![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Types of Cell to cell signalling |
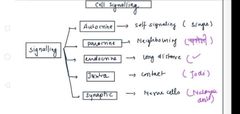
|
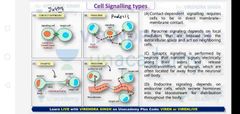
|
|
|
Hydrophilic and hydrophobic mol |

|
|
|
|
Signaling of acetylcholine |
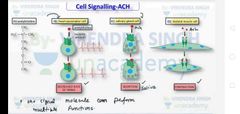
One signal molecule can perform numerical function 1. In heart pacemaker sale at decrease rate of_____ 2 it salivary gland cell it causes secretion 3 in skeletal muscle cell at causes contraction |
|
|
|
Major types of cell signaling receptor |
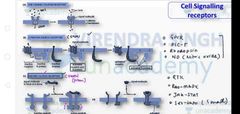
1.Ion channel coupled receptor 2.G protein coupled receptor 3.enzyme coupled receptor |
|
|
|
Cell signaling by phosphorylation and GTP binding |
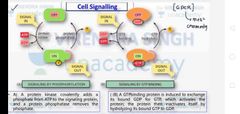
|
|
|
|
Regulation of Monomeric GTPase enzyme |
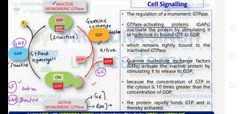
|
G proteins belong to the larger group of enzymes called GTPases, that bind to the nucleotide guanosine triphosphate and hydrolyze it to guanosine diphosphate. |
|
|
How does upstream signal effects gene expression |
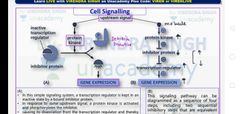
|
Upstream signals are those signal which comes from outside |
|
|
What is scaffold protein and how does it work |
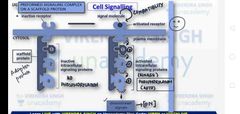
Scaffold proteins are adaptor like protein A ligand would bind to a receptor and it will activate intracellular signaling proteins( by auto posphorylation). |
|
|
|
Write a short note on G-protein couple receptor |
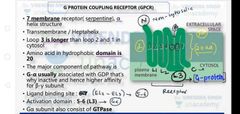
|
|
|
|
Note on sub units of g protein. Name Effector of protein |

|
|
|
|
does affector activate g protein or does g protein activate affector. |
Adenyl cyclase is example of effector enzyme and it is activated by g protein G-a subunit |
|
|
|
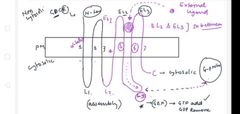
describe the sub units of g protein and The working and reaction that occurs in g protein when the receptor is activated (What is Gs and AH domain) |
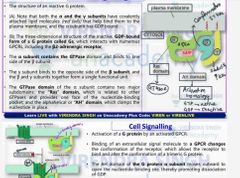
|

|
|
|
How is cAMP formed and degraded. Which enzyme does catalysis and hydrolysis of cAMP |

|
|
|
|
Give few examples of hormone their target tissue and major responses by them. |
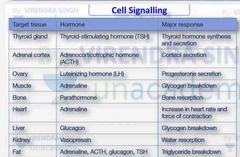
|
|
|
|
Activation of pka and its function |

|
Cyclic amp dependent protein kinase |
|
|
Terms a.Effector molecule , b.2° messenger c. Upstream signal d.Scaffold protein |
an effector molecule is usually a small molecule that selectively binds to a protein and regulates its biological activity 2° messenger is an intracellular molecule the changes in concentration in response to environmental signal and involve when conveying info inside the cell. Upstream signal bahar se aaya Hua signal hai. Scaffold protein is also known as adaptor protein Scaffold has many binding sites which when not phosphorylated is known as inactive intracellular signalling protein |
|
|
|
What is Autocrossphosphorylation |
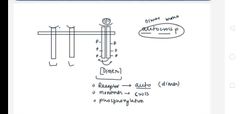
In Autocrossphosphorylation- from protein dimer Pov the dimer is phosphorylating itself but from the monomer pov monomers are phosphorylating each other(hence Cross word );Ex rtk It is also known as trans-auto-phosphorylation
Pov- point of you |
|
|
|
What is domain |
It is a region of protein's polypeptide chain that is cell stabilizing and that fold independently from the rest. It is compact 3D structure they often form functional unit. It often form functional unit (protein polypeptide ki voh region jo ki khud se fold kar leta hai aur khud ko stable kar leta hai. Aur usko Baki polypeptide ke region se Koi Lena Dena nahin Hai.) |
|
|
|
Activation curve of allosteric protein |
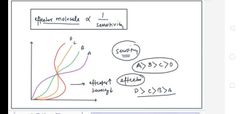
X axis is effector molecule and y axis is sensitivity (In "A" thode se Hi effector molecule mein vohhighly sensitive tha .in D itne sare effector molecule hone ke bad halka sa sensitivity show ki usne D ne) |
|
|
|
Coincidence signal detector |
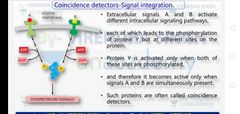
|
|
|
|
Gpcr 1° AC pathway |
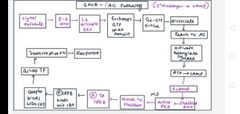
|

CRE- cAMP response element CREB - c a m p response element binding protein Cbp - c r e b binding protein. |
|
|
Draw table of some member of g protein family and write the function. |

|
|
|
|
Gpcr plc B pathway |
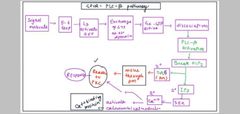
|
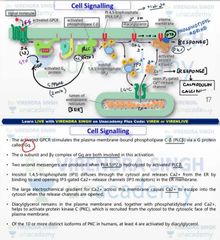
|
|
|
Step wise activation of cam kinase II pathway |

|
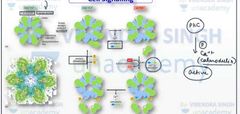
|
|
|
Component of rhodopsin |
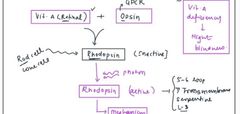
|
|
|
|
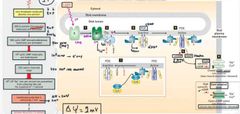
Activation of rhodopsin molecule |

|
|
|
|
What is PDE in rhodopsin cell signalling |
Pde is cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase. It Breaks cGMP( cyclic) into GMP(linear). |
|
|
|
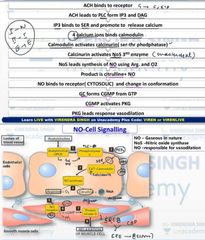
NO cell signaling breif . three types of nos enzyme, where are they found. And which is the only free radical beneficial to human |
|

|
|
|
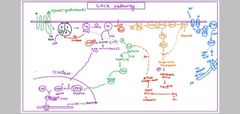
In brief draw all the five cell signal in pathway in one picture ( master slide ) |
|
|
|
|
Glycogen pathway .( Which type of liver cell produce which hormone and its effects) |
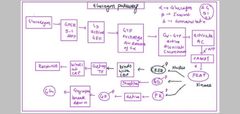
Revise form L4 in beganing (Mnemonic AG bids)
|
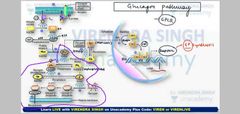
|
|
|
What are the gpcr regulation pathways and describe densitization |
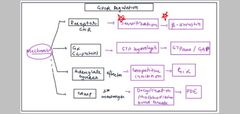
|
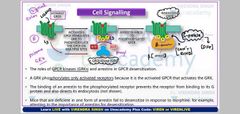
|
|
|
What signaling molecule causes glucose storage and mobilization. write a short flow chart summary of all the increasing and decreasing level of molecule example camp, glucagon with respect to each other(glucagon signaling pathway) |

Glycogen phosphorylase is activated in the response to glucagon and ephinephrin. Where as glycogen synthase is activated in response to insulin. |
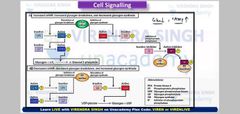
|
|
|
Which molecules get active while phosphorylation or dephosphorylation in glucagon pathway |

|
|
|
|
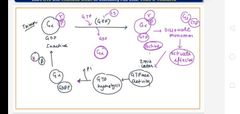
Summary of G- protein association and association on getting signal |
|
|
|
|
Read lecture 3 of unit 4 from PPT |
. |
|

