![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
93 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Histology |
Study of cell types |
|
|
Cells |
Focused on one main task |
|
|
Tissues |
Groups of cells that carry out particular function and have structural similarities |
|
|
Organs |
Interconnected group of structures in the body that perform a particular function |
|
|
Epithelium |
* Cells fit tightly together to form continuous layer (sheet) of cells-->facilitates barrier formation
* Stick to each other and the basement membrane * Regulates entry/exit of substances to and from the body-->allows for diffusion & responsible for secretion * Lining ducts/tubes * Cells surrounding a lumen or clear space
|
|
|
Desmosomes |
* Very dense assemblies of cadherin proteins cause desmosomes to make very strong focal contacts between cells
* Provide very strong connections between cells, preventing epithelial cell layers from being torn apart under stress * Ex//: Childbirth |
|
|
Hemidesmosomes |
Connect the cytoskeleton to the basal lamina, anchoring the cell to the ECM |
|
|
Integrins |
Transmembrane receptors that are bridges for cell-cell and cell-ECM interactions |
|
|
Tight junctions |
* Establish a seal between adjacent cells
* Rows of tight junction proteins form a "gasket" around the cells * Tight junctions are much more prevalent in the epithelial cells than other types of cells and make the epithelial barrier "leak proof" |
|
|
Gap junctions |
* Allow cells to communicate with each other by channels
* Made of connexin proteins * Provide direct cytoplasmic communication between adjacent cells --> only very small molecules and ions can pass through |
|
|
Adherens junction |
* Connect cells of the same type
* Cadherin proteins |
|
|
Cadherin |
* Calcium-dependent adhesion proteins that allow cells to bind to each other
* Many different kinds of cadherins-->different cell types express each cadherin * Bind homotypically |
|
|
Apical surface |
Faces the "outside" |
|
|
Basal surface |
Faces the basement membrane |
|
|
Basement membrane |
* Extracellular matrix (ECM) that includes the basal and reticular lamina
|
|
|
Extracellular matrix |
2 main components * Ground substance * Proteinaceous fibers produced by cells secreted into extracellular environment 1. Collagen for strength 2. Elastin for stretch 3. Reticular fibers for crosslinking
|
|
|
Basal lamina |
Secreted by epithelial cells |
|
|
Reticular lamina |
Secreted by underlying connective tissue |
|
|
Regeneration |
Process of renewal, restoration and growth that makes genomes, cells, organisms and ecosystems resilient to natural fluctuations or events that cause disturbance or damage |
|
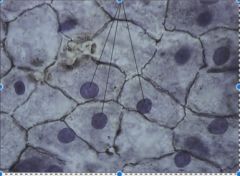
|
Simple Squamous Epithelium Main locations * Air sacs of lungs; lining of blood vessels* Passage of materials where little or no protection is needed and where diffusion is major form of transport * Cells are flat and arranged as single layer |
|
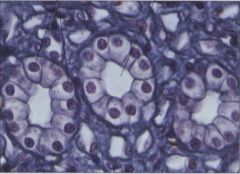
|
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Main locations * Linings of kidney tubules; gland ducts* Secretion and absorption * Single layer of cells; LM shows cross section through tubules; from the side of each cell looks like a short cylinder; some have microvilli for absorption |
|
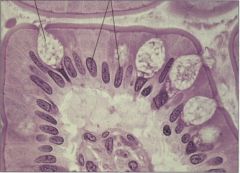
|
Simple Columnar Epithelium Main locations * Linings of much of digestive tract and upper part of respiratory tract* Secretion, especially of mucus; absorption; protection; moves layer of mucus * Single layer of columnar cells; sometimes with enclosed secretory vesicles (in goblet cells); highly developed Golgi complex; often ciliated |
|
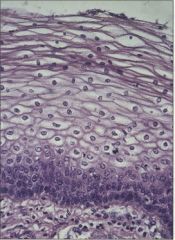
|
Stratified Squamous Epithelium Main locations * Skin; mouth lining; vaginal lining* Protection only; little or no absorption or transit of materials; outer layer continuously sloughed off and replaced from below * Several layers of cells, with only the lower ones columnar and metabolically active; division of lower cells causes older ones to be pushed upward toward surface, becoming flatter as they move |
|
|
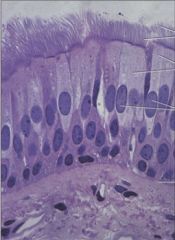
Pseudostratified Epithelium Main locations * Some respiratory passages; ducts of many glands* Secretion; protection; moves layer of mucus * Ciliated, mucus-secreting, or with microvilli; comparable in many ways to columnar epithelium except that not all cells are the same height; so, though all cells contact the same basement membrane, the tissue appears stratified |
|
|
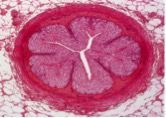
Transitional Epithelium Main locations * Lines urinary tract* Layers are protective * Shape-shifting allows expansion and contraction when necessary * Cuboidal to squamous based on what's going on around it |
|
|
Respiratory System |
Biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for the process of respiration in an organism |
|
|
Alveoli |
Epithelial structures made of simple squamous epithelium to allow gasses to diffuse into the bloodstream |
|
|
Gland |
1+ epithelial cells specialized to produce secretions (enzymes, mucus, hormones, etc) |
|
|
Goblet cells |
Specialized mucus-secreting cells |
|
|
Duct |
Tube |
|
|
Exocrine Glands |
Secrete their products directly into its destination usually through a duct (sweat, saliva, etc)-->goblet cells/sweat glands * Simple tubular gland (intestine)* Compound tubular gland (seminiferous tubules) |
|
|
Endocrine Glands |
* Lack ducts
* Release their secretions into the interstitial fluid where it diffuses into the blood and travels throughout the body Ex//: Hormones |
|
|
Interstitial Fluid |
Tissue fluid |
|
|
Ciliated |
* Often seen in columnar epithelial cells, cilia beat in coordinate way to move materials over the tissue surface
* Most of upper respiratory tract is lined with ciliated columnar epithelium
|
|
|
Microvilli |
* In intestine the apical surface of cells has a "brush border" to increase surface area
* Specialized for secretion, absorption, protection |
|
|
Connective tissue |
* Framework that supports and cushions body * Relatively few cells
* Contains 3 types of fibers 1. Collagen 2. Elastic 3. Reticular |
|
|
Mesoderm |
* Middle germ layer (tissue layer) and made up of cells that migrate between the endoderm and ectoderm
* Contributes tissues to many organs: heart, blood vessels, muscles, bones |
|
|
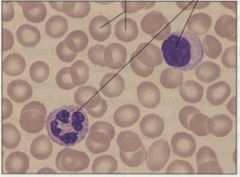
Blood Main locations * Within heart and blood vessels of circulatory system* Transports oxygen, nutrients, wastes, and other materials * Consists of cells dispersed in fluid intercellular substance (plasma) |
|
|
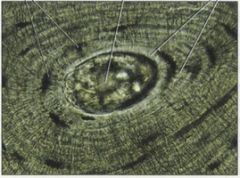
Bone Main locations * Forms skeletal structure in most vertebrates* Supports and protects internal organs; calcium reservoir; skeletal muscles attach to bones * Osteocytes in lacunae; in compact bone, lacunae embedded in lamellae, concentric circles of matrix surrounding Haversian canals |
|
|
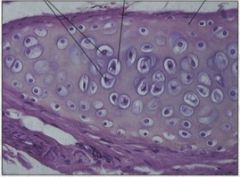
Cartilage Main locations * Support in skeletons in sharks/rays; ends of bones in mammals and some other vertebrates; supporting rings in walls of some respiratory tubes; tip of nose; external ear* Flexible support * Cells (chondrocytes) separated from one another by intercellular substance; cells occupy lacunae |
|
|
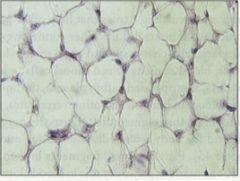
Adipose Main locations * Subcutaneous layer; pads around certain internal organs* Food storage; insulation; supports organs such as mammary glands, kidneys * Fat cells are star shaped at first; fat droplets accumulate until typical ring-shaped cells are produced |
|
|
Ground substance |
* Can be liquid, gel-like, or solid
* Solidity determined by ratio of water:polymer * Composed of proteins and carbohydrates * Function-->reservoir for water, ions, etc |
|
|
Collagen |
* Group of fibrous proteins found in all animals (most abundant protein)
* Very tough * Tensile strength (ability to stretch without tearing) is comparable to steel * Wavy and flexible allowing them to remain intact when tissue is stretched |
|
|
Tendon |
* Cords that connect muscles to bone
* Made of dense connective tissue-->dominant fiber is collagen |
|
|
Ligament |
* Cables that connect bones to one another
* Made of dense connective tissue-->dominant fiber is collagen arranged in definite pattern |
|
|
Elastin |
Protein that makes up elastic fibers |
|
|
Elastic fibers |
* Branch and fuse to form networks
* Stretched by force and then (like stretched rubber band) return to original size/shape when force is removed |
|
|
Reticular fibers |
* Very thin, branched fibers that form delicate networks joining connective tissue to neighboring tissue
* Consists of collagen and some glycoprotein |
|
|
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) |
* Most associate to form proteoglycans * Found in ECM * Long polysaccharides 1. Negatively charged 2. "Hold water" 3. Highly viscous 4. Not compressible 5. Can provide lubrication to joints |
|
|
Hyaluronic acid |
* Unique in that it isn't covalently attached to a protein to form a proteoglycan
* Proper support relies on a balance of ECM components
|
|
|
Glucosamine |
* Monosaccharide
* Amino sugar with amino group in place of hydroxyl group * Compound that is important in ECM where form parts of glycoproteins |
|
|
Chondroitin sulfate |
Component of ECM secreted by chondrocytes |
|
|
Proteoglycans |
Carbohydrate groups with proteins attached, some GAGs are found in proteoglycans |
|
|
Glycoproteins |
Proteins with carbohydrate groups attached |
|
|
Mucopolysaccharides |
Another name for GAGs when not associated with protein |
|
|
Calcium phosphate |
Mineralizes ground substance (hydroxyapatite) |
|
|
Hydroxyapatite |
* Major component and essential ingredient in bone/teeth
* Makes up bone mineral and the matrix of teeth * Gives bones/teeth rigidity |
|
|
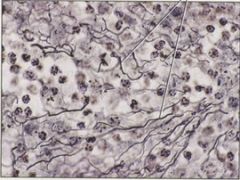
Loose connective tissue Main locations * Everywhere that support must be combined with elasticity, such as subcutaneous tissue (the layer of tissue beneath dermis of the skin)* Support; reservoir for fluids and salts * Fibers produced by fibroblast cells embedded in semifluid matrix and mixed with miscellaneous other cells |
|

|
Dense connective tissue Main locations * Tendons; many ligaments; dermis of skin* Support; transmits mechanical forces * Collagen fibers may be regularly or irregularly arranged |
|

|
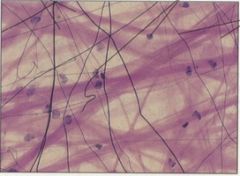
Elastic connective tissue Main locations * Structures that must both expand and return to their original size, such as lung tissue and large arteries* Confers elasticity * Branching elastic fibers interspersed with fibroblasts |
|
|
Reticular connective tissue Main locations * Framework of liver; lymph nodes; spleen* Support * Consists of interlacing reticular fibers |
|
|
Areolar tissue |
Fills gaps and spaces in loose connective tissue |
|
|
Fibroblasts |
Connective tissue cells that produce the fibers as well as protein and carbohydrate complexes of the matrix |
|
|
Chondrocytes |
* Cells that secrete hard, rubbery matrix that surrounds them
* Secrete collagen fibers which become embedded in the matrix and strengthen it * Eventually come to lie singly or in groups of 2 or 4 in lacunae |
|
|
Lacunae |
Small cavities in the matrix |
|
|
Osteocytes |
* Bone cells that are contained within lacunae
* Secrete and maintain matrix * Communicate with one another and with (canaliculi) that contain long cytoplasmic extensions of the osteocytes
|
|
|
Osteoblasts |
Cells with a single nuclei that synthesize bone |
|
|
Osteoclasts |
Cells that degrade bone to initiate normal bone remodeling and mediate bone loss in pathologic conditions by increasing their resorptive activity |
|
|
Fibrinogen |
Glycoprotein in vertebrates that helps in formation of blood clots |
|
|
Fibrin |
Fibrous non-globular protein involved in clotting of blood |
|
|
Red blood cells |
* No DNA or nucleus-->enucleated
* Contain respiratory pigments that transport oxygen |
|
|
White blood cells |
Defend body against disease-causing microorganisms |
|
|
Muscle |
* Animals move by contracting long, cylindrical or spindle shaped cells of muscle tissue (contain muscle fibers) * 3 types 1. Skeletal (striated) 2. Cardiac 3. Smooth (visceral) |
|

|
Skeletal (striated) muscle * Location - Attached to skeleton* Type of control - Voluntary * Composed of incredibly large cells due to fusion of hundreds of normal-sized cells * Has striped/striated appearance due to organization of proteins * Each muscle fiber is a single multi-nucleated cell |
|
|
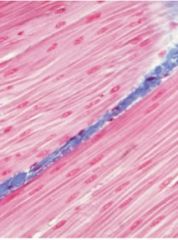
Smooth (visceral) muscle * Location - Walls of stomach, intestines, blood vessels, etc* Type of control - involuntary * Generally organized into sheets * Layers arranged perpendicular to each other
|
|
|
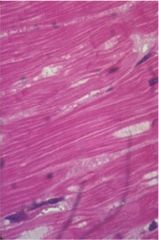
Cardiac muscle * Location - Walls of heart* Type of control - Involuntary * Striated * Mono/dinucleate * Branched interlocked * Contain intercalated discs * Facilitates synchronous contraction
|
|
|
Thermoregulation |
Process that allows the human body to maintain its core internal temperature (state of having even, internal temperature is homeostasis) |
|
|
Muscle fiber |
Muscle cells - contain many myofibrils |
|
|
Multinucleate |
Cells formed in development through fusion of many individual embryonic muscle cells called myoblasts |
|
|
Intercalated disc |
Dense assemblages of gap junctions |
|
|
Nervous tissue |
Consists of neurons and glial cells |
|
|
Neurons |
Take in sensory stimuli, transmit signals throughout the body Ex//: Neurons tell muscle cells to contract at neuromuscular junction |
|
|
Glia |
Support function of neurons * Protect* Nourish * Electrical insulation |
|
|
Central nervous system |
In vertebrates, formed by the brain and spinal cord and it communicates with the rest of the body via the peripheral nervous system |
|
|
Peripheral nervous system |
Portion of the nervous system that transmits information to and form the central nervous system, consisting of neurons that extend or reside outside the brain or spinal cord and their supporting cells |
|
|
Synapse |
Junctions at which neurons communicate |
|
|
Axon |
Transmits signals - nerve impulses - away from cell body (longer than dendrites) |
|
|
Schwann cells |
A type of glial cell that myelinates axons in the peripheral nervous system |
|
|
Myelin sheath |
A fatty, axon-enwrapping sheath that serves to speed up neural conduction, formed by concentric layers of Schwann's cell (peripheral) or oligodendrocyte (CNS) membranes |
|
|
Dendrites |
Cytoplasmic extensions specialized for receiving signals and transmitting them to the cell body |
|
|
Cell body |
Soma - part of neuron that contains the nucleus |
|
|
Neutrotransmitter |
A substance produced in and released by a neuron (the presynaptic cell) that diffuse across a synapse and excites or inhibits another cell (the postsynaptic cell) |
|
|
Nerve |
Consists of a great many neurons bound together by connective tissue |

