![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define and give examples of Cohesive soil
|
Soil which is very soft and has a high moisture content.
Cohesive soils suffer from long slow settlement. Significant Seasonal variation in Moisture Content And so lots of movement Usually more stable at 1m deep. Examples: Clay, Silts. |
|
|
Define and give examples of Non-Cohesive soil
|
Soil which is made up f large pieces.
Fast settlement, pieces slip until lock together as load is applied. Good Drainage properties - Risk water could wash away leaving the soil unstable. Examples: Gravel & Sand |
|
|
What is a site which formerly would have been a valley or a quarry, but is now a brownfield site ready for development, likely to be?
|
Fill
|
|
|
What Foundations should be used on a Filled site?
|
Choose one of a few:
Piles - End Bearing Piles - Friction Piles - Displacement Piles Raft Foundations |
|
|
Common properties and dimensions of a strip foundation
|
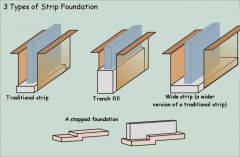
minimum 500mm width for 2 storey building
- 600mm not uncommon, JCB bucket size is 600mm Width is determined by load bearing capacity, proximity of trees, moisture content, location (nearby stream or river?) Minimum depth in a cohesive soil is 1000mm Minimum depth in a Non-Cohesive soil is 750mm |
|
|
750mm is the limit at which _______ is unlikely to ______ ________.
|
750mm is the limit at which frost is unlikely to freeze services.
|
|
|
What is a stepped foundation?
|
ADD STEPPED FOUNDATION IMAGE/ SEE PREVIOUS CARD ON STRIP FOUNDATIONS
(Upload not working 02/05/14) |
|
|
What is a Stepped Footing?
|
Footing which steps out from the width of the wall, imagine staircase from the wall to the top of the concrete. Also commonly used in Large Victorian property/buildings.
|
|
|
Key Facts about Piles - Replacement Piles:
Diameter Centre distribution Depth |
Replacement Piles:
Diameter depends on load (100mm - 750mm) Commonly Distributed at 2.4 - 3.0m centres 8 or 10m deep is not uncommon, depends on exact ground conditions. |
|
|
Strip Foundation Width Summary:
Gravel or sand (medium dense) (Non-cohesive) |
Requires pick axe for excavation.
50mm wooden peg hard to drive more than 150mm 20kN/m (single storey building) 250mm 40 kN/m (two-storey) Min 400mm 60 kN/m (three storey) Min 600 mm |
|
|
Strip Foundation Width Summary:
Firm clay, firm sandy clay |
Thumb makes impression easily
20 kN/m (single storey) Min 300 mm 40 kN/m (two-storey) Min 450mm 60 kN/m (three storey) Min 750mm (maybe not economical) |
|
|
Strip Foundation Width Summary:
Loose clay, Loose sand (Cohesive) |
Can be excavated with a spade. 50mm wooden peg easily driven
20kN/m (single storey building) 400mm 40 kN/m (two-storey) Special Design required 60 kN/m (three storey) Special Design required |
|
|
Raft Foundations
|
Special Designed by Structural Engineer
Reinforced Concrete slab, with varied thickness to improve strength for point loads. Usually toe at edges, allows additional brick to hide concrete raft. |

