![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The anesthesia breathing system is an extension of this airway...
|
The patient's upper airway
|
|
|
The point of maximal resistance in the intubated patient
|
The y-piece/circut connector
|
|
|
The point of maximal resistance in the unintubated patient
|
the expiratory valve in a semi-closed system
|
|
|
The angles w/i the breathing system are...
|
less than 20degrees
|
|
|
The flow of a gas is dependent on these two gas properties:
|
density and viscosity
|
|
|
The ______ of a gas determines flow at high flow rates.
|
Density
|
|
|
The ______ of a gas determines flow at low flow rates.
|
Viscosity
|
|
|
In you (incr/decr) the length of tubing you (incr/decr) the flow
|
Incr tubing, decr flow
Poiseulilles Law |
|
|
Reynold's number measures what?
|
viscosity of gases.
Ratio of the gas's viscosity to its density. |
|
|
The Reynold's number at which circut flow becomes turulent?
|
<2100
<100 at an abrupt orifice. |
|
|
What variables can be manipulated by knowing the Re#?
|
radius or velocity
|
|
|
What are some examples of open non-breathing systems?
|
Insufflation & open drop
|
|
|
What are the disadvantages of open systems?
|
anesthetic gas pollution
risk of hypoxia inability to maintain airway poor control of anesthesia no conservation of h/h |
|
|
A semi-open system has...
|
a reservoir bag
|
|
|
The FGF for a semi-open system is...
|
3-8L/min
**decr rebreathing** |
|
|
A system with a reservoir and partial rebreathing is a...
|
semi-closed system
|
|
|
The semi-closed system FGF is...
|
1.5-2L/min
|
|
|
In a semi-closed system, the pCO2 depends on _______ not FGF.
|
ventilation.
|
|
|
In a closed system, the _____ is closed.
|
APL
|
|
|
The FGF in a closed system is...
|
1:1 with the patient; ~150-500ml/min
|
|
|
The Mapleson system is this type of breathing system...
|
Semi-open
|
|
|
Mapleson systems lack...
|
unidirectional valves & carbon neutralization
|
|
|
The amount of rebreathing in a semi-open system is dependent on...
|
the FGF
**rebreathing will only occur when inspiratory flow > FGF** |
|
|
The major advantage of the mapleson system is...
|
minimal dead space, low resistence
|
|

Mapleson A
|
Magill circut
- Used for SV - APL valve & high FGF = adequate CO2 elimination - SV FGF = 2xMV - CV FGF = 3xMV w/ closed APL **ideal for peds transport** |
|
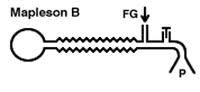
Mapleson B
|
- FGF & APL close together to decr rebreathing
- less efficient system then A - SV & CV FGF = 2-2.5xMV |
|
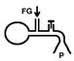
Mapleson C
|
- No corrugated tubing
- SV FGF = 2xMV - CV FGF = 2-2.5xMV |
|
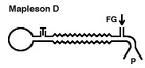
Mapleson D
|
- Reversed version of A
- FGF near pt ensures adequate CO2 elimination - Easy gas scavenging during CV - SV FGF = 2xMV - CV FGF = 1-2xMV |
|
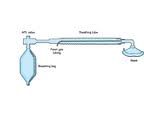
Bain Circut
|
FGF enters corrugated tubing
- Maintains h/h - Incr resistence in "airway" - SV FGF = 2xMV - CV FGF = 2-2.5xMV |
|
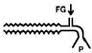
Mapleson E
|
Ayer's T-Piece
- No res bag - exhalation tubing volume > Tv to decr rebreathing SV FGF = 2-3xMV CV FGF = 3xMV *ideal use prior to extubation* |
|

Mapleson F
|
Jackson-Rees'
- Ayer's t-piece w/ a bag - SV FGF = 2-3xMV - CV FGF = 2xMV **ideal for adult transport** |
|
|
A > D > C > B for what type of ventilation
|
spontaneous
All dogs can bite |
|
|
D > B > C > A for what type of ventilation
|
controlled
Dead bodies can't argue |
|
|
The APL valve should be situated where in the breathing system?
|
on expiratory limb before absorber to incr efficiency
|
|
|
The most accurate place to measure airway pressure is...
|
y-piece
|
|
|
The ____ size of soda lime is 4-8.
|
Mesh
|
|
|
The correct mesh size for bara lime is...
|
4-8
|
|
|
(Soda/Bara) lime requires silica additive to incr it's absorptive properties
|
Soda lime
|
|
|
(soda/bara) lime changes violet w/ exhaustion.
|
Soda
|
|
|
When _____ is exhausted, it turns blue-grey.
|
Bara lime
|
|
|
The absorptive capacity of soda lime is...; for bara lime...
|
14-23 LCo2/100g granules
9-18 L CO2/100g granules |
|

What system is this?
|
Mapleson A
|
|
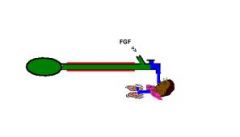
What system is this?
|
Mapleson B
|
|

What system is this?
|
Mapleson C
|
|

What system is this?
|
Mapleson D
|
|
What system is this?
|
Bain Circuit
|
|
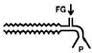
What system is this?
|
Mapleson E
|
|

What system is this?
|
Mapleson F
|
|
|
Bags =< 1.5L
|
Pressure >30 and <50cm H2O when 4x its size
|
|
|
Bags >1.5L
|
Pressure >35 and <60cm H2O when 4x its size
|
|
|
Relative humidity in the OR is...
|
55-60%
|
|
|
The maximum mass of water vapor which can be carried by a given volume of air is...
|
the absolute humidity
**determined by temperature** |
|
|
The iron lung is an example of ...
|
negative pressure ventilation.
|
|
|
Examples of positive pressure ventilation are...
|
CPAP, BiPAP and PSV
|
|
|
Ventilation which varies inspiratory duration and pressure in order to deliver a preset volume is called...
|
volume cycled ventilation...
i.e. CMV **no pt resp effort** |
|
|
Assist-control ventilation is ventilation which delivers a preset _____ and _____; it (does/does not) all a patient to trigger spontaneous breaths.
|
tidal volume & rate
does **Spontaneous breaths are of a set tidal volume** |
|
|
A ventilator setting which allows a patient to take spontaneous breathes of variable tidal volumes is _______; there (is/is not) predetermined TVs and rate set?
|
Intermediate mandatory ventilation (IMV)
IS |
|
|
SIMV prevents...
|
the ventilator from giving preset breathe when patient initiates a breath
|
|
|
Normal lung compliance is...
|
10-12ml/kg
**abnormal 6-10ml/kg** |
|
|
This ventilator setting helps prevent alveolar collapse.
|
PEEP
|
|
|
Barotrauma, decr CO, incorrect CVP/PAP findings, alveoli overdistention, incr WOB and incr ICP are side-effects of ...
|
PEEP
|
|
|
This mode of ventilation utilizes pressure to augment TV...
|
PSV
|
|
|
Pressure ventilation that utilizes preset max pressure limits to ventilate patients is called...
|
PCV
|
|
|
To improve oxygenation and decrease barotrauma with slow inspiratory flows is the effect of this ventilator theory...
|
inverse I:E ratio
|
|
|
Three lung zones of ARDS
|
- Zone of consolidated disease alveoli that cannot be recruited
- Zone of collapsed yet recruitable alveoli - Zone of normal alveoli (25-30%) available for ventilation |
|
|
Controlled hypoventilation and permissive hypercapnea is permitted in ...
|
ARDS
|
|
|
This high-frequency ventilation is utilized in the OR for upper airway & bronchial procedures
|
HFJV
|
|
|
The diameter of the circuit tubing is .....mm.
|
22mm wide
|
|
|
The internal volume of the circuit tubing is....
|
400-500ml/meter length
|
|
|
The resistance to flow in the circuit tubing is...
|
1mmH2O/L/min flow
|
|
|
If you increase the tubing length, you (incr/decr) the humidity and efficiency of tubing.
|
Decreased
|
|
|
Ideal heat & humidity in the OR?
|
9mg/L in normal room air at 20*C and 50% humidity
|

