![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
middle eastern cystitis
|
schistosomiasis
|
|
|
immunosuppressed w cystitis
|
candidal and cryptococcal
|
|
|
common infectious agents of cystitis
|
E. coli, proteus, klebsiella, enterobacter
|
|
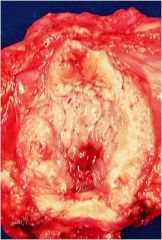
hunner ulcer
|
hemorrhagic defect in interstitial cystitis; like UTI w noe vidence of bacterial infection or STDs, cytoscopy shows mucosal involvement
|
|
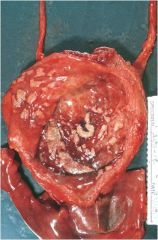
malacoplakia
|
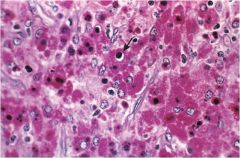
gross: soft yellow raised mucosal plaques
micro: infiltrate w foamy macrophages, occasional multinucleate giant cells and lymphocytes (Michaelis Gutman bodies, macrophages w granula rPAS positive cytoplasm) associated with chronic bacterial infection in immunosuppressed |
|
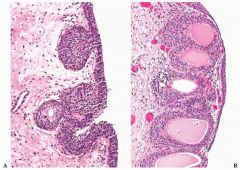
|
Brunns nests and cystitis cystica
metaplastic lesions |
|
|
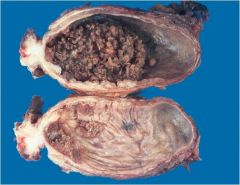
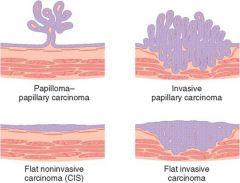
urothelial neoplasms
|
|
|
squamous bladder cell carcinoma
|
ass w chronic bladder irritatio nand infection, 3-7% of bladder caners in US
|
|
|
risks for bladder cancer (painless hematuria)
|
smoking
industrial arylamines shistosoma (egypt/sudan/middle east) chronic analgesics cyclophosphamide irdiation |
|
|
mcc of bladder obstruction in males
|
nodular hyperplasia of the prostate
|
|
|
urethritis is also ass w what syndrome
|
Reiter syndrome (arthritis, conjunctivits, urethritis)
|
|
|
urethritis w leukocytes containing gram negative diplococci
|
gonorrhea (but could still have chlamydia or other nongonococcal urethritis)
|
|
|
smal red painful mass located at urehtral meatus
|
urethral caruncle; extremely friable, inflammed granulation tissue polyp
|
|
|
prox vs distal urethal neoplasms
|
prox = urothelial differentiation
distal = squam cell carc |
|
|
hypospadias
|
abnormal opening on ventral penis due to failure of urethral folds to close
more common than epispadias, fix to prevent UTIs, hypo = below |
|
|
epispadias
|
abnormal opening on superior/dorsal side of penis due to faulty positioning of genital tubercle
exstrophy of bladder associated w epispadias, when you have epispadias you hit your Eye when you pEE. |
|
|
paraphymosis
|
retracted foreskin cant be put back own glans
|
|
|
phimosis
|
orifice too small to allow normal retraction
can be caused by balanoposthitis (inflammation of glans, often 2 poor hygiene in uncircum males w smegma as irritant) |
|
|
HPV 16, younger age mult red/brown papular lesions, never invasive, sex active adults
|
Bowenoid papulosis
indistinguishable from Bowen dz |
|
|
Erythroplasia of Queyrant
|
carcinoma in situ that can occur on the glans and prepuce; has velvety red, well marginated appearance
|
|
|
involvement of corpus cavernosum w fibrous bands
|
Peyronie dz
painful erection and curvature of the penis, micro exam = dense fibrosis |
|
|
cells that secrete testosterone in the testis
|
Leydig cells
|
|
|
Sertoli cells
|
columbar/pyramidal cell sthat surround cells of spermatogenic linease; function as suport cells (secrete mullerian inhibiting substance); blood testis barrier formed from tight occluding junctions between basolateral membranes of adjacent sertoli cells
|
|
|
Leydig (interstitial) cells
|
produce testosterone
|
|
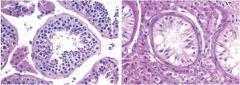
cryptorchidism
|
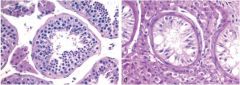
abnormal testicle descent
transbaodminal phase (mullerian inhibiting substance) inguinoscrotal phase (androgen dependent) |
|
|
torsion
|
twisting of spermatic cord blocks venous drainage but arteries still patent, hemorrhagic infarc, urologic emergency
|
|
|
hemorrhagic cystitis
|
often due to adenovirus
|
|
|
sterile pyruria (WBC in urine) + negative culture after 24 hrs
|
always think renal TB
could also be chlamydia trachomatis |
|
|
complications of cyclophosphamide
|
1. hemorrhagic cystitis
2. transitional carcinoma of the bladder |
|
|
Epididimytis < 35 ys old and > 35 ys old
|
<35: a. GC, chalmydia trachomatis
> 35: E. coli, pseudomonas |
|
|
testicle w bluish black color + absent cremasteric reflex
|
gross torsion of testicle; drawn up into the inguinal canal, surgery imperative
|
|
|
mc testicular cancer
|
seminoma
|
|
|
testicular cancer on transillumination
|
NO transillumination (bc not fluid filled; painless mass
|
|
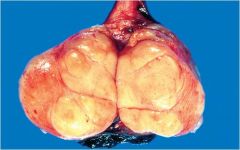
seminoma MC testicular cancer
|
a. cryptorchid relationship: risk extends to normal testicle as well
b. most radiosensitive c. para-aortic lymph node metastasis positive staining for placental alkaline phosphatase (PLAP) neoplastic cells divided into lobules separated by delicate septa |
|
|
seminomatous tumors
|
cells resemble primordial germ cells or early gonocytes
|
|
|
identical tumor to seminoma but in women
|
dysgerminoma, occur sin ovary
|
|
|
mc testicular cancer in children
|
yolk sac tumor
|
|
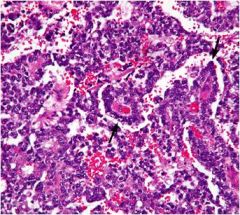
yolk sac tumor mc testicular cancer in children
|
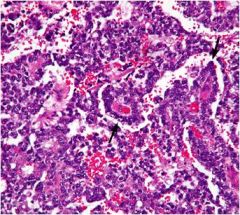
a. endodermal sinus tumor
b. schiller duval bodies (look like glomerulus) c. INCREASED AFP and alpha-1 antitrypsin (eosinophilic hyaline like globules) |
|
|
most malignant testicular cancer
|
choriocarcinoma
|
|
|
choriocarcinoma most malignant testiuclar cancer
|
a. increased B-hCG from syncytiotrophoblast
b. may produce gynecomastia c. lung metastasis |
|
|
teratoma
|
teratocarcinoma mc ass w increase in AFP and B-hCG: embryonal carcinoma _ teratoma
|
|
|
elderly male w low back pain
|
do a rectal to r/o prostate cancer before any other test
if alk phos elevated = osteoblastic metastasis from prostate |
|
|
tumor staging
|
1. confined to primary site
2. confined to primary site + regional nodes 3. metastases to other organs |
|
|
AFP for test tumors
|
yolk sac tumors
|
|
|
HCG for test tumors
|
choriocarcinoma
|
|
|
Lactate dehydrogenase and testicular tumors
|
correlates w tumor cell mass
|
|
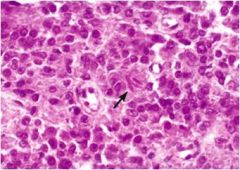
reinke crystals
|
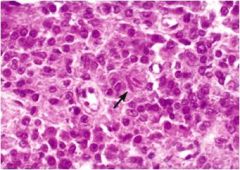
seen in leydig cell tumor
|
|
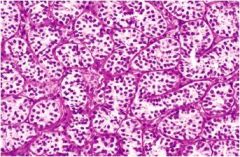
sertoli cell tumor
|
usually present as a testicular mass and are hormonally silent
10% malig tumor cells arranged as trabeculae forming cordlike structures and tubules |
|
|
chylocele
|
lymph in tunica vaginalis
|
|
|
spermatoele
|
cystic accumulation of semen in efferent ducts or dete testis
|
|
|
varicocele
|
dilated veins in spermatic cord
|
|
|
hematocele
|
blood in tunica vaginalis
|
|
|
hydrocele
|
collection of serous fluid in tunica vaginalis
|
|
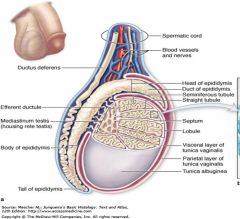
tunica vaginalis
|
mesothelial lined surface exterior to the testis
|
|
|
cryptorchidism
|
undescended testis (one or both); lack of spermatogenesis due to increased body temp; ass w increased risk of germ cell tumors. Prematurity increases the risk of cryptorchidism
|
|
|
mc etiology of granulomatous prostitis
|
BCG instillation into the bladder (attenuated strain of mycobacteira, used to tx baldder cancer)
|
|
|
prostatic hyperplasia
|
1. develops in transitional zone around the urethra - prostate cancer is in the peripheral zone (outside) and detected by rectal exam
2. DHT and estrogen mediated 3. clinical a. dribbling b. urinary retention is more likely benign than malignant c. PSA does not distinguish hyperplasia from cancer d. PSA NOT increased after rectal |
|
|
tx of BPH
|
a1 antagonists (terzosin, tamsulosin) which cause relaxation of smooth muscle
5-alpha reductase inhibition - inhibits synthesis of DHT and physically shrinks the prostate transurethral resection of the prostate; removals periurethral prostate tissue |
|
|
cancer staging abbreviation
|
TNM (tumor, nodes, metastasis)
|
|
|
PSA density =
|
total PSA/estimated gland volume
|
|
|
epi/risk factors of prostate cancer
|
age is greatest risk factor
a. increasd risk w 1 degree relative b. smoking c. MC cancer in men d. second mc cancer killer in men |
|
|
screening test for prostate cancer
|
rectal exam + PSA
|
|
|
confirmatory test for prostate cancer
|
transrectal ultrasound w Bx, watch for osteoblastic metastasis w elevated alk phos
|
|
|
hormone mediation of prostatic hyperplasia vs prostate cancer
|
prostatic hyperplasia = DHT and estrogen mediated
cancer = DHT |
|
|
Endometriosis
|
Non-neoplastic endometrial glands/stroma in abnormal locations outside the uterus
a. mc due to reverse menses b. metaplasia c. hematogenous/lymphohematogenous spread d. only occurs in reproducive life |
|
|
clinical features of endometriosis
|
a. mcc of secondary dysmenorrhea
b. ovaries most often involved (chocolate cysts) c. induration in pouch of Douglas (pain on defecation) d. dyspareunia e. intestinal obstruction laparoscope best for Dx and Rx |
|
|
mc benign tumor in women
|
leimyoma
a. sometimes claled fibrinoids b. mc tumor of GI tract: mc in stomach whorled pattern of smooth muscle bundles cause of menorrhagia, obstructive delivery |
|
|
leiomyoma epi
|
mc benign tumor in women
|
|
|
Asherman Syndrome
|
acquired uterine disorder characterized by intrauterine adhesions
|
|
|
polycystic ovarian syndrome pathogenesis
|
increased LH production leads to anovulation (via testosterone and 17-ketosteroids)
enlarged bilateral cystic ovaries manifest clinically w amenorrhea, infertility, obesity and hirsutism increased LH -> increased testosterone/17KS (hirsutism) -> increased adipose aromatizes androgens to estrogens (endometrial hyperplasia/cancer) -> estorgen inhibits FSH and enhances LH release -> continued cycle of LH stimulation -> lack of FSH causes atresia of follicles and large ovaries w subcortical cysts |
|
|
clinical symptoms of PCOS
|
obesity, hirsutism, irregular menses, infertility, endometrial carcinoma
tx w birth control pills to suppress LH, clomiphene if pt wants to become pregnant |
|
|
pelvic inflammatory dz
|
c. trachomatis (subacute, often undiagnosed), n. gonorrhoae (acute, high fever), cervical motion tenderness (chandelier sign), purulent cervical discharge
PID may include salpingitis, endometritis, hydrosalpinx, tuboovarian abscess. Can lead to Fitz-Hugh Curtis syndrome - infection of the liver capsule and violin string adhesions o fpartietal peritoneum to liver |

