![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
136 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Pathophysiology of Wilson's disease
|
inadequate copper excretion
|
|
|
Wilson disease gene, what is it responsible for?
|
ATP7B, which is responsible for proper Cu excretion into the bile
|
|
|
Presentation of Wilson's disease in children
|
highly variable: hepatomegaly, fatty liver, reccurent gallstones
* can be with or without symptoms: fatigue, anorexia, abdominal pain |
|
|
Presentation of Wilson's disease in adults
|
chronic liver disease: splenomegaly, ascites
OR *** Fulminant hepatic failure: - low alk. phos, high bili (AP/Bil < 4) - AST/ALT > 2 (typically low levels <1500, unlike other FHF) - AKI: hemolysis |
|
|
WIlson disease neurologic presentaiton:
|
- movement disorders (juvenile parkinson's)
- rigid dystonia - hypophonia (soft voice) - *Normal IQ* |
|
|
Wilson disease ocular findings on slit lamp exam? What other symptoms are usually present
|
Kayser-Fleischer rings (Cu deposition in Descemet's membrane of the cornea)
- usually present in CNS/psych involvement (>95%) - absent in 40-60% w/ only hepatic involvement |
|
|
Wilson disease labs for anemia:
|
Coombs' negative hemolytic anemia (b/c not immune hemolysis)
|
|
|
Treatment for wilson disease
|
chelator agents
|
|
|
HFE-related hereditary hemochromatosis inheritance, usual age of onset, & demographics
|
- AR
- caucasian male, 40-50 y/o |
|
|
Typical presentation of HFE-related hereditary hemochromatosis (list 3)
|
- fatigue
- dark skin - hepatomegaly |
|
|
Typical presentation of HJV (juvenile) hereditary hemochromatosis (list 3)
|
- impotence/amonorrhea
- cardiomyopathy |
|
|
hereditary hemochromatosis pathophysiology
|

|
|
|
hereditary hemochromatosis significantly increases the risk for what other liver conditions?
|
HCC
|
|
|
bronze diabetes
|
The classic triad of hemochromatosis is cirrhosis, diabetes mellitus, and skin pigmentation.
|
|
|
Dx of HH
|
- elevated transferrin saturation (serum Fe/TIBC) x 100%
- elevated serum ferritin - if either abnormal → HFE mutation analysis |
|
|
Treatment of HH
|
phlebotomy
|
|
|
α1-antitypsin deficiency genetics
|
autosomal codominant
|
|
|
α1-AT deficiency w/ 0 protein →
|
COPD but NOT liver problems
|
|
|
Pathophysiology of liver disease in α1-AT deficiency
|
abnormally folded proteins accumulate within the liver → fibrosis
|
|
|
Replacement therapry w/ purified α1-AT is beneficial....
|
in lung disease ONLY; no benefit in liver disease
|
|
|
autoimmune hepatitis sex predominance
|
4:1 female to male
|
|
|
Etiology of autoimmune hepatitis
|

+ molecular mimicry: multiple antigens w/ the same or similar epitopes can activate CD4 cells b/c of incomplete specificity of T-cell antigen receptors
|
|
|
Clinical spectrum of autoimmune hepatitis
|
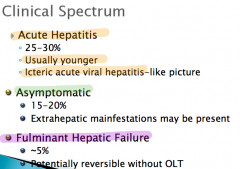
|
|
|
Auto antibodies seen in AIH
|
usually ANA &/or SMA
|
|
|
histopathology of AIH
|
- inface hepatitis
- lymphocytic infiltrate |
|
|
primary treatment modality for AIH
|
immune supression: steroids are first line
|
|
|
Primary Biliary Cirrhosis (PBC) pathophysiology
|
breach in immunologic tolerance → aberrant recognition of mitochondrial self antigens → activation of immune/inflammatory response → inflammation & fibrosis of the bile ducts
* PBC is NOT just an auto-immune process, it is a combination of genetic pre-disposition w/ environmental insults |
|
|
Which labs are usually elevated in primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC)?
|
- alk phos (indicative of cholestasis)
AMA: anti-mitochondrial antibody |
|
|
epidemiology of PBC
|
female > 40
|
|
|
What is the pathognomonic histopathological presentation of primary biliary cirrhosis?
|
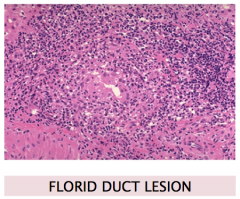
distorted bile duct w/ inflammatory infiltrate
|
|
|
Clinical presentation of primary biliary cirrhosis
|
- majority of new cases are asymptomatic
- jaundice is a late event |
|
|
Which autoimmune disease is most commonly associated with primary biliary cirrhosis?
|
Sjogen's/Sicca Syndrome: dry eyes & dry mouth
|
|
|
Drug tx for PBC
|
UDCA
|
|
|
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) pathophysiology
|
inflammation, obliteration & fibrosis of intra- & exra-hepatic bile ducts
etiology: unknown |
|
|
Cholangiocraphic findings in primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC)
|
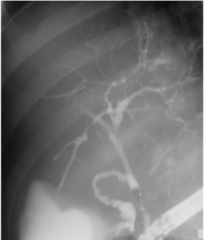
multifocal bile duct strictures & dilations
|
|
|
What is the characteristic (but not pathognomonic) histologic presentation of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC)?
|
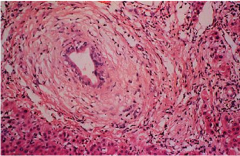
"onion-skinning" of the bile duct
|
|
|
70-80% of the cases of primary sclerosing cholangitis are associated with __________, therefore at the time of diagnosis of PSC all patients should undergo _____________ (diagnostic test)
|
IDB; colonscopy
|
|
|
Patiens with PSC have an ↑ risk of developing (2 cancers)
|
cholangiocarcinoma & colon CA
|
|
|
Medical treatment for PSC
|
no proven medical treatment; only symptomatic management & surveillance for CRC, GB Ca & CCA
|
|
|
Gender predominance PBC vs PSC
|

|
|
|
Bile ducts effected in PBC vs PSC
|
PBC: intrahepatic (small)
PSC: inra- & extrahepatic |
|
|
ERCP findings in PBC vs PSC
|
PBC: normal (b/c can't see the the small intrahepatic bile ducts)
PSC: abnormal |
|
|
Increased risk of cholangiocarcinoma: PBC vs PSC
|
PBC: no
PSC: ↑ risk |
|
|
age range of Dx for PBC vs PSC
|
PBC: 30-65
PSC: 4-65 (* effects peds) |
|
|
Which type of hepatitis is transmitted via fecal-oral?
|
Hep A & Hep E
|
|
|
Which type of hepatitis leads to a chronic infection?
|
Hep B, C, & D
|
|
|
What kind of virus is Hep A? What kind of infection does it cause (chronic/acute?)
|
RNA virus
causes an acute infection (much more serious in adults than in children) |
|
|
Of the patients with Hep A, which age group is most likely to get jaundice?
|
older (> 14 y/o)
|
|
|
In an acute infection of Hep A, what would be expected to be elevated?
|
ALT & IgM anti-HAV
|
|
|
What does an elevated total anti-HAV with no IgM anti-HAV indicate?
|
likely person that was previously infected; this indicated elevated IgG which is a sign of previous infection
|
|
|
How is Hep A transmitted?
|
fecal-oral: very easily transmissible
- close personal contact - contaminated food & H2O |
|
|
Incubation period for Hep A vs Hep B
|
Hep A: ~ 30 days
Hep B: ~ 60-90 days |
|
|
Hep B modes of transmission
|
- sexual
- parenteral (IVDA) - perinatal (most common worldwide) |
|
|
Surface antigen vs IgM core antibody in Hep B
|
Surface antigen: present in chronic or acute
IgM core antibody: recent acute hep B infection |
|
|
anti-HBE (E antigen) levels in chronic hep B
|
usually present, although can be absent
|
|
|
What antibody elevations would you expect to see in a a person with chronic hep B?
|
- anti-HBs (antibody to surface antigen)
- anti-HBe (antibody to E) - IgG anti-HBc (antibody to core) |
|
|
What would be the difference in labs in a patients with chronic hep B versus someone who was vaccinated?
|
pt w/ chronic infection:
- anti-HBs (antibody to surface antigen) - anti-HBe (antibody to E) - IgG anti-HBc (antibody to core) vaccinated: anti-HBs ONLY |
|
|
Why can you never completely get rid of Hep B? What is the significance of that?
|
it has cccDNA (covalently closed circular DNA), therefore must use caution with immunosupression as it can cause reactivation of the virus
|
|
|
Patients w/ chronic hep b have ↑ risk for...
|
HCC
|
|
|
Hep D
|
acute infection that occurs as a co-infection with Hep B (must have Hep B in order to get infected w/ Hep D)
|
|
|
What labs are elevated in acute HCV infection?
|
HCV RNA
|
|
|
Patients with resolved Hep C will have ↑ _________ .
|
anti-HCV
|
|
|
What 2 labs define chronic Hep C infection?
|
presence of anti-HCV ALT elevation
|
|
|
Common extrahepatic manifestations of HCV
|
- mixed cryoglobuinemia
- vasculitis |
|
|
Hep E greatest fatality rate is in (which group of people)
|
pregnant women
|
|
|
AST: ALT in alcholoic hepatitis
|
AST: ALT >2
|
|
|
Major histological feature of alcoholic hepatitis
|
mallory bodies
|
|
|
The prevalence of Hep __ is much higher among alcoholics.
|
C
|
|
|
Most drug hepatotoxicity affects which population?
|
women > 40
|
|
|
antidote for acetaminophen hepatotoxicity
|
n-acetyl cysteine (it promotes glutathione)
|
|
|
What is the most common hepatic manifestations of statin drugs?
|
asymptomatic elevations in aminotransferase levels
|
|
|
In a patient with unexplained jaundice you should think of.....
|
drug hepatotoxicity
|
|
|
NAFL vs NASH
|
NASH (nonalcoholic steatohepatitis) is a subgroup of NAFL (nonalcholic fatty liver) in which steatosis co-exists w/ liver cell injury & inflamation
|
|
|
NAFL is most common in which ethnicity?
|
hispanics
|
|
|
How does metabolic syndrome contribute to NAFL?
|

there is an imbalance between pro-inflammatory & anti-inflammatory mediators as a result of increased visceral fat
|
|
|
What is more severe: microvesicular or macrovesicular steatosis?
|
microvesicular; poor prognosis (usually death)
|
|
|
Six F's: Risk Factors for Cholesterol Gallstones
|
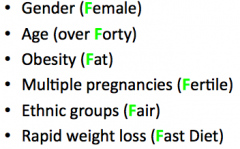
|
|
|
What is a common cause of black pigmented gall stones? What gives it the black color?
|
hemolytic disorders; ↑ levels of unconjugated bilirubin
|
|
|
Brown gallstones have an increased composition of _______. They are usually caused by...
|
fatty acids; bacterial infection causes by bile stasis
|
|
|
Murphy's sign
|
P/E finding in acute cholecystitis: right subcostal tenderness w/ pain & respiratory arrest during palpation
|
|
|
Diagnostic criteria for acute acalculous cholecystitis
|
thickened gallbladder wall in the absence of ascites & hypoalbuminemia
|
|
|
Classic presentation (3 things) of acute ascending cholangitis
|
fever, jaundice & abdominal pain
|
|
|
etiology of acute ascending cholangitis
|
bacterial infection
|
|
|
What is characteristically seen on imaging of ascending cholangitis?
|
bile duct dilation
|
|
|
Presentation of primary sclerosis cholangitis (list 4 things)
|
jaundice, fever, pruritus, & abdominal pain
|
|
|
Ultrasound of gallbladder polyps vs stones
|
Polyps do not move or case a shadow like stones
|
|
|
What is the most common location of cholangiocarcinoma?
|
bifurcation of bile ducts
|
|
|
2 causes of prehepatic portal HTN
|
- portal vein thrombosis
- splenic vein thrombosis |
|
|
Causes of posthepatic portal hypertension
|
- cardiomyopathy, valvular disease, constrictive pericarditis
- budd-chiari syndrome, IVC blockage |
|
|
Variceal bleeding prevention
|
non-selective beta-blockers (propanolol, nadolol, or timolol)
|
|
|
Pharmacological treatment for acutely bleeding varices (3 drugs)
|
- somatostatin
- vasopressin - non-selective beta-blockers |
|
|
most common site of variceal bleeding
|
distal esophagus
|
|
|
How does the TIPS procedure work to reduce the portal HTN?
|
a direct connection is formed between the hepatic veins & the portal venous system, thus bypassing the intrahepatic restrictions
|
|
|
Serum-ascities albumin gradient (SAAG) in portal HTN vs everything else
|
portal HTN: SAAG > 1.1 (indicates that it is high in protein)
everything else SAAG < 1.1 |
|
|
Testing of ascites fluid
|
- cell count (WBC/RBC)
- serumm albumin - ascites gradient (SAAG) - cultures |
|
|
Medical management of ascites
|
- salt restricted diet
- diuretics |
|
|
primary diagnostic test in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP)
|
PMN cell count > 250
|
|
|
empiric medical therapy for hepatic encephalopathy
|
- lactulose
- Abx - dietary protein restriction |
|
|
pathophysiology of hepatorenal syndrome
|
- peripheral arterial vasodilation
- markedly increased renal vascular resistance |
|
|
most common benign liver tumor
|
hemangioma
|
|
|
epidemiology of hemangiomas (benign liver tumor)
|
women ages 30-50
|
|
|
clinical features of hemangiomas
|
mostly small & asymptomatic
|
|
|
Hemangiomas on US & contrast CT
|
US: hyperechoic
CT: early arterial peripheral nodular enhancement |
|
|
Fibronodular hyperplasia (benign liver tumor) epidemiology
|
same as hemangiomas: women ages 30-50
|
|
|
clinical features of Fibronodular hyperplasia (FNH)
|
- usually asymptomatic
- normal P/E - imagining: CT may reveal central scar |
|
|
pathognomonic presentation of fibronodular hyperplasia (FNH) on contrast CT
|

central stellate scar
|
|
|
Hepatic Adenoma symptoms (anything serious?)
|
Abd pain
*** can have life threatening bleeding *** |
|
|
What is seen on CT of a hepatic adenoma?
|
hyper-intense capsule
|
|
|
treatment of hepatic adenomas
|
- stop OCP
- surgical resection if solitary & large |
|
|
Oral contraceptive use must be stopped in which benign hepatic lesion?
|
hepatic adenoma
|
|
|
most common liver tumor in childhood
|
hepatoblastoma
|
|
|
In an infant > 1 y/o, what lab test is suspicious for hepatoblastoma?
|
↑ AFP (alpha fetal protein)
|
|
|
Presentation of gallbladder carcinoma
|
- incidental finding @ cholecystectomy
- RUQ pain found in 80% of pts |
|
|
______________ is the most common site for metastastasis.
|
Liver
|
|
|
Major causes of HCC
|
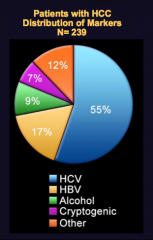
|
|
|
2 components for the diagnosis of HCC
|
AFP > 500 + solid liver nodule on imaging
|
|
|
Staging system for HCC
|
BCLC staging, NOT TNM
|
|
|
definition of acute liver failure
|
coagulation abornomality (INR > 1.5)
AND any degree of mental alteration in a pt w/o pre-existing cirrhosis & w/ an illness of less than 26 weeks duration |
|
|
3 variables to predict outcome in acute liver failure
|
- degree of encephalopathy
- prothrombin time/INR - etiology |
|
|
What is a life-threatening neurological complication of acute liver failure aside from encephalopathy?
|
cerebral edema/increased ICP
|
|
|
Two common complications of acute liver failure
|
- infection (50-80% of pt w/ develop bacteremia w/in 1st few days after onset of ALF)
- coagulopathy (FFP only given in setting of active hemorrhage) |
|
|
What is the most common indication for liver transplantation in the United States?
|
HCV
|
|
|
MELD score uses which 3 lab tests?
|
- INR
- Total Bilirubin - Creatinine |
|
|
What are the poorest prognostic indicators of a patient requiring liver transplant?
|
↑ INR & ↑ creatinine
|
|
|
MELD > ___ = transplant list
|
15
|
|
|
What do changes in ALT & AST indicate?
|
hepatocyte damage, they DO NOT measure function
|
|
|
What is the primary lab test for cholestasis?
|
alklaline phospatase
|
|
|
Causes of ↑ unconjugated bilirubin (list 4)
|
- hemolysis
- resporption hematoma - gilbert syndrome - drugs ie. rifampin |
|
|
Causes of ↑ conjugated bilirubin (list 3)
|
- liver disease
- biliary obstruction (most common cause) - inheritied (Dubin-Johnson, Rotor) |
|
|
What causes aminotransferase elevations > 1000?
|
- acute viral hepatitis
- toxins - ischemia |
|
|
Common symptoms of primary biliary sclerosic (PBC)
|
- pruritus
- fatigue - abdominal pain |
|
|
UDCA treatment in PBC vs PSC
|
PBC: reduction in morbidity/mortality
PSC: only improves #s, no improvement in morbidity/mortality |
|
|
Progression of Hep B when acquired in childhood vs adulthood
|
Children --> chronic Hep B
Adults --> resolve |
|
|
What is the only liver disease which can end in HCC without first developing cirrhosis?
|
Hep B: 5-10% of people can go from chronic Hep B --> HCC
|
|
|
Gallstones in the biliary ducts can lead to... (name 3 conditions)
|
- obstructive jaundice
- ascending cholangitis - acute pancreatitis |
|
|
Which type of HCC effects young people without underlying liver disease?
|
fibrolamellar
|

