![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
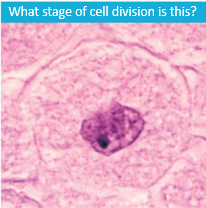
|
Interphase |
|
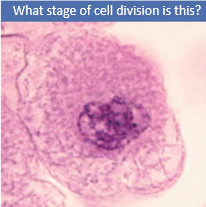
|
Interphase |
|
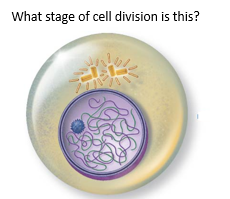
|
Early Prophase |
|
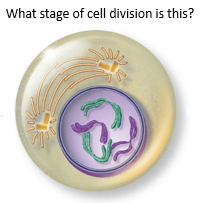
|
Early Prophase |
|
|
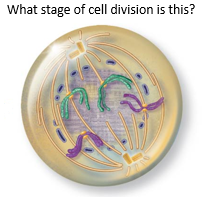
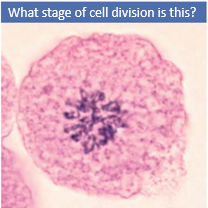
Late Prophase |
|
|
Late Prophase |
|
|
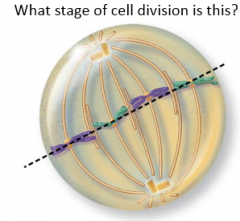
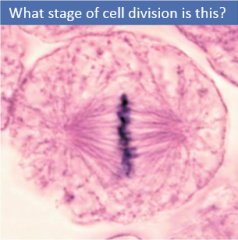
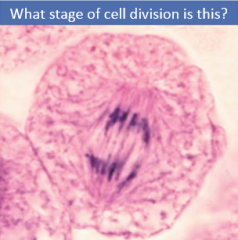
Metaphase |
|
|
Metaphase |
|
|
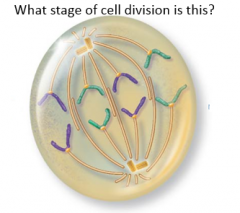
Anaphase |
|
|
Anaphase |
|
|
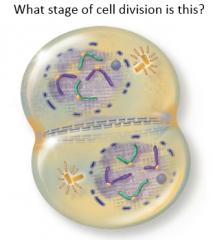
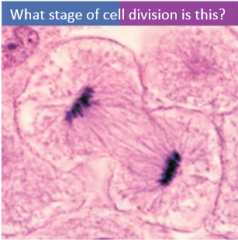
Telophase |
|
|
Telophase |
|
|
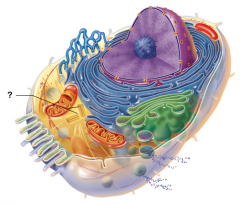
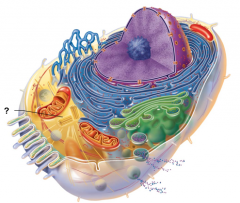
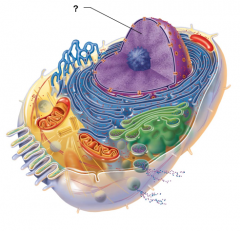
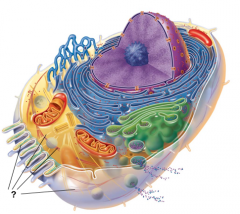
Centrioles |
|
|
Centrosome Matrix |
|
|
Chromatin |
|
|
Cytoskeletal Elements |
|
|
Cytosol |
|
|
Golgi Apparatus |
|
|
Intermediate Filaments |
|
|
Lysosome |
|
|
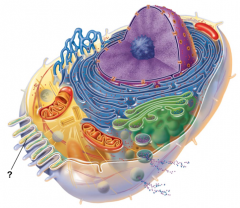
Microfilament |
|
|
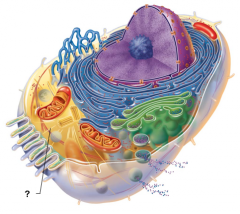
Microtubule |
|
|
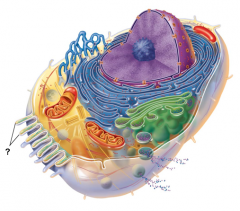
Microvilli |
|
|
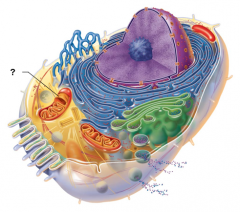
Mitochondrion |
|
|
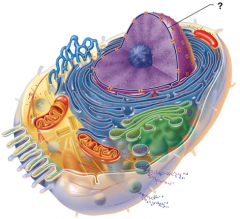
Nuclear Envelope |
|
|
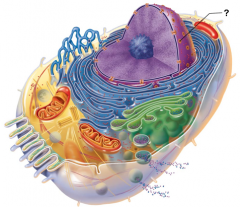
Nuclear Pore |
|
|
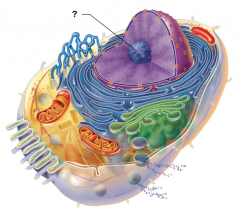
Nucleolus |
|
|
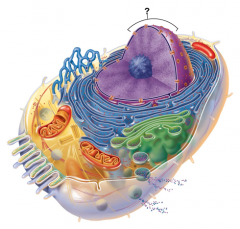
Nucleus |
|
|
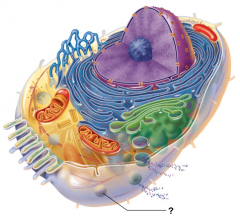
Peroxisome |
|
|
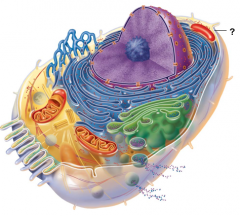
Plasma Membrane |
|
|
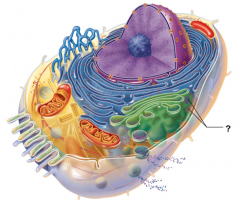
Ribosomes |
|
|
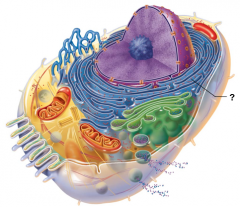
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum |
|
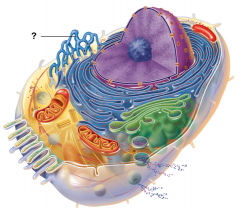
|
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum |
|
|
Provide the location and function for ribosomes within the cell. |
Location: Floating in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough ER
Function: Site of protein synthesis |
|
|
Provide the function of the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum. |
Ribosomes attached to rough ER synthesize proteins, tubules in rough ER provide storage and transportation of the proteins synthesized. |
|
|
Provide the function of the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum. |
Smooth ER is the site of lipid and steroid sythesis, lipid metabolism, and drug detoxification. |
|
|
Provide the function of the Golgi Apparatus. |
Plays a role in packaging proteins or other substances for export from the cell or incorporation into the plasma membrane. |
|
|
Provide the function of lysosomes. |
Sacs containing digestive enzymes which function to digest worn out organelles and foreign cells. Also, suicide cells. |
|
|
Provide the function of Peroxisomes. |
Detoxify alcohol, free radicals, and other harmful chemicals. |
|
|
Provide the funnction of Mitochondrion. |
Contains enzymes that oxidize foodstuffs to produce ATP. |
|
|
Provide the function of centrioles. |
Direct the formation of mitotic spindles during cell division. |
|
|
Provide the functions of microfilaments. |
Microfilaments are composed mainly of actin (contractile protein) and are thus important in cell mobility. |
|
|
Provide the functions of intermediate filaments. |
Stabilizing elements composed of proteins that resist mechanical forces acting on cells.
|
|
|
Provide the function of microtubules. |
Form the internal structure of centrioles and help to determine cell shape. |

