|
|
|
Real Axis |
the line in the complex plane corresponding to zero imaginary part |
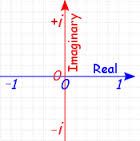
|
|
|
Rose |
a sinusoid plotted in polar coordinates |

|
|
|
Spiral of Archimedes |
a curve defined by a polar equation of the form r = θa, with special names being given for certain values of a |
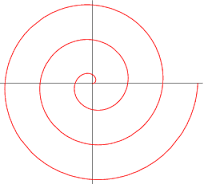
|
|
|
Trigonometric Form |
Same as polar complex form |
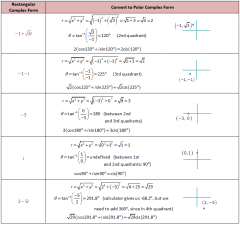
|

