![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Re: the components of the glomerular filtration barrier:
- which is the major size barrier? - charge barrier? |
- podocytes (visceral epithelial cells)
- glomerular basement membrance |
|
|
What are the two basic mechanisms of glomerular injury?
|
- Immune complex mediated: deposition of antigen-antibody complexes
- nonimmune complex mediated: DESTRUCTION of the functioning nephrons... scarring--> irreversible damage |
|
|
Is scarring in the kidney irreversible damage?
|
yes.
|
|
|
- Nephrotic syndrome
- Asym Hematuira and recurrent gross hematuria - nephritic syndrome + "rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis" - glomerulonephritis associated with systemic dz What are theses? |
The 4 Glomerular clinico-pathologic syndromes... basically how our pts will present, in spite of whatever dz they actually have.
|
|
|
What is the clinical definition of nephrotic syndrome?
|
excessive permeability of glomerular capillary wall to plasma proteins
>3.5g protein/24hr urine. |
|
|
In adults, what is the most common cause of nephrotic syndrome?
- two others? |
Membranous Glomerulopathy
- immune mediated - has primary and 2ndary forms Focal and Segmental Glomerulosclerosis - not immune mediated Kidney dz associated w/ systemic dz (eg diabetes, amyloid, lupus etc.) |
|
|
In children, what is the most common cause of nephrotic syndrome?
- mechanism? |
Minimal change dz (70%)
- nonimmune - injury to the podocyte (vis epithelial cell) |
|
|
What are the complications of nephrotic syndrome?
|
-tendency to thrombosis
-propensity for infection |
|
|
Only __% of all asymptomatic hematuria is of glomerular origin.
What do we do to dx? - three possible findings? |
10%; most is the bladder, prostate, urethral)
Renal biopsy - no abnormalities (30%) - thin basement mem dz (26%) - IgA nephtropathy (28%) |
|
|
How do we tell if blood is actually coming from an intra-renal origin?
|
look for dysmorphic RBCs and RBC casts in urine.
|
|
|
What is nephritic syndrome characterized by clinically?
|
Hematuria PLUS:
- elevated serum BUN and creatinine - oliguria (decreased urine output) - edema - HTN - **Proteinuria** |
|
|
Lost of >50% of renal function w/i days to weeks is termed...
aka... |
...Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis.
"Crescentic glomerulonephritis" |
|
|
Severe renal failure manifests clinically as...
|
...nausea, vomiting, hiccups, dyspnes, lethargy, pericarditis, encephalopathy, CHF, PulmEdema
|
|
|
What are the three major categories of RPG?
Basically, when you have Lost of >50% of renal function w/i days to weeks, you have to class it as one of 3 things. How do you differentiate between the 3? |
- immune
- Anti-GBM (glomerula basement mem) dz - ANCA (anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody) associated dz Immunohistochem staining |
|
|
circulating anti-GBM antibodies with linear glomerular IF staining is dx of what?
Glomerular immune complex localization w/ *granular* IF staining? Little or no glomerular IF Ig staining? |
anti GBM RPG.
Immune complex RPG ANCA RPG |
|
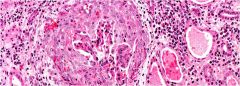
What are the features seen in this slide?
|
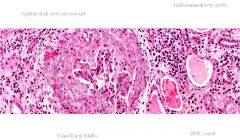
This is a pictures of crescentic Glom nephritis
|
|
|
What the 3 major categories of the tubular dz we should know?
90% of which is caused by e.coli infection? |
- drug induced tubulointerstiail nephritis
- acute pyelonephritis - Acute kidney injury / ATN acute pyelonephritis |
|
|
what is the classic triad of clinical manifestations associated with drug induced interstitial nephritis?
- seen in what % of pts with this dz? |
low grade fever, skin rash, arthralgias
- 15% |
|
|
What drug that pts often don't tell us about can cause:
- interstital nephritis - nephrotic range proteinuria - minimal change dz |
NSAIDs
|
|
|
What are the three mechanisms of injury in drug induced tubulointerstiatial nephritis?
|
HyperS - synth penicillins
Nephrotoxicity - aminoglycosides Progressive Cumulative injury - analgesic abuse |
|
|
Casts of neutrophils in urine sediment is dx of what?
|
acute pyelonephritis
|
|
|
No matter what the etiology is, all thrombotic microangiopathies all cause what?
Most common etiologies? (2) Does it matter if we catch these early? |
endothelial cell injury
HUS and TTP yes, because scarring is irreversible. Changes just in the glomeruli are less permenant than those in the vasculature. |
|
|
The triad of hemolytic anemia, relative thrombocytopenia, and acute renal failure can be clinically suggestive of what?
|
thrombotic microangiopathies.
|

