![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
ROM Test:
•ROM 1: Pelvic Approximation •LowerBody ROM 1: Straight leg, internal rotation of the femur Muscle Test: •Patient Supine, flex hip to 75º. Cross foot against opposite knee. Adduct hip with 30º pelvic rotation. •TVA has horizontal fibers; because of this we test both fibers with a rotation component. •Depending on which side of TVA was weak, test that side TVA Tester: •TREAT: The leg that moves into rotation is the same side TVA. For the rotation component you would think “right lower TVA and left upper” and vice versa. •Body: Stand on opposite side •Stabilizing Hand: Involved Thorax (not stabilizing pelvis, stabilizing below the ribs on thorax). •Action Hand: Medial contact on involved knee •FORCE: Abduct thigh to counter rotate pelvis Applied Force •Abduct thigh to counter rotate pelvis Palpation/Function: •If you see limited hip rotation in anything, add lower fibers of TVA to list of possible weaknesses. •The lower fibers aid in rotating the trunk. Similar to the “Serratus” of the pelvis. T-12 – L5 Spinous Processes & Sacrum: •Sidelying, come to 12th (T12), and work from T12 down to the end of the SP’s on sacrum. Make sure you are palpating the correct side of the spinous processes. •Vertical palpations on spinous processes all the way until you finish the sacrum. Iliac Crest (Anterior ½: •Supine (optional), find the high point of the iliac crest. Or you can landmark ASIS & PSIS, find halfway point, and palpate all the way to the ASIS. •The TVA comes of the Iliac Crest and runs medial; you want to try to get inside the lip a little, but not as far in as Iliacus. Superior medial on lip. •Trying to “curl around the iliac crest. Inguinal Ligament (Lateral 1/3 – 1/2): •Curl fingers into inguinal ligament. Coming medial and superior to inguinal ligament, and curling lateral and inferior toward you. Lateral 1/3-1/2 Pubic Bone (Superior Medial): •Start around belly button, moving down and pressing into skin to find pubic bone. •2 Fingerwidths on the lateral side of pubic symphysis. Linea Alba: •Come up the linea alba to the umbilicus. Sink into the linea alba and curl back towards the belly of the muscle. Come down into linea alba, and palpate and pull back towards muscle belly, so pull towards you. •Anytime it’s a tendinous palpation like linea alba, always treat “towards the belly of the muscle”. |
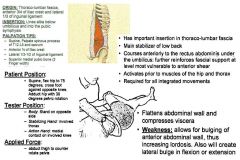
Transverse Abdominis: Lower Fibers
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•ROM 7: 30º Hip Flexion •LowerBody ROM 1: Straight leg, internal rotation of the femur Muscle Test: •Supine, flex hip 30º and rotate 45º to face opposite hip. Extend thoracics (more of a neutral spine, make sure they are not flexed). Cross Arms •TVA has horizontal fibers; because of this we test both fibers with a rotation component. •This is not a good muscle to start with until the person proves they can maintain stability in an extreme position of trunk motion. Tester: •TREAT: The opposite side that they are rotating, or “same side” shoulder. •Body: Stand on same side •Stabilizing Hand: Brace Across Thighs •Action Hand: Reach across with mid clavicular contact Applied Force: •Counter rotate trunk through transverse plane. You do not need to push hard, gravity already applies a significant force. Palpation/Function: •The upper fibers aid in some flexion and rotation of the trunk. Xyphoid Process: •Supine, (go to opposite side) palpate the lateral side of xyphoid that correlates to the side of the TVA weakness. Ribs: •Stand on opposite side & go from side of xyphoid, under the ribs. “push into” inferior ribs, so it’s more superficial. You are under the ribs, but its not as deep as the diaphragm, it’s the medial aspect and slightly posterior. •From xyphoid, palpate along ribs (inferior) until it angles backwards & you run into the 11th rib. Linea Alba: •Palpate down the linea alba from xyphoid to umbilicus. •Stand on same side for linea alba and “curl into muscle belly”. You can stand on opposite side with “straight fingers” and push into the muscle belly. |
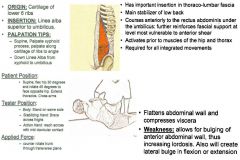
Transverse Abdominis: Upper Fibers
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•ROM 2: 120º Hip Flexion •ROM 6: Full Hip Flexion, Full Rotation, Full TRUNK FLEXION & Full Sidebend (Anteriorly) Muscle Test: •Supine, fully flex hip 110º and rotate 20º. Cross Arms. Tester: •TREAT: The opposite side that they rotate. •Body: Stand on side being tested. •Stabilizing Hand: Stabilize across thighs. •Action Hand: Brace involved shoulder at mid-clavicle (mid-line). Have them cross arms and put your hands on theirs (about midline). Applied Force: •Extend trunk through sagittal plane. Palpation/Function: •Shaped like a pyramid, it is a small muscle that anchors the rectus abdominis. •Its primary function is assisting the rectus abdominis in flexion of the trunk. Helps anchor the linea alba. •If it is weak, it can stress the lower back muscles. Activating the Pyramidalis can help stabilize the trunk and pelvis. Pubic Bone: •Medial side of pubic bone. Palpate 2-3 fingerwidths lateral on medial side of pubic bone, similar to lower TVA. Linea Alba: •Have them place finger on their belly button. From pubic bone, come into linea alba and pull (curl) towards you 2/3 of the way up. Pubis (Lateral): •Figure out where you where on the lateral pubic bone, and angle down and out from linea alba to pubic bone. Palpating down and IN towards the belly of the muscle. •Mark the lateral pubis & angle down to the lateral aspect, push into it, don’t curl underneath. Make a straight line from linea alba to lateral pubic bone. Should feel a “ridgeline”. |
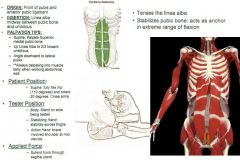
Pyramidalis:
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•ROM 2: 120º Hip Flexion •Anytime there is limited ROM in trunk flexion (primarily sagittal plane), test all of the rectus. Muscle Test: •Supine. Flex hip 90º & rotate 20º to face opposite knee. Trunk Flexed. Cross Arms. Position them to mid-calf on table. Tester: •TREAT: Opposite side of rotation (think of them taking the side we are treating over the axis to midline). •Body: Stand on involved Side, •Stabilizing Hand: Stabilize across thighs, place other hand on sacrum to make sure hip flexion is maintained. •Action Hand: Mid-Clavicular contact Applied Force: •Extend trunk through sagittal plane. Palpation/Function: •All fibers flex & rotate the trunk & spine. Each fiber has a slightly different function relative to degree of flexion and amount of trunk rotation. •Have them flex rectus at times to feel where you are. •Lower fibers – involve greater degree of trunk & spine flexion. Umbilicus Fascial Line: •Find the fascial line just below the umbilicus. Palpate across fascial line palpating downwards towards belly of first section of rectus. Linea Alba: •Come down linea alba towards pubic bone, pulling into the muscle belly towards you. Pubic Bone: •Come across the top of the pubic bone. Palpating upwards toward the center of the belly. Apeneurosis: •Have them flex abs (lift up), and palpate upwards on the lateral aspect of the rectus, palpating inwards toward the muscle belly. |
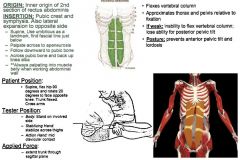
Rectus Abdominis: First Section
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•Anytime there is limited ROM in trunk flexion (primarily sagittal plane), test all of the rectus. Muscle Test: •Supine. Flex hip 90º & rotate 20º to face opposite knee. •Trunk Extended. Cross Arms. Tester: •TREAT: Opposite side of rotation. •Body: Stand on involved Side •Stabilizing Hand: Stabilize across thigh, place other hand on sacrum to help maintain NEUTRAL extension. •Action Hand: Mid-Clavicular contact Applied Force: •Extend trunk through sagittal plane. Palpation/Function: •Lower fibers – involve greater degree of trunk & spine flexion. 2nd Level of Abs (Bottom): •Find umbilicus as landmark. Find bottom of the 2nd level of abs. Palpate ACROSS, pulling up into the belly of the muscle. Apeneurosis: •Come to the lateral aspect of rectus. Come upwards and push inwards into the muscle belly. Superior Fascia: •Come back across, and pull downwards into the muscle belly. (For the top of the 2nd section). Linea Alba: •Get to midline, and come back down the linea alba, pulling outwards towards muscle belly. |
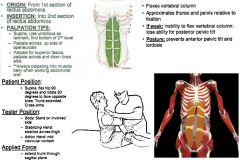
Rectus Abdominis: Second Section
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•Anytime there is limited ROM in trunk flexion (primarily sagittal plane), test all of the rectus. Muscle Test: •Supine. Flex hip 70º & rotate 20º to face opposite knee. Cross Arms. Tester: •TREAT: Opposite side of rotation. •Body: Stand on involved Side •Stabilizing Hand: Brace both knees •Action Hand: Mid-Clavicular contact Applied Force: •Extend trunk through sagittal plane. Palpation/Function: 2nd Level of Abs (Top): •Come across bottom of 3rd pulling upwards into muscle belly. Apeneurosis (Up-Side: •Come up the lateral aspect of the rectus pushing inwards toward muscle belly. Superior Fascia: •Come across the top and pull downwards into muscle belly. Linea Alba: •Back to midline of body, go down the middle pulling outwards towards muscle belly. |
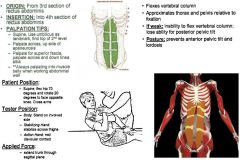
Rectus Abdominis: Third Section
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•ROM 7: 30º Hip Flexion •Anytime there is limited ROM in trunk flexion (primarily sagittal plane), test all of the rectus. Muscle Test: •Supine. Flex hip 45º & rotate 45º to face opposite knee. The 45º of rotation brings lateral fibers “more” in the sagittal plane. Cross Arms. Tester: •TREAT: Opposite side of rotation. •Body: Stand on involved Side •Stabilizing Hand: Brace both knees. •Action Hand: Mid-Clavicular contact Applied Force: •Extend trunk through sagittal plane. Palpation/Function: •Upper fibers – involve lesser degree of trunk & spine flexion. •TREAT 4th SECTION AS A WHOLE. 6th & 7th Ribs (Anterior Portion): •Use xyphoid process move across and up to lower level of 5th rib against the sternum. •Start at the xiphoid process come up and into the 5th rib. Come across the 5th rib, and down and across into the bottom of the 6th rib, then down and across to the bottom of the 7th rib. Lateral Apeneurosis & Inferior Attachment: •Come down the lateral aspect of the 4th, right to the edge of the rib cage. Then come across the bottom of the 4th pulling upwards. Linea Alba to Xyphoid Process: •A Come up the center of the 4th rectus on the linea alba pulling outwards into muscle belly. |
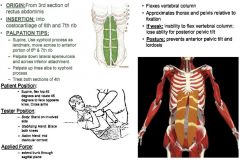
Rectus Abdominis Fourth Section: Lateral
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•ROM 7: 30º Hip Flexion •Anytime there is limited ROM in trunk flexion (primarily sagittal plane), test all of the rectus. Muscle Test: •Supine. Flex hip 45º & rotate 20º to face opposite knee. Cross Arms. Tester: •TREAT: Opposite side of rotation. •Body: Stand on involved Side •Stabilizing Hand: Brace both thighs •Action Hand: Mid-Clavicular contact Applied Force: •Extend trunk through sagittal plane. Palpation/Function: •Upper fibers – involve lesser degree of trunk & spine flexion. •TREAT 4th SECTION AS A WHOLE. 5th Rib (Lower Level Against Sternum): •Use xyphoid process move across and up to lower level of 5th rib against the sternum. •Start at the xiphoid process come up and into the 5th rib. Come across the 5th rib, and down and across into the bottom of the 6th rib, then down and across to the bottom of the 7th rib. Inferior Attachment: •Come down the lateral aspect of the 4th, right to the edge of the rib cage. Then come across the bottom of the 4th pulling upwards. Linea Alba to Xyphoid Process: •Come up the center of the 4th rectus on the linea alba pulling outwards into muscle belly. |
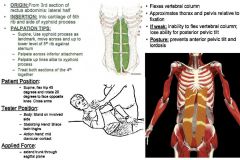
Rectus Abdominis Fourth Section: Medial
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•ROM 1: Pelvic Approximation •ROM 3: 90º Hip Flexion & Full Rotation Muscle Test: •Supine. Flex hip 90º and rotate 45º. Cross Arms. Tester: •TREAT: Opposite side of rotation. •Body: Stand on opposite side. •Stabilizing Hand: Hook & Stabilize both thighs Hand: Brace involved shoulder at corocoid. Applied Force: •Counter rotate and extend trunk. Push opposite shoulder into rotation. •Upon applying resistance, make sure they do not go into flexion (sign of compensation). Palpation/Function: •If one is weak, treat external obliques AS A WHOLE. •External Obliques interdigitate with Serratus Anterior on ribs. •External Obliques help you rotate to the opposite side. •Anterior fibers – involves more flexion & rotation of the trunk & spine. Ribs 5-12 (Anterior/Inferior Aspects): •Sidelying. Use xyphoid process as landmark, go up and over to 5th rib, anterior to Serratus. •Come to midline of the body on 5th rib, get 2-3 fingerwidths out, and palpate 2-3 fingerwidths. Move down to 6th rib, palpate another 2-3 fingerwidths out, and continue this all the way to the 12th rib, gradually working more posterior. Slightly overlapping each time. •Feel for between the ribs in the spaces. Ex. Get between 5th -6th ribs, and come right up into 5 on anterior inferior surface and the drop down over 6th rib, come between 6th - 7th ribs slide up into the inferior surface. (continue). Ilium (Superior/Anterior ½) to ASIS: •Come onto the superior border of the ilium, don’t curl into the ilium, but palpate onto the superior aspect. Inguinal Ligament (All of it): •Come down whole inguinal ligament all the way to corner of pubic bone. Aponeurosis: •Have them flex, and come up the side of the rectus abdominis. |
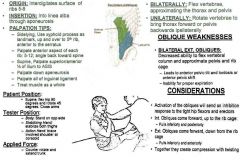
External Obliques: Anterior Fibers
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•ROM 4: 90º Hip Flexion, Full Rotation & Sidebend (Anteriorly) •ROM 5: 90º Hip Flexion with Full Sidebend Muscle Test: •Supine. Abduct both legs together 10º and elevate thighs 2 inches (Patient holds table) Tester: •TREAT: Whichever side the legs are abducting, you are treating that side oblique. •Body: Stand at base of table •Stabilizing Hand: Grab both ankles. Applied Force: •Adduct legs toward midline. Palpation/Function: •If one is weak, treat external obliques AS A WHOLE. •Lateral fibers – involves more lateral flexion (side bending) and rotation of the trunk & spine. Ribs 5-12 (Anterior/Inferior Aspects): •Sidelying. Use xyphoid process as landmark, go up and over to 5th rib, anterior to Serratus. • Come to midline of the body on 5th rib, get 2-3 fingerwidths out, and palpate 2-3 fingerwidths. Move down to 6th rib, palpate another 2-3 fingerwidths out, and continue this all the way to the 12th rib, gradually working more posterior. Slightly overlapping each time. •Feel for between the ribs in the spaces. Ex. Get between 5th -6th ribs, and come right up into 5 on anterior inferior surface and the drop down over 6th rib, come between 6th-7th ribs slide up into the inferior surface. (continue). Ilium (Superior/Anterior ½) to ASIS: •Come onto the superior border of the ilium, don’t curl into the ilium, but palpate onto the superior aspect. Inguinal Ligament (All of it): •Come down whole inguinal ligament all the way to corner of pubic bone. Aponeurosis: •Have them flex, and come up the side of the rectus abdominis. |
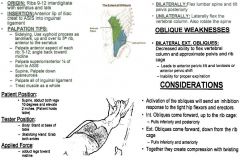
External Obliques: Lateral Fibers
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•ROM 1: Pelvic Approximation •ROM 3: 90º Hip Flexion & Full Rotation Muscle Test: •Supine. Flex trunk 90º and rotate 45º, sidebend to same side. Tester: •TREAT: Same side oblique as rotation. •Body: Stand on same side of oblique being tested; behind the body. •Stabilizing Hand: Stabilize across both thighs. •Action Hand: Posterior shoulder Applied Force: •Go 45 degrees to shoulder & push up & away out of sidebend & rotation. Counter rotation and sidebend. Palpation/Function: •TREAT AS A WHOLE. •Internal obliques interdigitate with external obliques on ribs. •Located under the external oblique and to the side of the rectus abdominis. •Internal obliques help you rotate to the “same” side. •Anterior fibers – involves flexion, rotation & lateral flexion of the spine (sitting up, rotating & side-bending). Ribs 8-12 (Anterior Surfaces): •Ribs 8-12. Start at medial border of ribs, more medial and anterior than external obliques. Move anterior on ribs and inferior. Overlap a little bit for where you where for external obliques. •Internal obliques are more medial and anterior on ribs than external obliques, which is more lateral and posterior. T-12 – L5 & Sacrum (Spinous Processes): •Palpate the spinous processes of T12 – Sacrum. •Have them lie on side or prone. Ilium (Superior/Middle 1/2): •Supine. Palpate the middle half of the superior Ilium. •Landmark PSIS & ASIS, go right in between to be on middle ½ of ilium. Inguinal Ligament (Lateral 2/3): •Medial/superior 2/3 = lateral aspect of inguinal ligament. Aponeurosis: •Palpate the lateral aspect of rectus abdominis, curl lateral towards you. •Another option is to have “stiff” fingers and perform a scraping motion. •Have them flex abs (or lift head) to feel lateral aspect. |
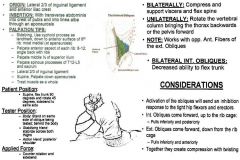
Internal Oblique: Anterior Fibers
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•ROM 4: 90º Hip Flexion, Full Rotation & Side Bend (Anteriorly) •ROM 5: 90º Hip Flexion with Full Sidebend Muscle Test: •Supine. Flex hip 100º and rotate 45º to face opposite knee. Fully laterally bend & flex at trunk (opp. side) toward involved knee. Cross Arms. Tester: •Body: Stand on same side as oblique being tested. •Stabilizing Hand: Stabilize involved thigh. •Action Hand: Brace lateral shoulder. Applied Force: •Opposite sidebend. Palpation: •If one fiber is weak, TREAT AS A WHOLE. •Lateral fibers – involves flexion, rotation & lateral flexion of the spine (sitting up, rotating & side-bending). Ribs 8-12 (Anterior Surfaces): •Ribs 8-12. Start at medial border of ribs, more medial and anterior than external obliques. Move anterior on ribs and inferior. Overlap a little bit for where you where for external obliques. •Internal obliques is more medial and anterior on ribs than external obliques, which is more lateral and posterior. T-12 – L5 & Sacrum (Spinous Processes): •Palpate the spinous processes of T12 – Sacrum. •Have them lie on side or prone. Ilium (Superior/Middle 1/2): •Supine. Palpate the middle half of the superior Ilium. •Landmark PSIS & ASIS, go right in between to be on middle ½ of ilium. Inguinal Ligament (Lateral 2/3): •Medial/superior 2/3 = lateral aspect of inguinal ligament. Aponeurosis: •Palpate the lateral aspect of rectus abdominis, curl lateral towards you. •Another option is to have “stiff” fingers and perform a scraping motion. •Have them flex abs (or lift head) to feel lateral aspect. |
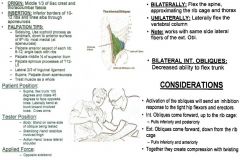
Internal Obliques: Lateral Fibers
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•ROM 8: Straight Legs & Full Sidebend •ROM 11: Straight Legs & Hip Hike Muscle Test: •Supine. Abduct both legs at same time 2º with slight lordosis (Patient holds table).Make sure they maintain neutral spine/hips. •WRONG PICTURE. Tester: •Treat the side that the legs are abducting. •Body: Stand at opposite side of table/muscle. •Stabilizing Hand: Ilium/Hip. Applied Force: •Adduct legs toward midline. Palpation/Function: •TREAT AS A WHOLE •Some consider QL to be a deep abdominal muscle rather than a deep muscle of the back. •Along with the psoas and iliacus muscles, the QL is a stabilizer of the pelvis and lumbar spine. Iliac Crest (Posterior/Superior ¼): •Sidelying. Landmark PSIS to the spine. Find PSIS and curl onto the superior/posterior aspect of crest of the ilium. Treat the posterior ¼, curling right on. 12th Rib (Posterior/Inferior): •Posterior/inferior aspect of 12th rib. Go straight to TP, sink down toward. •Find 12th rib and come up under the 12th rib getting the inferior aspect. L1 – L4 Transverse Processes: •From 12th rib come in from the side and come down on the sides of the TP’s, down and in. Have to angle in and around the ilium (L1-L4). •Have them lie on side, come down & in angling from ilium down to lateral aspects of TP’s. From sidelying position, the TP’s lie close together. •Follow 12th rib over to TP (L1) & work down to L4. |
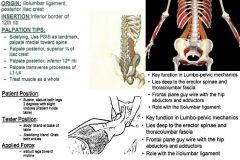
Quadratus Lumborum: Costal Fibers
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•ROM 8: Straight Legs & Full Sidebend •ROM 11: Straight Legs & Hip Hike Muscle Test: •Supine. Abduct both legs at same time 10º with slight lordosis (Patient holds table). Neutral spine/hips •WRONG PICTURE. Tester: •TREAT: Side that legs are abducting. •Body: Stand at opposite side of table/muscle. •Stabilizing Hand: Ilium/Hip. Applied Force: •Adduct legs toward midline. Palpation/Function: •TREAT AS A WHOLE Iliac Crest (Posterior/Superior ¼): • Sidelying. Landmark PSIS to the spine. Find PSIS and curl onto the superior/posterior aspect of crest of the ilium. Treat the posterior ¼, curling right on. 12th Rib (Posterior/Inferior): •Posterior/inferior aspect of 12th rib. Go straight to TP, sink down toward. •Find 12th rib and come up under the 12th rib getting the inferior aspect. L1 – L4 Transverse Processes: •From 12th rib come in from the side and come down on the sides of the TP’s, down and in. Have to angle in and around the ilium (L1-L4). •Have them lie on side, come down & in angling from ilium down to lateral aspects of TP’s. From sidelying position, the TP’s lie close together. •Follow 12th rib over to TP (L1) & work down to L4. |

Quadratus Lumborum: Spinal Fibers
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•ROM 10: Straight Legs & Full Sidebend with Hip External Rotation. Muscle Test: •Supine. Abduct both legs 10º with full external rotation of involved femur (leg opposite of tester). Patient holds table. •WRONG PICTURE. Tester: •TREAT: Whichever leg is externally rotated. •Body: Stand at side of table. •Stabilizing Hand: Ilium. Applied Force: •Adduct legs toward midline. Palpation/Function: •Opposite side rotator. Sacrum (Posterior Surface into SP’s): •Prone. Fill in whole half of sacrum of involved side, palpate into side of medial PSIS as well. Don’t need to palpate on coccyx. L5 – T11 SP’s: •Similar to Lat, palpate down and into SP’s at 45º angle. L5-T11. Lumbar Mamillary Processes (Shift off SP’s/Vertical): •Halfway between SP’s and TP’s edge, come straight down & in from SP’s to mammillary. •Slide off of SP & sink to mammillary & palpate downward onto mammillary. Attached to mamillary’s at 45º angle. •Come down lateral to TP’s and find out where lateral border is. Come halfway between the TP’s and SP’s, and palpate down into the mamillary processes. •You’re not going to “feel” a specific bump like the SP’s, but looking for a little rise/ridgeline halfway between the edge of TP’s and SP’s. •The mamillary process of L1 is around T11, L2 is around T12. |

Multifidus: Lumbo-Sacral
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•ROM 10: Straight Legs & Full Sidebend with Hip External Rotation (leg opposite of tester). Muscle Test: •Supine. Abduct both legs 10º with full external rotation of involved femur (Patient holds table). Tester: •TREAT: Whichever leg is externally rotated. •Body: Stand on uninvolved side •Stabilizing Hand: Stabilize uninvolved thorax. •Action Hand: Reach arm under ankles and grab involved leg. Applied Force: •Adduct legs toward midline. Palpation/Function: •Opposite side rotator. T11 – C6 (Spinous Processes): •Prone. Palpate from T11-C6 SP’s. Push into SP’s at 45º angle. C7 – T12 Transverse Processes (Laterally): •Come up pretty high on C7, medial border of TP & curl toward you, stay medial on TP & curl lateral, end at 12th rib. •TP’s: Find band of tissue (erectors) about 1 ½ inches from SP, then sink medial to band of tissue, straight down to medial aspect of TP’s. •Come off SP of C6, and shift to the coinciding TP of C7 – T12. Find band of tissue, on medial border of TP, curling towards you. Working way down the TP’s. |
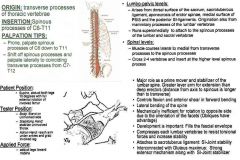
Multifidus: Thoraco-Lumbar
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•ROM 9: Straight Legs & Full Sidebend with Hip Internal Rotation. Muscle Test: •Supine, abduct both legs 10º with full internal rotation of involved femur (Patient holds table). •WRONG PICTURE. Tester: •TREAT: Side of body that leg is internally rotated. •Body: Stand at side of table. •Stabilizing Hand: Ilium. Applied Force: •Adduct legs toward midline. Palpation/Function: •Function: Rotation, side-bending, and extension of the spine. These muscles also stabilize the spine. Sacrum (Posterior/Superior) – L1 SP’s: •Prone. Get at PSIS & follow 45º line inferior/medial toward sacrum SP’s. Can palpate a little on ilium as well. Lower 7 Ribs. (Inferior Portion/Angles): •Prone. Come off and up and into the ribs. Come on inferior surface of 12th rib – 6 ribs, end at inferior angle of scapula. Come up between 11 and 12 and get on inferior/posterior surface of 11 (continue this to 6th rib). Work right up to the 6th rib and end near the inferior angle of the scapula. •You can feel tissue on the posterior ribs running vertically (slight angle), you can feel when you come off the side of it and its just rib, it will be at edge on lateral border of QL. |
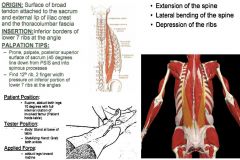
Iliocostalis Lumborum:
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•ROM 9: Straight Legs & Full Sidebend with Hip Internal Rotation. Muscle Test: •Supine, abduct both legs 10º with full internal rotation of involved femur (Patient holds table) Tester: •TREAT: Side of body that leg is internally rotated. •Body: Stand on uninvolved side. •Stabilizing Hand: Stabilize uninvolved thorax. •Action Hand: Reach arm under ankles and grab involved leg. Applied Force: •Adduct legs toward midline. Palpation/Function: •Function: Rotation, side-bending, and extension of the spine. These muscles also stabilize the spine. Ribs 12 - 7 (Upper Portion/Angles): •Prone. Find 12th rib, come up between 11th & 12th & palpate down on 12th, then come between 11 and 10 and palpate down on superior portion of 11. Do this until 7th rib (stand by their head facing toward their feet & palpate downward). Coming up medial to the scapula. Ribs 6 - 1 (Inferior Border/Angle): •Change position & palpate towards their head, upward. •Change and to the opposite, now coming on top of 7th rib palpating upward on inferior portion of 6th rib, then come between 6 and 5, and palpate upward on inferior portion of 5th rib. Do this until you get to the first rib. C7 Transverse Process (Angle in): •Once at 1st rib, angle at C7 TP and palpate angling inwards. |
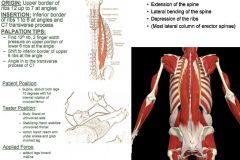
Iliocostalis Thoracics:
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•ROM 8: Straight Legs & Full Sidebend Muscle Test: •Supine. Abduct both legs 10º. 20º lateral trunk flexion. Slight lordosis (patient holds table). Tester: •TREAT: The “sidebend” side. •Body: Stand at side of table. •Stabilizing Hand: ilium. Applied Force: •Adduct legs toward midline. Palpation/Function: •Function: Rotation, side-bending, and extension of the spine. These muscles also stabilize the spine. L1 – S1 (Palpate Spinous Processes): •Start at L1, and palpate downward at 45º angle on SP’s all the way until you finish all the sacrum. Ribs 12 – 9 (Lateral to TP/Pressure on Inferior Portion): •Find 12th rib lateral to TP, palpate inferior portion ribs 9-12 (barely lateral to TP’s at junction, should bump into TP. Find band of tissue, drop just lateral onto ribs 9-12. •Palpating the inferior portion of ribs. |
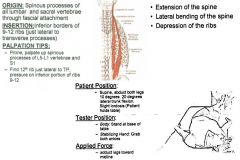
Longissimus Lumborum:
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•ROM 8: Straight Legs & Full Sidebend Muscle Test: •Supine. Abduct both legs 10º. 20º lateral trunk flexion. Slight lordosis (patient holds table). Tester: •Body: Stand on uninvolved side. •Stabilizing Hand: Stabilize uninvolved thorax. •Action Hand: Reach arm under ankles and grab involved leg. Applied Force: •Adduct legs toward midline. Palpation/Function: •Function: Rotation, side-bending, and extension of the spine. These muscles also stabilize the spine. T1 – T12 Transverse Processes: •You CAN come off the TP & then the adjacent rib above at the same time, 45º angle down into TP’s (advanced). •Find the TP’s come into the sides of TP’s from a little superior/lateral. Once you get to the T9, you need to start palpating ribs (don’t have to at the same time). •Find band of tissue for the TP’s. Ribs 1 – 9 (Adjacent to TP’s at Junction/Inferior): •Inferior portion at junction of TP’s & ribs. Palpate 2 fingerwidths on ribs. |
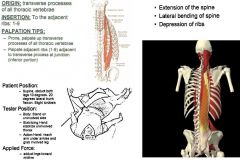
Longissimus Thoracics:
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•ROM 12: Prone Spinal Extension Muscle Test: •Supine. Abduct both legs 10º. Arch back (slight spinal extension) Patient holds table. Tester: •Body: Stand at side of table. •Stabilizing Hand: Ilium. Applied Force: •Adduct legs toward midline. Palpation/Function: •TREAT AS WHOLE. •On the Spinalis, palpation is not everything. Even though they are the same palpation, you might treat one and test the other & it stay weak, and have to treat it again. The muscle test is basically an isometric that reinforces the work and is a big piece. •The erector muscles closest to the middle of the spine are called the spinalis muscles. Vertical muscle. . •Function: Rotation, side-bending, and extension of the spine. These muscles also stabilize the spine. T2 - Sacrum Spinous Processes: •Palpate downward from T2 to the Sacrum on the lateral aspects of SP’s at 45º angle. |
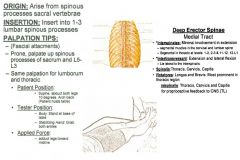
Spinalis Lumborum:
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•ROM 12: Prone Spinal Extension Muscle Test: •Supine. Abduct both legs 10º Arch back (slight spinal extension). Tester: •Body: Stand on uninvolved side. •Stabilizing Hand: Stabilize uninvolved thorax. •Action Hand: Reach arm under ankles and grab involved leg. Applied Force: •Adduct legs toward midline. Palpation/Function: •TREAT AS WHOLE. •On the Spinalis, palpation is not everything. Even though they are the same palpation, you might treat one and test the other & it stay weak, and have to treat it again. The muscle test is basically an isometric that reinforces the work and is a big piece. •The erector muscles closest to the middle of the spine are called the spinalis muscles. Vertical muscle. •Function: Rotation, side-bending, and extension of the spine. These muscles also stabilize the spine. T2 - Sacrum Spinous Processes: •Palpate downward from T2 to the Sacrum on the lateral aspects of SP’s at 45º angle. |
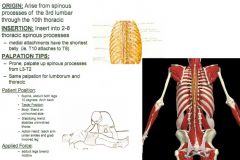
Spinalis Thoracis:
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•ROM 12: Prone Spinal Extension Muscle Test: •Prone. Extend and rotate thorax 20º. Arms to sides. Tester: •TREAT: Muscle to the opposite side of rotation. •Body: Stand on same side as muscle being tested. •Stabilizing Hand: Stabilize uninvolved PSIS from behind. •Action Hand: Brace across to posterior shoulder. Applied Force: •Flex trunk into counter-rotation. Push the shoulder down & away. Palpation/Function: •Function: Rotation (opposite side), side-bending, and extension of the spine. These muscles also stabilize the spine. T12 – C4 Spinous Processes: •Start at T12 and palpate upward at 45º angle into SP’s to C4. T1 – T12 Transverse Processes: •Find band of tissue around T1. TP’s: Find band of tissue (erectors) about 1 ½ inches from SP, then sink medial to band of tissue, straight down to medial aspect of TP’s, work from T1 to T12. |

Semispinalis Thoracis:
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•None Muscle Test: •Supine. Flex hip 80º. Extend through lumbar spine. Slightly rotate. Cross Arms. Tester: •TREAT: Opposite side of rotation. •Body: Stand on opposite side of muscle being tested. •Stabilizing Hand: Stabilize involved thigh from behind. •Action Hand: Brace lateral shoulder. Applied Force: •Flex trunk into counter-rotation. Come perpendicular to shoulder & push into rotation. Palpation/Function: •Muscle fibers run horizontal. Opposite side rotator. Sacrum (Superior/lateral) & Lumbar TP’s (All): •Palpate vertically on TP’s, as you follow TP’s down go right into medial PSIS & palpate superior/lateral sacrum (near PSIS) there. •TP’s in lumbar spine are outside of the mamillary processes. L5 – T12 Spinous Processes: •Palpate 45º on SP’s. |
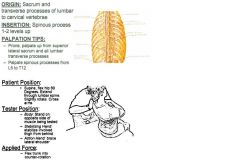
Rotatores Lumborum:
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•None Muscle Test: •Supine. Flex hip 80º. Extend through thoracic spine. Slightly rotate. Cross Arms. Tester: •TREAT: Opposite side of rotation. •Body: Stand on opposite side of muscle being tested. •Stabilizing Hand: Stabilize involved thigh from behind. •Action Hand: Brace lateral shoulder. Applied Force: •Flex trunk into counter-rotation. Come perpendicular to shoulder & push into rotation. Palpation/Function: •Function: Rotation (opposite side), side-bending, and extension of the spine. These muscles also stabilize the spine. T1 - T12 TP’s: •Palpate vertically on TP’s, as you follow TP’s down from T1 to T12 •Find band of tissue around T1. TP’s: Find band of tissue (erectors) about 1 ½ inches from SP, then sink medial to band of tissue, straight down to medial aspect of TP’s, work from T1 to T12. T11- C7 Spinous Processes: •Start at T11 and work up to C7 palpating the SP’s at 45º angle vertically. |
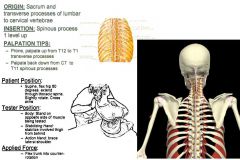
Rotatores Thoracis:
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•None Palpation: •A L2 – T11 Spinous Processes: •A Ribs 9-12 (Inferior Aspects/Medial to Angles) •A |
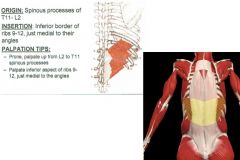
Serratus Posterior: Inferior Fibers
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•ROM 12: Prone Spinal Extension Palpation: •Must move scapula out of the way. C6 – T2 Spinous Processes: •Prone, have client abduct scapula. •Using C7 as a landmark, palpate spinous processes from C6 to T2. Ribs 2 – 5 (Body of Ribs at angles): •A |
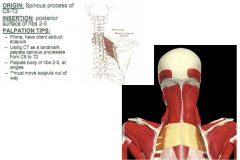
Serratus Posterior: Superior Fibers
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•None Palpation: •A Clavicle (Inferior/Medial & 1 Inch Lateral) Left Side Only: •A Rectus Abdominis 4th Section (Superior/Medial Portion): •A |

Sternalis:
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•None Palpation: •Women sidelying position. Ribs 2 – 10 (Around the angle): •A Ribs 1-12 (Superior & Inferior Aspects): •A |
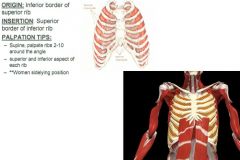
Anterior Intercostals:
|
|
|
ROM Test:
•None Palpation: •Similar to iliocostalis but both superior and inferior. Ribs 2 – 12 (Lateral/Superior Border): •A Ribs 1 – 11 (Inferior Border): •A |

Posterior Intercostals:
|
|
|
Spinal Muscles
|

Spinal Muscles
|
|
|
Respiratory Muscles
|
Respiratory Muscles
|
|
|
Abdominal Muscles
|

Abdominal Muscles
|

