![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
Cell |
The smallest functional and structural unit of life; usually consists of a nucleus, cytoplasm, and a membrane |
|
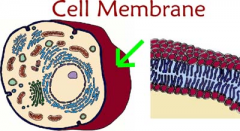
Cell Membrane |
A layer that cover a cell's surface and acts as a protect barrier for the cell
|
|
|
Organelle |
A small body in a cell's cytoplasm that are specialized to perform a specific function |
|
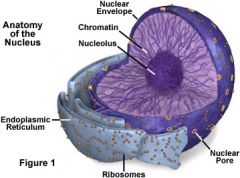
Nucleus |
In eukaryotic cells, a membrane-bound organelle organelle that contains the cell's DNA |
|
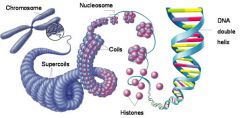
Chromosomes |
In eukaryotic cells, one of the structrures in the nucleus that are made up of DNA and protein. *Prokaryotic = main ring of DNA |
|
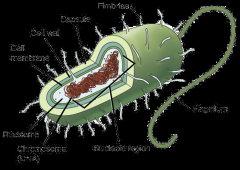
Prokaryotes |
a single-celled organism that does not have a nucleus *archaea *bacteria |
|
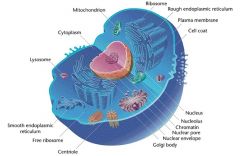
Eukaryotes |
An organism made up of cells that have a nucleus enclosed by a membrane *protists *animals *plants *fungi |
|
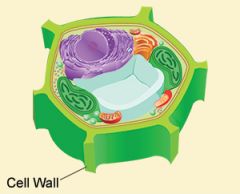
Cell Wall |
A rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane and provides support to the cell |
|
Cytoskeleton |
A network of protein fibers and helps with the cells shape and movement |
|
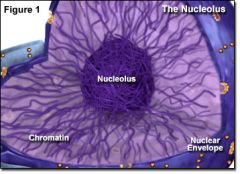
Nucleolus |
Inside of the nucleus; makes ribosomes |
|
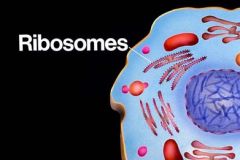
Ribosomes |
An organelle composed of RNA and protein; the site of protein synthesis |
|
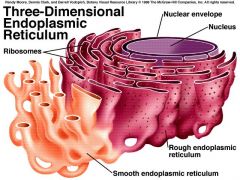
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) |
A system of membranes that assists in prodution of proteins and lipids and transports proteins *Rough ER = covered in ribosomes -usually found near the neucleus |
|
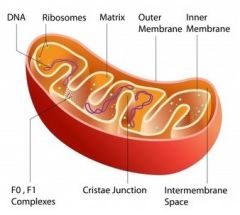
Mitochondria |
Site of cellular resperation/the power house *energy released = ATP |
|

Chloroplast |
Site of photosynthesis in plants and algae. They also have chlorophyll, a green pigment, in them |
|

Golgi Complex |
An organelle that helps make and trasport materials out of the cell (UPS of the cell) |
|
|
Vesicle |
a small cavity or sac that contains materials in a eukaryotic cell |
|

Lysosomes |
organelle that contains digestive enzymes (angry Pacman) |
|
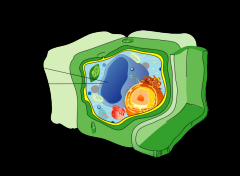
Vacuoles |
They aid in digestion within cells *another type of vesicle |
|
|
Organism |
A livinf thing; anything that can preform life processes independendtly |
|
|
Function |
The proper activity of an organ or part |
|
|
Structure |
The arrangement of parts in an organism |
|
|
Tissue |
a group of similar cells that preform a common function |
|
Organ |
A collection of tissues that carry out specialized function of the body |
|
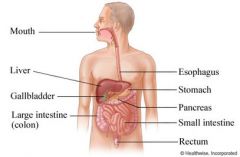
Organ System |
A group of organs that work together to preform body functions |
|
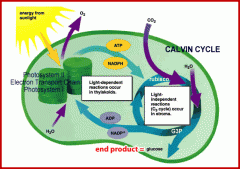
Photosynthesis |
The process where plants, algae and some bacteria, use sunlight, carbin dioxide, and water to make food |
|
|
Cellular Resperation |
the process where cells use oxygen to produce engery from food |
|
|
Fermentation |
The breackdown of food without the use of oxygen |
|
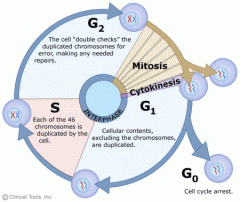
Cell Cycle |
the life cycle of a cell |
|
|
Interphase - G1 |
*8-10 hours *Produces mRNA, proteins help S phase happen *Organelles duplicate |
|
|
Interphase - S Phase |
*creates double DNA (sister chromotids *6-8 hours - ATP dependant |
|
|
Interphase - G2 Phase |
*Rapid growth phase *makes space for mitosis to happen *some cells skip this phase *4-6 hours |
|
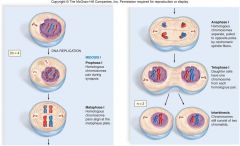
Mitosis |
In eukaryotes, a process of cell devision that forms two nuclei, each has the same number of chromosomes |
|
|
Prophase |
Nuclear memebrane disolves and chromatids condense *Phase 1 in Mitosis |
|
|
Metaphase |
The chromatids met at equator and the spindle dibers push them push them there |
|
|
Anaphase |
Spindle fibers pull one copy of each chromatids towards a pole. |
|
|
Telophase |
Neclear membrane reappears and chromatids elongate. *spindle fibers disappear *cell plate forms in plants *animal - pinch |
|
|
Cytokinesis |
the moment the two cells seprate |
|
|
Feedback |
*happens inbetween phases *tells the cell whether or not a cell can continue through the cycle *reports on the health and needs of a cell |

