![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
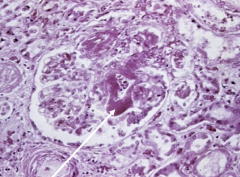
Pt is a child with concurrent hemorrhagic GI infection |
Hemolytic-Uremic Syndrome
*caused by verrotoxin producing E. coli *arrow shows thrombin clot occluding capillary |
|
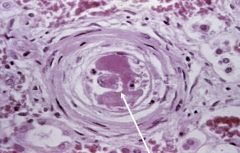
Pt has a BP of 200/180 and is found to have underlying defect in ADAMS-13 |
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP) with Malignant HTN
*DIC like situation where there is improper cleaving of vWF *Malignant HTN causes proliferation of smooth mm around arterioles causing "onion-skin" appearance |
|
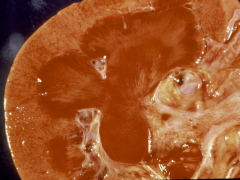
Pt recently started on an aminoglycoside |
Nephrotoxic Acute Tubular Necrosis (ATN)
*Causes: Aminoglycoside, Myoglobin (crush injuries), lead, mercury, radiocontrast dye *proximal tubule mainly effected |
|
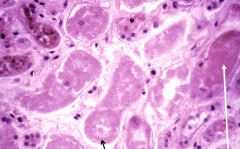
Pt has hypotension secondary to a massive hemorrhage |
Ischemic ATN
*Causes: Hypotension, CHF, Sepsis, Shock, Hemorrhage *Tubule cells die and undergo coagulative necrosis w/ loss of nuclei [BLACK] and slough off into lumen to form casts [WHITE] |
|
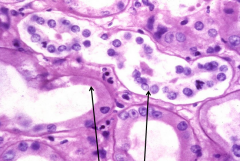
Pt also has CHF |
Ischemic ATN
*Causes: Hypotension, CHF, Sepsis, Shock, Hemorrhage *Tubule cells die and undergo coagulative necrosis w/ loss of nuclei [LEFT] and slough off into lumen [RIGHT] |
|

Pt has flank pain and a fever |
Acute Pyelonephritis
*Most commonly due to ascending ifxn from E coli, Klebsiella, Proteus, Enterbacter |
|
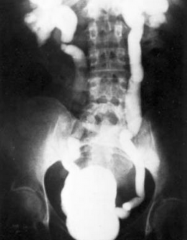
What is this patient more at risk for? |
Acute Pyelonephritis - image demonstrates Vesiculoureteral reflux |
|
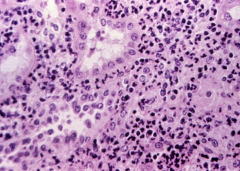
Pt has fever and flank pain |
Acute Pyelonephritis
* neutrophils in tubules, interstitium, and pretty much everywhere |
|
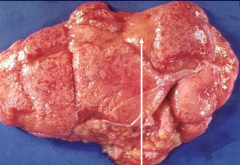
|
Scarring from Chronic Pyelonephritis
- probably due to obstruction based diffuse scar pattern (reflux has scars at poles only) |
|
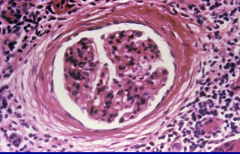
What predisposing conditions may this pt had? |
Chronic Pyelonephritis - predisposistions = Vesiculouretral relfex or chronic obstructing kidney stones
*Periglomular fibrosis & Interstitial lymphocytes |
|
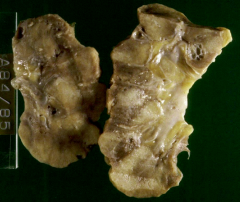
|
Scarring from Chronic Pyelonephritis
- probably due to obstruction based diffuse scar pattern (reflux has scars at poles only) |
|
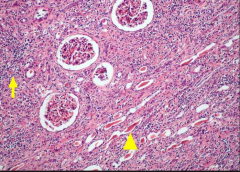
|
Chronic Pyelonephritis
* arrows show "thyroidization" of kidney due to tubules filling with eosinophilic casts |
|
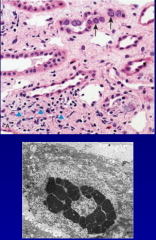
Pt has fever and flank pain and is a transplant pt |
Pyeolnephritis due Papilloma virus
*latent ifxn that reemerges w/ immunosuppressive transplant meds |
|
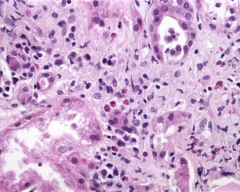
Pt has eosinophilia, azotemia, rash, and oligouria |
Drug-Induced Tubulointerstitial Nephritis
*Occurs 1-2 wks after starting penicillins, diruetics, NSAIDs *notice that all inflammatory cells are in interstitium |
|
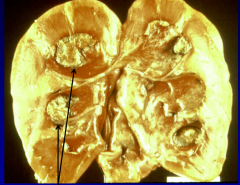
|
Papillary Necrosis due to Chronic Tubulointerstial Nephritis from chronic analgesic abuse (acetominophen, phenacetin) |
|
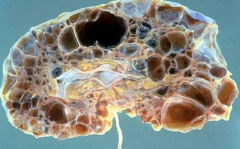
|
Adult Polycystic Kidney Disease
*bilaterally enlarged kidneys, hematuria, HTN, flank pain * due to AD mutation in PKD1 on chr 16 most commonly causing defective polycystin used in cell-to-cell interactions *also have berry aneurysms & liver cysts |
|
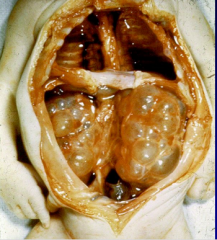
|
Infantile Polycystic Kidney Disease
* due AR mutation that can cause oligohydraminos -> potter sequence *associated w/ hepatic cysts -> hepatic fibrosis -> portal HTN |
|
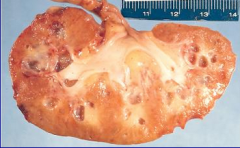
|
Medullary Cystic Kidney Disease
* AD defect causing cyst formation in medulla and CD's that leads to progressive renal failure * bilaterally shrunken kidneys |

