![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Qualification of president |

|
|
|
Composition of electoral college |
Elected members of state legislative assemblies,rajya sabha,lok sabha and union territories |
|
|
Term of president |
Elected for 5 years but can be removed before expiry of his term by impeachment |
|
|
Reason for indirect election of president |
*president is only a nominal head while the actual head of the government lies with the prime minister and his council of ministers *Direct election would involve campaigns of different parties and hence could make the president like a nominee of his ruling party and a lot of time and money would be involved for an ornamental position. |
|
|
Components of union executive |
President vice president prime minister |
|
|
Position of president |
Highest executive authority Head of state Supreme Commander of defence forces of India Nominal head First citizen |
|
|
When does the office of President fall vacant? |
If president: Dies Resigns Removed by impeachment Term of five years expires |
|
|
Procedure for impeachment |
A list of charges must be drawn and supported by 1/4 of the total members after a 14 days notice in any of the house the resolution is moved. It must then be passed by 2/3 majority of the house.the other house will investigate the charges and confirm it by 2/3 of majority to have the president impeach.
|
|
|
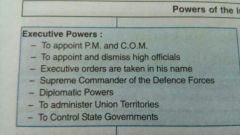
Executive power of president |
|
|
|
Legislative powers of president |

|
|
|
Financial powers of president |

|
|
|
Judicial powers |

|
|
|
Emergency powers |

|
|
|
Qualification of vice president |

|
|
|
Term of vice president |

|
|
|
Powers of vice president |

|
|
|
Appointment of PM |
Appointed by president who invited the leader of the ruling party in the lok sabha |
|
|
Coalition government |
Different political parties come together and form an alliance to prove majority to the lok sabha |
|
|
Power of PM |
Head of union of council of ministers Head of union government |
|
|
PM- president |
-Chief adviser of president -advises to summon and prorogue the sessions of the parliament -Conveys cabinets decisions to president -Advises president on appointing and removing high officials and commissions |
|
|
PM-Cabinet |
Head of cabinet Forms the council of ministers Decides the categories of ministers and their portfolios Can remove a minister from the council of ministers Can reallocate portfolios Summons the meetings of council of ministers Decides agenda of meetings Co ordinates the policies and working of different Dept of govt The whole council of ministers resigns with prime minister resignation |
|
|
Pm-parliament |
Leader of lok sabha Chief spokesman and defender of government Makes all important announcements of government policies Lok sabha can be dissolved on his advice Can intervene in any debate in the lok sabha Makes concluding speech in the house and before voting of non-confidence motion in the house and before voting of non-confidence motion |
|
|
PM-foreign affairs |
Represents India in foreign,international conferences Makes agreement with foreign countries Empowered to commit nation to certain international obligation
|
|
|
PM-leader of nation |
Chief spokesperson of nation Ex officio chairperson of planning commission Focus of the administration and takes crucial decisions on foreign policies and national crisis |
|
|
Categories of ministers |
Cabinet Ministers of state Deputy |
|
|
Cabinet ministers |
Core team of council Have right to attend cabinet meetings and decide the policies of government Key portfolios of home, external affairs, railways, defence, finance,agriculture,industries,sports,welfare |
|
|
Ministers of state |
Part of extended council Attend cabinet meetings only when invited Control less important portfolios |
|
|
Deputy minister |
Assist senior cabinet ministers Do not hold independent charge of any portfolio Do not take part in cabinet meetings only if specially invited |
|
|
Term of PM |
5 years |
|
|
Cabinet-appointment,term |
15 to 18 minister Appointed by president on advices of prime minister Continues in office until they enjoy the confidence of the lok sabha Resigns if lok sabha passes the no confidence motion |
|
|
Cabinet Secretariat |
Plan meetings and agenda of cabinet Headed by cabinet secretary,Ex officio chairman of civil services board Keeps record of all cabinet decisions Communicates decisions of cabinet to council
|
|
|
Difference between council of ministers and the cabinet |

Prime minister always consult cabinet only All decision taken by cabinet are binding on the entire council |
|
|
Collective responsibility |

|
|
|
Individual responsibility |

Each minister is accountable for changes in the official policy of the department,personal mistakes that results in financial losses breaking the oath of secrecy of office |
|
|
Executive power of cabinet |

|
|
|
Legislative power of president |

|
|
|
Financial powers of cabinet |

|
|
|
Adminstrative power of cabinet |

|
|
|
Policy making function of cabinet |

|

