![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
43 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Name 3 components which make up a nucleotide |
Organic Base Phosphate group Deoxyribose Sugar |
BPS |
|
|
Describe how the two strands of DNA are held together |
Weal hydrogen bonds between complementary bases |
2 marks |
|
|
Describe the shape of a DNA molecule |
Double helix |
1 mark |
|
|
What does complementary mean? |
Two (or more) things together that form a satisfactory or balanced whole |
1 mark |
|
|
What does complementary mean when referring to DNA structure? |
Pairs of nucleotides which are able to join together with hydrogen bonds e.g A-T, C-G |
1 mark |
|
|
What does antiparallel mean? |
Parallel but running in opposite directions |
1 mark |
|
|
What does antiparallel mean when referring to DNA structure? |
One strand runs 3' to 5' and the other runs 5' to 3' |
1 mark |
|
|
Describe the structure of a DNA molecule |
>made up of nucleotides >nucleotide made up of BPS >strands linked by sugar-phosphate backbones >bases; A,T,C,G >bases are complementary >antiparallel strands with sugar at 3' and 5' >double helix |
Any 6 marks |
|
|
What is a Prokaryote? |
Organism with a single cell which lacks a true membrane-bound nucleus E.g. Bacteria |
3 marks |
|
|
Where is a Prokaryotic cell's genetic information stored? |
In the circular chromosome located in the cytoplasm |
2 marks |
|
|
What is the additional DNA in a Prokaryotic cell called |
A plasmid |
1 mark |
|
|
A picture of a Prokaryote |
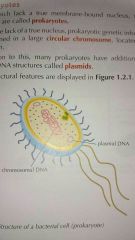
|
|
|
|
What is a Eukaryote |
An organism made of cells which contains a true membrane-bound nucleus
E.g. Animals and plants |
3 marks |
|
|
Picture of a Eukaryotic plant cell |

|
|
|
|
What is unusual about yeast cells? |
They are Eukaryotes that contain plasmids |
2 marks |
|
|
Name three key differences between Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes |
EU = true membrane-bound nucleus PR= no true membrane-bound nucleus -------------------------------------------------------- EU= chromosome structure is linear and circular PR= circular chromosome structure -------------------------------------------------------- EU= genetic material located in nucleus, chloroplast, mitochondria PR= genetic material located in cytoplasm and plasmids |
3 marks |
|
|
How does DNA fit in the cell |
It is tightly coiled and packaged with associated proteins |
2 marks |
|
|
What are weak hydrogen bonds? |
Bonds between the base pairs which hold both sides of a DNA molecule together |
1 mark |
|
|
What is DNA polymerase? |
Enzymes which adds complementary nucleotides to the Deoxyribose (3') end of the DNA strand |
2 marks + possible location |
|
|
What is a primer? |
Short, single strand of DNA required for replication to begin. |
1 mark |
|
|
What is required for DNA replication? |
DNA template Free DNA nucleotide bases Enzymes (DNA polymerase & ligase) Primers ATP |
6 marks |
|
|
How many stages are there in DNA replication? |
4 |
1 mark |
|
|
Describe each stage of DNA replication vaguely |
Stage 1 - separation of 2 parental DNA strands Stage 2 - free DNA nucleotides pair with complementary bases on template strands Stage 3 - sugar-phosphate backbones form on new strands Stage 4 - two daughter DNA molecules are formed which are genetically identical to their parental DNA |
8 marks |
|
|
What is PCR? |
Polymerase Chain Reaction In Vitro method of amplifying a sequence of DNA |
2 marks |
|
|
What is meant by amplifying DNA? |
Creating many copies of a fragment of DNA |
1 mark |
|
|
Where does PCR tend to take place? |
In a thermal cycler |
1 mark |
|
|
What is required for PCR? |
DNA template Free DNA nucleotides Heat tolerant DNA polymerase Primers |
4 marks |
|
|
How many DNA molecules are there after 1 cycle Of PCR? |
Double the amount |
1 mark |
|
|
What can PCR be used for? |
DNA sequencing Genetic mapping studies Forensic and parental testing Sex determination in pre-natal cells Screening for/diagnosis of genetic disorders e.g cystic fibrosis |
4 of any 5 |
|
|
Describe the key difference between the leading & lagging strand in replication |
Leading strand replicated continuously Lagging strand replicated in fragments. Ligase used to join fragments. |
2 marks |
|
|
What is gene expression? |
The process involving transcription and translation where DNA sequences are used to direct the production of proteins |
2 marks |
|
|
Describe Transcription |
Making a primary transcript of mRNA using a DNA sequence Takes place in the nucleus of a cell |
2 marks |
|
|
Describe translation |
Production of a polypeptide chain informed by an mRNA sequence Takes place in a ribosome |
2 marks |
|
|
What is RNA? |
Ribonucleic Acid A molecule similar to DNA and is essential for protein synthesis |
2 marks |
|
|
What is a phenotype? |
Genetically determined characteristics of an organism |
1 mark |
|
|
What are the three main forms of RNA? |
Messenger RNA Ribosomal RNA Transfer RNA |
3 points for 1 mark |
|
|
Describe mRNA |
Carries a copy of the DNA code from the nucleus to the ribosome Linear form Has codons |
3 marks |
|
|
Describe rRNA |
Forms protein synthesising organelles called ribosomes with ribosomal protein |
2 marks |
|
|
Describe tRNA |
Molecules each carry a specific amino acid and are involved in the 2nd part of protein synthesis Folded shape Has anticodon |
3 marks |
|
|
What is a codon? |
Triplet of bases in mRNA that codes for specific amino acids which is carried by tRNA |
3 marks |
|
|
What is an anticodon? |
Triplet of bases in tRNA that codes for specific amino acids and is complementary to a specific codon in mRNA |
3 marks |
|
|
Describe protein synthesis |
A process in which instructions from DNA sequences are carried to ribosomes and proteins and are synthesised |
3 marks |
|
|
What is RNA polymerase? |
Enzyme that unwinds DNA during transcription Adds free nucleotides to a single strand of DNA to form a single strand of mRNA |
4 marks |

