![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
17 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
In what situation do we use analysis of variance?
|
When comparing three or more groups to see if they come from the same population.
|
|
|
How does ANOVA establish whether groups are from the same population?
|
ANOVA compares how spread out groups are from each other relative to how spread out individuals are within groups.
|
|
|
What two estimates of the population variance are compared in ANOVA?
|
Between-groups variance (spread among groups) and within-groups variance (spread among individuals).
|
|
|
What does between-groups variance tell us?
|
How spread out groups are from each other.
|
|
|
What does within-groups variance tell us?
|
How spread out individuals are within groups.
|
|
|
In calculating between-groups variance, what does "n" represent?
|
The number of cases in any *one* group.
|
|
|
What is the grand mean?
|
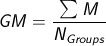
The average of the group means.
|
|
|
How do you calculate the within-groups variance?
|
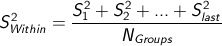
Take the average of the population variance estimates from all groups.
|
|
|
What is the F-ratio?
|
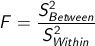
The comparison of between-groups variance to within-groups variance.
|
|
|
How do you calculate the between-groups degrees of freedom?
|
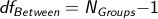
Number of groups - 1
|
|
|
How do you calculate within-groups degrees of freedom?
|
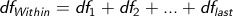
Add up the degrees of freedom from each group.
|
|
|
What is another term for "between-groups degrees of freedom"?
|
Numerator degrees of freedom
|
|
|
What is another term for "within-groups degrees of freedom"?
|
Denominator degrees of freedom
|
|
|
How do you calculate the variance of the means?
|
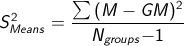
Divide the sum of squared deviations of the sample means from the grand mean by the number of groups minus one.
|
|
|
How do you calculate the between-groups variance?
|
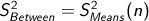
Multiply the variance of the means by the number of cases in any *one* group (n).
|
|
|
What does it mean when you have a large F ratio?
|
Groups are more spread out than individuals, so group membership has an effect on the variable of interest.
|
|
|
What does it mean when the F-ratio is small?
|
The groups are not very spread out, so any variability is likely to be random error among individuals. There is likely not any group effect on the variable of interest.
|

