![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
160 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Heteroloboseids is |
A brain eating amoeba |
|
|
Bacteria & Archaea mass |
10 times greater than all eukaryotes |
|
|
What 2 organelles evolved from prokaryotes? |
Mitochondria and chloroplasts |
|
|
2 main branches of prokaryotes evolution are? |
Bacteria and Archaea |
|
|
Shapes: spheres, rods, and helical are named what? |
Cocci, bacilli, spirilla |
|
|
Nearly all prokaryotes have a _____ external to the plasma membrane |
Cell wall |
|
|
Cell walls in prokaryotes have what 3 functions? |
1 maintain cell shape 2 afford physical protection 3 prevent bursting in hypotonic environments |
|
|
________ is a cell wall made of sugars linked with polypeptides |
Peptidoglycan |
|
|
Archaea cell walls contain _______&______ but lack peptidoglycan. |
Polysaccharides proteins |
|
|
Gram positive bacteria have a _______ layer of peptidoglycan and will stain the color _________. |
Thick, purple or blue |
|
|
Among pathogens, gram ___________ are more threatening than gram __________. |
Negative, positive |
|
|
What makes gram negative bacteria more threatening? |
Lipopolysaccharides are toxic (their otter most layer) Outer membrane protects against host defenses Greater resistance to antibiotics |
|
|
_________ inhibits xlink formation and interferes with cell wall function |
Penicillin |
|
|
Protective layer that is dense and well defined is a _______ |
Capsule |
|
|
Protective layer that is NOT well defined or organized is a _________ |
Slime layer |
|
|
Capsules and slime layers are sticky to help with what 2 things? |
1 form colonies 2 protection from dehydration and shield from pathogens |
|
|
Some prokaryotes use ______, hair like appendages, to stick together. |
Fimbriae |
|
|
Some bacteria can withstand harsh conditions by forking resistant cells called ________ when they lack essential nutrients. |
Endospores |
|
|
In a heterogenous environment many prokaryotes are capable of ______ or directional movement. 2 examples are ____&_____ |
Taxis, chemotaxis, phototaxis |
|
|
3 major differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes |
Prokaryotes... 1 lack compartmentalization by internal membranes 2 have unfolded regions on plasma membrane 3 smaller, simpler genomes. Many w/ plasmids |
|
|
Certain antibiotics such as _________ and ___________ bind to prokaryotes ribosomes and block protein synthesis. |
Erythromycin, tetracycline |
|
|
Of bacteria, Archaea, and eukarya which have a nuclear envelope? |
Eukarya only |
|
|
Of bacteria, Archaea and eukarya which have membrane enclosed organelles? |
Eukarya only |
|
|
Of bacteria, Archaea and eukarya which have peptidoglycan in the cell wall? |
Bacteria only |
|
|
Of bacteria, Archaea and eukarya which respond to antibiotics streptomycin and chloramphenicol? |
Growth usually inhibited in bacteria but not in Archaea or eukarya |
|
|
Growth is prokaryotes refers to increase in _________ size |
Population |
|
|
Horizontal gene transfer facilitates rapid evolution by doing what? |
Bringing DNA of different species together |
|
|
What are the 3 mechanisms that prokaryotes use for gene transfer? |
Transformation, transduction, and conjugation |
|
|
Transformation |
Cells take up genes from surrounding environment |
|
|
Transduction |
Viruses transfer genes from one prokaryote to another |
|
|
Conjugation |
Direct transfer of genes from one prokaryote to another |
|
|
Phototrophs |
Use light energy |
|
|
Chemotrophs |
Energy from chemicals in environment |
|
|
Autotrophs |
Need only CO2 (inorganic) |
|
|
Heterotroph |
Require at least one organic nutrient |
|
|
Photoautotrophs |
Photosynthetic organisms use light energy to drive synthesis of organic compounds from CO2 (plants, algae) |
|
|
Chemoautotrophs |
Need only CO2, but oxidize inorganic substances for energy (H2S, NH3, Fe+2) |
|
|
Photoheterotrophs |
Use light for energy, obtain carbon in organic form |
|
|
Chemoheterotrophs |
Consume organic molecules for energy & carbon (protist, fungi, animals, some parasitic plants) |
|
|
Majority of prokaryotes are classified as what energy classification? |
Chemoheterotrophs |
|
|
Obligate aerobes |
Use O2 for cellular respiration & cannot grow without it |
|
|
Obligate anaerobes |
Poisoned by O2 and may use fermentation or anaerobic respiration |
|
|
Nitrogen fixation |
Converts N2 to ammonia (NH3) only biomechanism that makes atmospheric N2 available to organisms |
|
|
Photosynthesis and nitrogen fixation occur in different cells within the colony of _________ |
Anabaena |
|
|
Cooperation may occur in surface coatings known as _________ |
Biofilms |
|
|
Exotoxins |
Proteins secreted by prokaryotes (ex botulism) |
|
|
Endotoxins |
Lipopolysaccharides components of the outer membranes of certain gram-negative bacteria. Released when bacteria die. |
|
|
The taxonomic unit at any level of the hierarchy is called a ______ |
Taxon |
|
|
Monophyletic group is a ________ |
Clade |
|
|
Paraphyletic groups consist of ancestral species but not all the _______ |
Decendants |
|
|
Polyphyletic group consists of various species that ______ a common ancestor. |
Lack |
|
|
The clade Excavate is characterized by its _________ |
Cytoskeleton |
|
|
Euglenozoans clade main feature is |
A spiral or crystalline rod inside the flagella |
|
|
Kinetoplastids |
Single large mitochondria with DNA mass called kinetoplast |
|
|
Euglenids are often mixotrophs meaning they _________ |
Combine photosynthesis and heterotroph nutrition |
|
|
______ clade is a extremely diverse clade defined by DNA data |
SAR |
|
|
Stramenopiles are a group of _______ _______ that includes some of the most important photosynthetic organisms on earth. |
Marine algae |
|
|
__________ are unicellular algae with unique glass like walls made of hydrated silica. |
Diatoms |
|
|
_________ characterized by color that results from yellow and brown carotenoids. |
Golden algae |
|
|
__________ are the largest and most complex algae. |
Brown algae |
|
|
___________have membrane-enclosed sacs (alveoli) just under the plasma membrane. |
Alveolates |
|
|
_____________ are characterized by their 2 flagella. |
Dinoflagellates |
|
|
An example of a apicomplexans is _________ |
Malaria |
|
|
__________ are a large varied group of protists named for their use of Cilla to move and feed |
Ciliates |
|
|
Archaeplastida is a supergroup that includes _________, ______, and _______ |
Red algae, green algae, land plants |
|
|
________ are reddish in color die to an accessory pigment called phycoerythrin that masks green of chlorophyll |
Red algae |
|
|
Of the two groups of green algae, is charaphytes or chlorophytes closer related to land plants? |
Charaophytes |
|
|
Are plasmodial slime molds diploma or halpoid organisms? |
Diploid |
|
|
Are cellular slime molds diploid or halpoid organisms? |
Halpoid |
|
|
Single filament of a fungi is a ________ but a network forms the _________. |
Hyphae, mycelium |
|
|
Cell walls of fungi are built of ________ |
Chitin |
|
|
Some fungi are _______ where the hyphae is not divided called coenocytic fungi. |
Aseptate |
|
|
Parasitic fungi have modified hyphae called ________ that penetrate host tissue. |
Haustoria |
|
|
Some mycelium have become genetically heterogenous through the fission of 2 hyphae with genetically different nuclei, called _________ |
Heterokaryon |
|
|
Plasmogamy is |
The fusion of 2 parent cytoplasms |
|
|
Karyogamy is |
Fusion of halpoid nuclei |
|
|
Phylum Chytridomycota characteristics |
Uniflagellated spores, mainly aquatic |
|
|
Phylum Zygomycota characteristics |
Forms mycorrhizae, ex black bread mold |
|
|
Phylum Glomeromycota characteristics |
Arbuscular mycorrhizae (tree looking structures) mutualistic relationship with plants |
|
|
Phylum Ascomycota characteristics |
Sac fungi, like morel mushrooms |
|
|
Phylum Basidiomycota characteristics |
Have fruiting bodies, ex shelf fungi |
|
|
A mushroom is a ____________ |
Basidia |
|
|
Molds are rapidly growing, __________ reproducing fungi. |
Asexual |
|
|
Some molds have no known sexual stage, ______________ |
Deutermycetes (imperfect mushrooms) |
|
|
Most molds reproduce asexually using _________ |
Budding (simple cell division) |
|
|
_______ are often mistaken for mosses. |
Lichens |
|
|
Lichens are actually a symbiotic relationship between a ___________ and a _________, and is not truly a single organism. |
Cyanobacteria or algae, fungi |
|
|
Mycorrhizae refers to ______ _______ |
Fungus roots |
|
|
Almost all ______ _______ have mycorrhizae. |
Vascular plants |
|
|
_______ is the name for a fungal infection in an animal. |
Mycosis |
|
|
Systemic mycoses are fungal infections that shows throughout the body usually from _______ _______ |
Inhaled spores |
|
|
First animal fossils are ________ years old |
560 million |
|
|
Nearly all major body plans appear in ________ period rocks. |
Cambrian |
|
|
What caused the Cambrian explosion? |
1 new predator-prey relationships 2 change in O2 levels 3 variations in HOX genes |
|
|
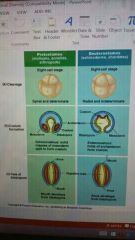
What are the 4 key evolutionary branch points? |
1 presence or absence of tissue 2 body symmetry 3 evolution of body cavities 4 protostome-deuterostome dichotomy |
|
|
Except for sponges, animal embryo becomes layered through process of ________ |
Gastrulation |
|
|
Embryo contains concentric layer of tissue called ________ ________ |
Germ layers |
|
|
Outer germ layer is called |
Ectoderm |
|
|
Inner germ layer is called |
Endoderm |
|
|
Animals with 2 germ layers are |
Diploblastic |
|
|
Animals with 3 germ layers are |
Triploblastic, has additional mesoderm |
|
|
Triploblastic animals without body cavity between gut and outer body wall are called ________. Example is______ |
Acoelomates, Flatworms |
|
|
Pseudocoelmate |
If a cavity is not completely lined with mesoderm |
|
|
Coelomates |
Animals with true coelom |
|
|
Coelomates can be broken into 2 developmental modes which are: |
Protostome and deuterostome |
|
|
Protostomes have cleavage that is _______, determinate cleavage. Each cell already has a ______ in embryo. |
Spiral, plan |
|
|
Protostomes coelom forms when mesoderm splits, called ________ development. |
Schizocoelous |
|
|
In protostomes the ________ develops from the blastopore. |
Mouth |
|
|
Deuterostomes have ________ indeterminate cleavage. |
Radial |
|
|
Deuterostomes mesoderm from the wall of archenteron hollows out to become _______ _______. This is __________ development. |
Coelomic cavity, enterocoelous |
|
|
Deuterostomes _______ forms from the blastopore and the _______ develops from a secondary opening. |
Anus, mouth |
|
|
Review graphics |
|
|
|
All animals share a common _______ |
Ancestor |
|
|
Sponges are ________ animals. |
Basal |
|
|
Eumetazoa is a clade of animals with _______ _________. |
True tissues |
|
|
Most animal phyla belong to the clade ___________ |
Bilateria |
|
|
There are ____ major clades of bilaterian animals. |
3 |
|
|
Bilateria clade deuterostomia is the only clade to include both ________ and ___________. |
Invertebrates, vertebrates |
|
|
Bilateria clade ecdysozoa include animals that _______ _______ as it grows. |
Sheds exoskeleton |
|
|
Bilateria clade lophotrochozoa refers to two different features observed in some members of this clade, lophophore and trochophore ________. |
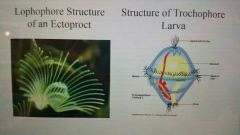
Larva |
|
|
The phylum poriferia include __________ |
Sponges |
|
|
Sponges feed by watery entering ______ called spongocoel into the central cavity and out through the __________. |
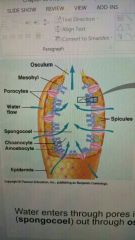
Pores, osculum |
|
|
Phylum cnidaria, an ancient phylum of eumeatzoa, include _______, _______, ________, and _________. |
Hydra, jellyfish, sea anemones, corals |
|
|
Phylum cnidaria have body plans containing sac with ______________ cavity and single opening. |
Gastrovascular |
|
|
Phylum cnidaria have 2 variations of body plans. Sessile polyp plans in ______, ______, and ________. Floating medusae in _________. |
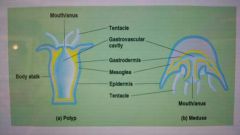
Hydra, sea anemones, corals. Jellyfish |
|
|
Tentacles lined with cnidocytes contain _______ _______. |
Stinging capsules (nematocysts) |
|
|
4 classes of cnidaria include: Hydrazoa which most alternate between _____ and ______ form. Scyphozoa which includes jellyfish and _______ form pervails. Cubozoa which are box shaped organisms with complex eyes in the ______ form. Anthozoa which includes sea anemones and coral and are ______ form only. |
Polyp, medusa, medusa, medusa, polyp |
|
|
Phylum ctenophora include _______. |
Tentafors |
|
|
Phylum platyhelminthes are_______ |
Flatworms |
|
|
Simple excretory apparatus to remove excess liquid in planarians are called ________ |
Flame cells |
|
|
The class trematodes are flukes, which are _________ _____ __________. |
Parasites on animals |
|
|
Class cestoda are _______ |
Tapeworms |
|
|
Phylum nemertea are _______ or _______ ________. |
Ribbon or proboscis worms |
|
|
Pseudocoelmate are known for a body cavity that's _is/is not_ completely lined with ________. |
Is not, mesoderm |
|
|
Pathenogenesis can reproduce with just _________ |
Females |
|
|
All 3 phyla of lophophorates (phoronida, ectoprocta, brachiopda) share common lophophore which is _________ ________ or circular fold of body wall with ________ tentacles around the mouth. |
Horseshoe shaped, ciliated |
|
|
Phoronids are ____________ |
Tube dwelling marine worms |
|
|
Bryozoans are |
Moss animals |
|
|
Brachiopods are ____________ |
Lamp shell organisms |
|
|
Phylum mollusca includes chitons, snails, ______, clams, octopi, and _________. |
Slugs, squids |
|
|
3 main parts of a mollusca organism are: |
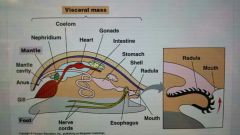
Muscular foot, visceral mass (contains internal organs), mantle (usually secretes shell) |
|
|
Class polyplacophora include chitons which are known for oval shells divided into _______ dorsal plates |
8 |
|
|
Class gastropoda include ______ & ________ and are known for torsion when one side of the visceral mass grows faster. |
Snails and slugs |
|
|
Class bivalvia including clams, oysters, mussels, and scallops have early ________. |
Eyes, can determine dark from light |
|
|
Class cephalopoda include _______&_________ |
Squids, octopi |
|
|
Cephalopods are the only mollusks with ________ circulatory systems, _______ of a shell, and ________ eyes. |
Closed, lack, developed |
|
|
Phylum annelida are ______ ________ |
Segmented worms |
|
|
The 3 classes of annelids are oligochaeta (ex. _________), polychaeta (ex. _________ with parapodia), and hirudinea (ex. ______) |
Earthworms, tube dwelling worms, leeches |
|
|
__________ is the foundation for specialization of body regions. |
Segmentation |
|
|
___________ phylum characteristics include segmentation, hard exoskeleton, and joint appendages. |
Arthropod |
|
|
Living arthropods have 3 major lineages: chelicerata, myriapoda, and hexapods & crustacea known as ____________. |
Pancrustaceans |
|
|
Chelicerata include spiders & ________ Myriapoda include milipedes & ______ Pancrustaceans include insects & ___ |
Scorpions, tics, mites Centipedes Crabs, lobsters, shimp, barnacles |
|
|
The only arthropods with 2 antenna are __________ |
Crustacea |
|
|
Hexapoda (insects) key to success was ________ |
Flight |
|
|
Insects have 3 body regions: |
Head, thorax and abdomen |
|
|
Thorax of insects have _____ pairs of walking legs. |
3 |
|
|
Insects have _______ circulatory system. So they have _________ _________ for gas exchange to outside through pores called spiacles. |
Open, tracheal system |
|
|
Phylum echinodermata (deuterostomes) have _______ _________ systems and tube feet. |
Water vascular |
|
|
Echinodermata include sea stars (asteroidea), brittle starts (ophiuroidea), ___ ________ (echinoidea), sea lilies (crinoidea), and ___ __________ (holothuroidea). |
Sea urchins or dollars Sea cucumbers |
|
|
Chordata phylum has _____ subphlya of invertebrates and _____ subphlylum of vertebrates. |
2, 1 |

